Abstract
Natural products are enriched with numerous compounds with a broad spectrum of therapeutics indication suggesting the role of functional moieties as a core pharmacophore. This review highlights the role of triterpene in targeting signaling pathways in cancer. Advancement in cellular, biochemical, experimental, and computational approaches provides new insights into various pathways in cancer. In signaling network, triterpenes primarily target membrane receptors which control and modulates expression level of the biological responses. Triterpenes are immunomodulatory targeting nuclear factor kappa B, toll-like receptors, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3, and PI3K/Akt/mTOR. Triterpenes isolated from plants and fungus mainly focus on the process of apoptosis while other signaling areas in the cancer are still shrouded. Some of the triterpenes have already passed the clinical trial, whereas many more have been proven to yield effective results. This review would help the researchers to study the role of triterpenes in cancer, thus, helping them to discover and design efficacious therapeutics agents.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Croce CM (2008) Oncogenes and cancer. N Engl J Med 358:502–511
Anand SS, Gill BS (2015) Breakthroughs in epigenetics. PharmaTutor 3:16–24
Negi A, Ramarao P, Kumar R (2013) Recent advancements in small molecule inhibitors of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R) tyrosine kinase as anticancer agents. Mini Rev Med Chem 13:653–681
Zwick E, Bange J, Ullrich A (2001) Receptor tyrosine kinase signalling as a target for cancer intervention strategies. Endocr Relat Cancer 8:161–173
Lemmon MA, Schlessinger J (2010) Cell signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell 141:1117–1134
Schlessinger J (2000) Cell signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell 103:211–225
Negi A, Gill B, Anand SS (2014) Tilling: versatile reverse genetic tool. PharmaTutor 2:26–32
Joshi G, Singh PK, Negi A, Rana A, Singh S, Kumar R (2015) Growth factors mediated cell signalling in prostate cancer progression: implications in discovery of anti-prostate cancer agents. Chem Biol Interact 240:120–133
Negi A, Gill B (2013) Success Stories of enolate form of drugs. PharmaTutor 1:45–53
Pezzuto JM (1997) Plant-derived anticancer agents. Biochem Pharmacol 53:121–133
Reynolds KA, Wallace KK, Handa S, Brown MS, McArthur HA, Floss HG (1997) Biosynthesis of the shikimate-derived starter unit of the immunosuppressant ascomycin: stereochemistry of the 1,4-conjugate elimination. J Antibiot 50:701–703
Yang H, Dou QP (2010) Targeting apoptosis pathway with natural terpenoids: implications for treatment of breast and prostate cancer. Curr Drug Targets 11:733
Yin M-C (2012) Anti-glycative potential of triterpenes: a mini-review. BioMedicine 2:2–9
Liby KT, Yore MM, Sporn MB (2007) Triterpenoids and rexinoids as multifunctional agents for the prevention and treatment of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 7:357–369
Jäger S, Trojan H, Kopp T, Laszczyk MN, Scheffler A (2009) Pentacyclic triterpene distribution in various plants–rich sources for a new group of multi-potent plant extracts. Molecules 14:2016–2031
Liang PH, Ko TP, Wang AHJ (2002) Structure, mechanism and function of prenyltransferases. Eur J Biochem 269:3339–3354
Bublil EM, Yarden Y (2007) The EGF receptor family: spearheading a merger of signaling and therapeutics. Curr Opin Cell Biol 19:124–134
Singh P, Alex JM, Bast F (2014) Insulin receptor (IR) and insulin-like growth factor receptor 1 (IGF-1R) signaling systems: novel treatment strategies for cancer. Med Oncol 31:1–14
Landman GW, Kleefstra N, van Hateren KJ, Groenier KH, Gans RO, Bilo HJ (2010) Metformin associated with lower cancer mortality in type 2 diabetes ZODIAC-16. Diabetes Care 33:322–326
