Abstract
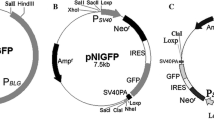
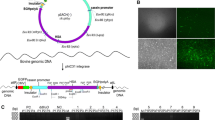
The aim of the present study was construction of mammary gland specific expression vector for high level of human insulin (hINS) expression in transgenic buffalo for therapeutic use. We have constructed mammary gland specific vector containing human insulin gene and there expression efficiency was checked into in vitro cultured buffalo mammary epithelial cells (BuMECs). Human pro-insulin coding region was isolated from human genomic DNA by intron skipping PCR primer and furin cleavage site was inserted between B–C and C–A chain of human insulin by overlap extension PCR. A mammary gland-specific buffalo beta-lactoglobulin promoter was isolated from buffalo DNA and used for human insulin expression in BuMEC cells. The construct was transfected into BuMECs by lipofection method and positive transgene cell clones were obtained by G418 selection after 3 weeks. Expression of hINS in transfected cells were confirmed by RT-PCR, Immunocytochemistry, Western Blotting and ELISA. The pAcISUBC insulin-expressing clones secreted insulin at varying levels between 0.18 - 1.43 ng/ml/24 h/2.0 × 106 cells.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Davidson HW, Rhodes CJ, Hutton JC (1988) Intraorganellar calcium and pH control proinsulin cleavage in the pancreatic beta cell via two distinct site-specific endopeptidases. Nature 333:93–96
Smeekens SP, Montag AG, Thomas G, Albiges-Rizo C, Carroll R, Bnig M, Phillips LA, Martin S, Ohagi S, Gardner P, Swir HH, Steiner DF (1992) Proinsulin processing by the subtilisin-related proprotein convertases furin, PC2, and PC3. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:8822–8826
Kaufmann JE, Irminger JC, Halban PA (1995) Sequence requirements for proinsulin processing at the B-chain/C-peptide junction. Biochem J 310:869–874
Dodson G, Steiner D (1998) The role of assembly in insulin’s biosynthesis. Curr Opin Struct Biol 8:189–194
Short DK, Okada S, Yamauchi K, Pessin JE (1998) Adenovirus mediated transfer of a modified human proinsulin gene reverses hyperglycemia in diabetic mice. Am J Physiol 275:E748–E756
Nakayama K (1997) Furin: a mammalian subtilisin/Kex2p-like endoprotease involved in processing of a wide variety of precursor proteins. Biochem J 327:625–635
Groskreutz DJ, Sliwkowski MX, Gorman CM (1994) Genetically engineered proinsulin constitutively processed and secreted as mature, active insulin. J Biol Chem 25:6241–6245
Vollenweider F, Kaufmann J, Irminger JC, Halban PA (1995) Processing of proinsulin by furin, PC2, and PC3 in (co) transfected COS (monkey kidney) cells. Diabetes 44:1075–1080
Efrat S (1998) Prospects for gene therapy of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 41:1401–1490
Thule PM, Liu J, Phillips LS (2000) Glucose regulated production of human insulin in rat hepatocytes. Gene Ther 7:205–214
Yamasaki K, Sasaki T, Nemoto M, Eto Y, Tajima N (1999) Differentiation-induced insulin secretion from nonendocrine cells with engineered human proinsulin cDNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 265:361–365
Chan SJ, Weiss J, Konrad M, White T, Bahl C, Yu SD, Marks D, Steiner DF (1981) Biosynthesis and periplasmic segregation of human proinsulin in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 78:5401–5404
Thim L, Hansen MT, Norris K, Hoegh I, Boel E, Forstrom J, Ammerer G, Fiil NP (1986) Secretion and processing of insulin precursors in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:6766–6770
Wang Y, Liang ZH, Zhang YS, Yao SY, Xu YG, Tang YH, Zhu SQ, Cui DF, Feng YM (2001) Human insulin from a precursor overexpressed in the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris and a simple procedure for purifying the expression product. Biotechnol Bioeng 73:74–79