Kelleher FC, O’Sullivan H, Smyth E, McDermott R, Viterbo A (2013) Fibroblast growth factor receptors, developmental corruption and malignant disease. Carcinogenesis. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgt254
Yadav VR, Prasad S, Sung B, Kannappan R, Aggarwal BB (2010) Targeting inflammatory pathways by triterpenoids for prevention and treatment of cancer. Toxins 2:2428–2466
Kuruvilla FG, Schreiber SL (1999) The PIK-related kinases intercept conventional signaling pathways. Chem Biol 6:R129–R136
Peltier J, O’Neill A, Schaffer DV (2007) PI3K/Akt and CREB regulate adult neural hippocampal progenitor proliferation and differentiation. Dev Neurobiol 67:1348–1361
Gill BS, Alex JM, Kumar S (2016) Missing link between microRNA and prostate cancer. Tumor Biol. doi:10.1007/s13277-016-4900-x
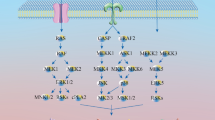
Dienstmann R, Rodon J, Serra V, Tabernero J (2014) Picking the point of inhibition: a comparative review of PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway inhibitors. Mol Cancer Therapeut 13:1021–1031
Whitman M, Downes CP, Keeler M, Keller T, Cantley L (1988) Type I phosphatidylinositol kinase makes a novel inositol phospholipid, phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate. Nature 332:644–646
Carpenter C, Duckworth B, Auger K, Cohen B, Schaffhausen B, Cantley L (1990) Purification and characterization of phosphoinositide 3-kinase from rat liver. J Biol Chem 265:19704–19711
Lawlor MA, Alessi DR (2001) PKB/Akt a key mediator of cell proliferation, survival and insulin responses? J Cell Sci 114:2903–2910
Andjelkovic M, Alessi DR, Meier R, Fernandez A, Lamb NJ, Frech M, Cron P, Cohen P, Lucocq JM, Hemmings BA (1997) Role of translocation in the activation and function of protein kinase B. J Biol Chem 272:31515–31524
Alessi DR, James SR, Downes CP, Holmes AB, Gaffney PR, Reese CB, Cohen P (1997) Characterization of a 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase which phosphorylates and activates protein kinase Bα. Curr Biol 7:261–269
J-i Okano, Gaslightwala I, Birnbaum MJ, Rustgi AK, Nakagawa H (2000) Akt/protein kinase B isoforms are differentially regulated by epidermal growth factor stimulation. J Biol Chem 275:30934–30942
Yang P-C, Yang C-H, Huang C-C, Hsu K-S (2008) Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activation is required for stress protocol-induced modification of hippocampal synaptic plasticity. J Biol Chem 283:2631–2643
Paez J, Sellers WR (2004) PI3K/PTEN/Akt pathway. In: Frank DA (ed) Signal transduction in cancer. Springer, Berlin, pp 145–167
Mamane Y, Petroulakis E, Rong L, Yoshida K, Ler LW, Sonenberg N (2004) eIF4E—from translation to transformation. Oncogene 23:3172–3179
Pommier Y, Sordet O, Antony S, Hayward RL, Kohn KW (2004) Apoptosis defects and chemotherapy resistance: molecular interaction maps and networks. Oncogene 23:2934–2949
Astrinidis A, Henske EP (2005) Tuberous sclerosis complex: linking growth and energy signaling pathways with human disease. Oncogene 24:7475–7481
Ruggero D, Pandolfi PP (2003) Does the ribosome translate cancer? Nat Rev Cancer 3:179–192
Liu J-P (1999) Studies of the molecular mechanisms in the regulation of telomerase activity. FASEB J 13:2091–2104
Hay N, Sonenberg N (2004) Upstream and downstream of mTOR. Genes Dev 18:1926–1945
Guertin DA, Sabatini DM (2007) Defining the role of mTOR in cancer. Cancer Cell 12:9–22
Jacinto E, Loewith R, Schmidt A, Lin S, Rüegg MA, Hall A, Hall MN (2004) Mammalian TOR complex 2 controls the actin cytoskeleton and is rapamycin insensitive. Nat Cell Biol 6:1122–1128
Kundu M (2014) Too sweet for autophagy: hexokinase inhibition of mTORC1 activates autophagy. Mol Cell 53:517–518
Page C, Lin H, Jin Y, Castle V, Nunez G, Huang M, Lin J (1999) Overexpression of Akt/AKT can modulate chemotherapy-induced apoptosis. Anticancer Res 20:407–416
Friedrichs WE, Russell DH, Donzis EJ, Middleton AK, Silva JM, Roth RA, Hidalgo M (2004) Inhibition of mTOR activity restores tamoxifen response in breast cancer cells with aberrant Akt activity. Clin Cancer Res 10:8059–8067
Bjornsti M-A, Houghton PJ (2004) The TOR pathway: a target for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 4:335–348
Beuvink I, Boulay A, Fumagalli S, Zilbermann F, Ruetz S, O’Reilly T, Natt F, Hall J, Lane HA, Thomas G (2005) The mTOR inhibitor RAD001 sensitizes tumor cells to DNA-damaged induced apoptosis through inhibition of p21 translation. Cell 120:747–759
Gill BS, Kumar S (2015) Differential algorithms-assisted molecular modeling-based identification of mechanistic binding of ganoderic acids. Med Chem Res 24:3483–3493
McConkey DJ, Zhu K (2008) Mechanisms of proteasome inhibitor action and resistance in cancer. Drug Resist Update 11:164–179
Rios J, Recio M, Escandell J, Andujar I (2009) Inhibition of transcription factors by plant-derived compounds and their implications in inflammation and cancer. Curr Pharm Des 15:1212–1237
Alghasham AA (2013) Cucurbitacins—a promising target for cancer therapy. Int J Health Sci 7:77–89
Klampfer L (2006) Signal transducers and activators of transcription (STATs): novel targets of chemopreventive and chemotherapeutic drugs. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 6:107–121
Catlett-Falcone R, Landowski TH, Oshiro MM, Turkson J, Levitzki A, Savino R, Ciliberto G, Moscinski L, Fernández-Luna JL, Nuñez G (1999) Constitutive activation of Stat3 signaling confers resistance to apoptosis in human U266 myeloma cells. Immunity 10:105–115
Mora LB, Buettner R, Seigne J, Diaz J, Ahmad N, Garcia R, Bowman T, Falcone R, Fairclough R, Cantor A (2002) Constitutive activation of STAT3 in human prostate tumors and cell lines direct inhibition of STAT3 signaling induces apoptosis of prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res 62:6659–6666
Duncan MD, Duncan KL (1997) Cucurbitacin E targets proliferating endothelia. J Surg Res 69:55–60
Escandell JM, Recio MC, Máñez S, Giner RM, Cerdá-Nicolás M, Ríos JL (2007) Cucurbitacin R reduces the inflammation and bone damage associated with adjuvant arthritis in Lewis rats by suppression of tumor necrosis factor-α in T lymphocytes and macrophages. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 320:581–590
Pathak AK, Bhutani M, Nair AS, Ahn KS, Chakraborty A, Kadara H, Guha S, Sethi G, Aggarwal BB (2007) Ursolic acid inhibits STAT3 activation pathway leading to suppression of proliferation and chemosensitization of human multiple myeloma cells. Mol Cancer Res 5:943–955
Hersh EM, Metch BS, Muggia FM, Brown TD, Whitehead RP, Budd GT, Rinehart JJ, Crawford ED, Bonnet JD, Behrens BC (1991) Phase II studies of recombinant human tumor necrosis factor alpha in patients with malignant disease: a summary of the Southwest Oncology Group experience. J Immunother 10:426–431
Schneider P, Thome M, Burns K, Bodmer J-L, Hofmann K, Kataoka T, Holler N, Tschopp J (1997) TRAIL receptors 1 (DR4) and 2 (DR5) signal FADD-dependent apoptosis and activate NF-κB. Immunity 7:831–836
Wajant H, Pfizenmaier K, Scheurich P (2003) Tumor necrosis factor signaling. Cell Death Differ 10:45–65
Herbst RS, Eckhardt SG, Kurzrock R, Ebbinghaus S, O’Dwyer PJ, Gordon MS, Novotny W, Goldwasser MA, Tohnya TM, Lum BL (2010) Phase I dose-escalation study of recombinant human Apo2L/TRAIL, a dual proapoptotic receptor agonist, in patients with advanced cancer. J Clin Oncol 28:2839–2846
Spierings DC, de Vries EG, Timens W, Groen HJ, Boezen HM, de Jong S (2003) Expression of TRAIL and TRAIL death receptors in stage III non-small cell lung cancer tumors. Clin Cancer Res 9:3397–3405
O’Neill L (2002) Signal transduction pathways activated by the IL-1 receptor/toll-like receptor superfamily. In: Wagner H, Beutler B (eds) Toll-like receptor family members and their ligands. Springer, Berlin, pp 47–61