Yanagita M, Nakayama K, Takeuchi T (1992) Processing of mutated proinsulin with tetrabasic cleavage sites to bioactive insulin in the non-endocrine cell line, COS-7. FEBS Lett 311:55–59
Arakawa T, Yu J, Chong DKX, Hough J, Engen PC, Langridge WHR (1998) A plant-based cholera toxin B subunit insulin fusion protein protects against the development of autoimmune diabetes. Nat Biotechnol 16:934–938
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA 4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software (version 4.0). Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599
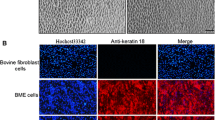
German T, Barash I (2002) Characterization of an epithelial cell line from bovine mammary gland. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 38:282–292
Kaushik R, Singh KP, Kumari A, Singh MK, Manik RS, Palta P, Singla SK, Chauhan MS (2013) Isolation, characterization and EGFP expression in the buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) mammary gland epithelial cell line. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 49(1):1–7
Zheng YM, He XY, Zheng Y (2010) Characteristics and EGFP expression of goat mammary gland epithelial cells. Reprod Domest Anim 45(6):e323–e331
Chi Q, Huang K (2007) Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of insulin. Anal Lett 40:95–102
Gerencser A, Barta E, Boa S, Kastanis P, Bosze Z, Bruce C, Whitelaw A (2001) Comparative analysis on the structural features of the 5′ flanking region of k-casein genes from six different species. Genet Sel Evol 34:117–128
Malewski T, Zwierzchowski L (2002) Genes expressed in the cow’s mammary gland computational analysis of 5′upstream sequences in search for factors conferring tissue and stage specific transcription. Anim Sci Papers Rep 20(1):5–20
Malewski T, Gajewska M, Zwierzchowski L (2005) Changes in DNA-binding activity of transcription factors in the differentiating bovine mammary gland. Anim Sci Pap Rep 23(2):75–84
Fuller RS, Brake AJ, Thorner J (1989) Intracellular targeting and structural conservation of a prohormone-processing endoprotease. Science 246:482–486
Van den Ouweland AMW, Van Duijnhoven HLP, Keizer GD, Dorssen LCJ, Van de Ven WJM (1990) Structural homology between the human fur gene product and the subtilisin-like protease encoded by yeast KEX2. Nucleic Acids Res 18:664
Barr PJ, Mason OB, Landsberg KE, Wong PA, Kiefer MC, Brake AJ (1991) cDNA and gene structure for a human subtilisin-like protease with cleavage specificity for paired basic amino acid residues. DNA Cell Biol 10:319–328
Kiefer MC, lbcker JE, Joh R, Landsberg KE, Saltman D, Barr PJ (1991) Identification of a second human subtilisin-like protease gene in the fes/fps region of chromosome 15. DNA Cell Biol 10:757–769
Yanagita M, Hoshino H, Nakayama K, Takeuchi T (1993) Processing of mutated proinsulin with tetrabasic cleavage sites to mature insulin reflects the expression of furin in nonendocrine cell lines. Endocrinology 133:639–644
Kasten-Jolly J, Aubrey MT, Conti DJ, Rosano TG, Ross JS, Freed BM (1997) Reversal of hyperglycemia in diabetic NOD mice by human proinsulin gene therapy. Transplant Proc 29:2216–2218
Gros L, Montoliu L, Riu E, Lebrigand L, Bosch F (1997) Regulation production of mature insulin by non-β-cells. Hum Gene Ther 8:2249–2259
Falqui L, Martinenghi S, Severini GM, Corbella P, Taglietti MV, Arcelloni C, Sarugeri E, Monti LD, Paroni R, Dozio N, Pozza G, Bordignon C (1999) Reversal of diabetes in mice by implantation of human fibroblasts genetically engineered to release mature human insulin. Hum Gene Ther 10:1753–1762
Ilan N, Barash I, Gootwine E, Shani M (1998) Establishment and initial characterization of the ovine mammary epithelial cell line NISH. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 34(4):326–332