Akira S, Takeda K (2004) Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat Rev Immunol 4:499–511
Shivakumar SB, Bharti D, Subbarao RB, Jang SJ, Park JS, Ullah I, Park JK, Byun JH, Park BW, Rho GJ (2016) DMSO-and serum-free cryopreservation of Wharton’s jelly tissue isolated from human umbilical cord. J Cell Biochem. doi:10.1002/jcb.25563
Gill B, Sharma P, Kumar R, Kumar S (2015) Misconstrued versatility of Ganoderma lucidum: a key player in multi-targeted cellular signaling. Tumor Biol 37:2789–2804
Meier P, Silke J (2003) Programmed cell death: superman meets Dr Death. Nat Cell Biol 5:1035–1038
Chu W-M (2013) Tumor necrosis factor. Cancer Lett 328:222–225
Ferrara N, Kerbel RS (2005) Angiogenesis as a therapeutic target. Nature 438:967–974
Folkman J (1995) Angiogenesis in cancer, vascular, rheumatoid and other disease. Nat Med 1:27–30
Safayhi H, Sailer E (1997) Anti-inflammatory actions of pentacyclic triterpenes. Planta Med 63:487–493
Sánchez-Quesada C, López-Biedma A, Gaforio JJ (2015) Maslinic acid enhances signals for the recruitment of macrophages and their differentiation to m1 state. Evid Based Complement Altern Med. doi:10.1155/2015/654721
Shyu K-G, Tsai S-C, Wang B-W, Liu Y-C, Lee C-C (2004) Saikosaponin C induces endothelial cells growth, migration and capillary tube formation. Life Sci 76:813–826
Y-x Zhou, Y-l Huang (2009) Antiangiogenic effect of celastrol on the growth of human glioma: an in vitro and in vivo study. Chin Med J 122:1666–1673
Kimura Y, Taniguchi M, Baba K (2001) Antitumor and antimetastatic effects on liver of triterpenoid fractions of Ganoderma lucidum: mechanism of action and isolation of an active substance. Anticancer Res 22:3309–3318
Takada Y, Aggarwal BB (2003) Betulinic acid suppresses carcinogen-induced NF-κB activation through inhibition of IκBα kinase and p65 phosphorylation: abrogation of cyclooxygenase-2 and matrix metalloprotease-9. J Immunol 171:3278–3286
Chintharlapalli S, Papineni S, Ramaiah SK, Safe S (2007) Betulinic acid inhibits prostate cancer growth through inhibition of specificity protein transcription factors. Cancer Res 67:2816–2823
Hsu Y-L, Kuo P-L, Lin L-T, Lin C-C (2005) Asiatic acid, a triterpene, induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest through activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways in human breast cancer cells. J Pharm Exp Ther 313:333–344
Yun K-J, Kim J-Y, Kim J-B, Lee K-W, Jeong S-Y, Park H-J, Jung H-J, Cho Y-W, Yun K, Lee K-T (2008) Inhibition of LPS-induced NO and PGE 2 production by asiatic acid via NF-κB inactivation in RAW 264.7 macrophages: possible involvement of the IKK and MAPK pathways. Int Immunopharmacol 8:431–441
Zhou C, Liu W, He W, Wang H, Chen Q, Song H (2015) Saikosaponin a inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis by suppressing NF-κB and MAPK pathways. Int Immunopharmacol 25:49–54
Pang X, Yi Z, Zhang X, Sung B, Qu W, Lian X, Aggarwal BB, Liu M (2009) Acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid inhibits prostate tumor growth by suppressing vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2-mediated angiogenesis. Cancer Res 69:5893–5900
Takada Y, Ichikawa H, Badmaev V, Aggarwal BB (2006) Acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid potentiates apoptosis, inhibits invasion, and abolishes osteoclastogenesis by suppressing NF-κB and NF-κB-regulated gene expression. J Immunol 176:3127–3140
Pang X, Yi Z, Zhang J, Lu B, Sung B, Qu W, Aggarwal BB, Liu M (2010) Celastrol suppresses angiogenesis-mediated tumor growth through inhibition of AKT/mammalian target of rapamycin pathway. Cancer Res 70:1951–1959
Kim Y, Kang H, Jang S-W, Ko J (2010) Celastrol inhibits breast cancer cell invasion via suppression of NF-κB-mediated matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression. Cell Physiol Biochem Int J Exp Cell Physiol Biochem Pharmacol 28:175–184
Weng C-J, Yen G-C (2010) The in vitro and in vivo experimental evidences disclose the Chemopreventive effects of Ganoderma lucidum on cancer invasion and metastasis. Clin Exp Metastasis 27:361–369
Thoennissen NH, Iwanski GB, Doan NB, Okamoto R, Lin P, Abbassi S, Song JH, Yin D, Toh M, Xie WD (2009) Cucurbitacin B induces apoptosis by inhibition of the JAK/STAT pathway and potentiates antiproliferative effects of gemcitabine on pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res 69:5876–5884
Zha Q-B, Zhang X-Y, Lin Q-R, Xu L-H, Zhao G-X, Pan H, Zhou D, Ouyang D-Y, Liu Z-H, He X-H (2015) Cucurbitacin e induces autophagy via downregulating mTORC1 signaling and upregulating AMPK activity. PLoS One 10(5):e0124355. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0124355
Ichikawa H, Takada Y, Shishodia S, Jayaprakasam B, Nair MG, Aggarwal BB (2006) Withanolides potentiate apoptosis, inhibit invasion, and abolish osteoclastogenesis through suppression of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) activation and NF-κB-regulated gene expression. Mol Cancer Ther 5:1434–1445
Subramanian C, White P, Gingrich A, Timmermann BN, Cohen MS (2015) Abstract B24: natural withanolides: A new group of anticancer drugs that selectively target the PI3K-mTOR pathway as novel potent therapeutics against colon cancers in vitro and in vivo. Mol Cancer Ther 14:B24–B24
Saleem M, Kaur S, Kweon M-H, Adhami VM, Afaq F, Mukhtar H (2005) Lupeol, a fruit and vegetable based triterpene, induces apoptotic death of human pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells via inhibition of Ras signaling pathway. Carcinogenesis 26:1956–1964
Saleem M, Afaq F, Adhami VM, Mukhtar H (2004) Lupeol modulates NF-κB and PI3K/Akt pathways and inhibits skin cancer in CD-1 mice. Oncogene 23:5203–5214
Mu X, Shi W, Sun L, Li H, Jiang Z, Zhang L (2012) Pristimerin, a triterpenoid, inhibits tumor angiogenesis by targeting VEGFR2 activation. Molecules 17:6854–6868
Li D-M, Guo Y-K, Li Q, Zhang J, Wang X-J, Bai J-G (2012) The pretreatment of cucumber with methyl jasmonate regulates antioxidant enzyme activities and protects chloroplast and mitochondrial ultrastructure in chilling-stressed leaves. Sci Horticult 143:135–143
Ahn KS, Hahn B-S, Kwack K, Lee EB, Kim YS (2006) Platycodin D-induced apoptosis through nuclear factor-κB activation in immortalized keratinocytes. Eur J Pharmacol 537:1–11
Ogasawara R, Sato K, Higashida K, Nakazato K, Fujita S (2013) Ursolic acid stimulates mTORC1 signaling after resistance exercise in rat skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 305:E760–E765
Xu Y-H, Zhao L-J, Li Y (2009) Alisol B acetate induces apoptosis of SGC7901 cells via mitochondrial and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases/Akt signaling pathways. World J Gastroenterol WJG 15:2870
Law BY, Wang M, Ma D-L, Al-Mousa F, Michelangeli F, Cheng S-H, Ng MH, To K-F, Mok AY, Ko RY (2010) Alisol B, a novel inhibitor of the sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase pump, induces autophagy, endoplasmic reticulum stress, and apoptosis. Mol Cancer Ther 9:718–730
Elumalai P, Arunkumar R, Benson CS, Sharmila G, Arunakaran J (2014) Nimbolide inhibits IGF-I-mediated PI3K/Akt and MAPK signalling in human breast cancer cell lines (MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231). Cell Biochem Funct 32:476–484
Menegazzi M, Di Paola R, Mazzon E, Genovese T, Crisafulli C, Dal Bosco M, Zou Z, Suzuki H, Cuzzocrea S (2008) Glycyrrhizin attenuates the development of carrageenan-induced lung injury in mice. Pharmacol Res 58:22–31
He S-Q, Gao M, Fu Y-F, Zhang Y-N (2015) Glycyrrhizic acid inhibits leukemia cell growth and migration via blocking AKT/mTOR/STAT3 signaling. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8:5175
Kuo H-P, Hsu S-C, Ou C-C, Li J-W, Tseng H-H, Chuang T-C, Liu J-Y, Chen S-J, Su M-H, Cheng Y-C (2013) Ganoderma tsugae extract inhibits growth of HER2-overexpressing cancer cells via modulation of HER2/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Evid Based Complement Altern Med. doi:10.1155/2013/219472
Baselga J, Swain SM (2009) Novel anticancer targets: revisiting ERBB2 and discovering ERBB3. Nat Rev Cancer 9:463–475
Li Y, Li T, Miao C, Li J, Xiao W, Ma E (2013) β-Eudesmol induces JNK-dependent apoptosis through the mitochondrial pathway in HL60 cells. Phytother Res 27:338–343
Wang Y-Y, Lv Y-F, Lu L, Cai L (2014) Oridonin inhibits mTOR signaling and the growth of lung cancer tumors. Anticancer Drugs 25:1192–1200
Maurya S, Devi S, Pandey V, Khosa R (1989) Content of betulin and betulinic acid, antitumor agents of Zizyphus species. Fitoterapia 60:468–469
Sánchez-Quesada C, López-Biedma A, Warleta F, Campos M, Beltrán G, Gaforio JJ (2013) Bioactive properties of the main triterpenes found in olives, virgin olive oil, and leaves of Olea europaea. J Agric Food Chem 61:12173–12182
Reyes-Zurita FJ, Rufino-Palomares EE, Lupiáñez JA, Cascante M (2009) Maslinic acid, a natural triterpene from Olea europaea L., induces apoptosis in HT29 human colon-cancer cells via the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. Cancer Lett 273:44–54
Huang L, Guan T, Qian Y, Huang M, Tang X, Li Y, Sun H (2011) Anti-inflammatory effects of maslinic acid, a natural triterpene, in cultured cortical astrocytes via suppression of nuclear factor-kappa B. Eur J Pharmacol 672:169–174
Martín R, Ibeas E, Carvalho-Tavares J, Hernández M, Ruiz-Gutierrez V, Nieto ML (2009) Natural triterpenic diols promote apoptosis in astrocytoma cells through ROS-mediated mitochondrial depolarization and JNK activation. PLoS One 4:e5975
Lu J, D-m Wu, Zheng Y-l HuB, Cheng W, Z-f Zhang, Shan Q (2011) Ursolic acid improves high fat diet-induced cognitive impairments by blocking endoplasmic reticulum stress and IκB kinase β/nuclear factor-κB-mediated inflammatory pathways in mice. Brain Behav Immun 25:1658–1667
C-t Tu, Li J, F-p Wang, Li L, J-y Wang, Jiang W (2012) Glycyrrhizin regulates CD4+ T cell response during liver fibrogenesis via JNK, ERK and PI3K/AKT pathway. Int Immunopharmacol 14:410–421
Xiao Z-Y, Zheng Q-Y, Jiang Y-Y, Zhou B, Yin M, Wang H-B, Zhang J-P (2004) Effects of esculentoside A on production of interleukin-1, 2, and prostaglandin E ~ 2. Acta Pharmacol Sin 25:817–821
Jiang J, Slivova V, Harvey K, Valachovicova T, Sliva D (2004) Ganoderma lucidum suppresses growth of breast cancer cells through the inhibition of Akt/NF-κB signaling. Nutr Cancer 49:209–216
Chen N-H, Liu J-W, Zhong J-J (2010) Ganoderic acid T inhibits tumor invasion in vitro and in vivo through inhibition of MMP expression. Pharmacol Rep 62:150–163
Weng C-J, Chau C-F, Hsieh Y-S, Yang S-F, Yen G-C (2008) Lucidenic acid inhibits PMA-induced invasion of human hepatoma cells through inactivating MAPK/ERK signal transduction pathway and reducing binding activities of NF-κB and AP-1. Carcinogenesis 29:147–156
Acknowledgments
Authors thank Central University of Punjab, Bathinda, for providing the necessary facilities to carry out the present work. Balraj Singh Gill thanks UGC for Maulana Azad National fellowship (F1-17.1/2011-12/MANF-SIK-HIM-3205).
Author’s contribution
Balraj Singh Gill: Preparation and writing of the whole manuscript. Sanjeev kumar: Addition and improvement of some parts of the manuscript. Navgeet: Idea and writing of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gill, B.S., Kumar, S. & Navgeet Triterpenes in cancer: significance and their influence. Mol Biol Rep 43, 881–896 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-016-4032-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-016-4032-9