Monzani PS, Bressan FF, Mesquita LG, Sangalli JR, Meirelles FV (2011) β-Casein gene expression by in vitro cultured bovine mammary epithelial cells derived from developing mammary glands. Genet Mol Res 10(2):604–614
Monzani PS, Sangalli JR, de Bem TH, Bressan FF, Fantinato-Neto P, Pimentel JR, Birgel-Junior EH, Fontes AM, Covas DT, Meirelles FV (2013) Breeding of transgenic cattle for human coagulation factor IX by a combination of lentiviral system and cloning. Genet Mol Res. 2013 Feb 28; 12 (AOP) [Epub ahead of print]
Zhang YL, Wan YJ, Wang ZY, Xu D, Pang XS, Meng L, Wang LH, Zhong BS, Wang F (2010) Production of dairy goat embryos, by nuclear transfer, transgenic for human acid beta-glucosidase. Theriogenology 73(5):681–690
Liu J, Luo Y, Liu Q, Zheng L, Yang Z, Wang Y, Su J, Quan F, Zhang Y (2013) Production of cloned embryos from caprine mammary epithelial cells expressing recombinant human β-defensin-3. Theriogenology 79(4):660–666
Shu JH, Zhang Y, Pan ZF, Peng SY, Cao JW, Li XC (2007) Construction of expression vector of human lactoferrin and its expression in bovine mammary epithelial cells. Belg J Zool 137(2):231–237
Van Kuik-Romeijn P, de Groot N, Hooijberg E, de Boer HA (2000) Expression of a functional mouse-human chimeric anti-CD19 antibody in the milk of transgenic mice. Trans Res 9(2):155–159
Wright G, Carver A, Cottom D, Reeves D, Scott A, Simons P, Wilmut I, Garner I, Colman A (1991) High level expression of active human alpha-1-antitrypsin in the milk of transgenic sheep. Biotechnology 9:830–834
Palmiter RD, Brinster RL, Hammer RE, Trumbauer ME, Rosenfeld MG, Birnberg NC, Evans RM (1982) Dramatic growth of mice that develop from eggs microinjected with metallothionein-growth hormone fusion genes. Nature 300:611–615
Palmiter RD, Brinster RL, Hammer RE, Trumbauer ME, Rosenfeld MG, Birnberg NC, Evans RM (1992) Dramatic growth of mice that develop from eggs microinjected with metallothionein-growth hormone fusion genes. Biotechnology 24:429–433
Reichenstein M, Gottlieb H, Damari GM, Iavnilovitch E, Barash I (2001) A new beta-lactoglobulin-based vector targets luciferase cDNA expression to the mammary gland of transgenic mice. Transgenic Res 10(5):445–456
Van der Hoff MJB, Labruyere WT, Moorman AFM, Lamers WH (1993) Mammary gene expression is improved by use of a longer SV40 early polyadenylation cassette. Nucleic Acids Res 21:4987–4988
Lily C, Chao AJ, Kim SJ, Huang L, Martinson HG (1999) Assembly of the cleavage and polyadenylation apparatus requires about 10 seconds in vivo and is faster for strong than for weak poly(A) sites. Mol Cell Biol 19:5588–5600
Alexander LJ, Stewart AF, Mackinlay AG, Kapelinskaya TV, Tkach TM, Gorodetsky SI (1998) Isolation and characterization of the bovine kappa-casein gene. Eur J Biochem 178:395–401
Malewski T (1998) Computer analysis of distribution of putative cis- and trans-regulatory elements in milk protein gene promoters. BioSystems 45:29–44
Rosen JM, Li S, Raughtt B, Hadsell D (1996) The mammary gland as bioreactor: factors regulating the efficient expression of milk protein-based transgenes. Am J Clin Nutr 63:627S–632S
Rosen JM, Wyszomierski SL, Hadsell D (1999) Regulation of milk protein gene expression. Ann Rev Nutr 19:406–436
O’Driscoll L, Gammell P, Clynes M (2002) Engineering Vero cells to secrete human insulin. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 38(3):146–153
Kim JH, Park SN, Suh H (2007) Generation of insulin-producing human mesenchymal stem cells using recombinant adeno-associated virus. Yonsei Med J 48:109–119
Shen K, Qin X, Xiao H, Zhang X, Xu X, Han Z (2002) Mature insulin production by engineered non-beta cells. Chin Med J (Engl) 115(4):532–535
Rasouli M, Ahmad Z, Omar AR, Allaudin ZN (2011) Engineering an L-cell line that expresses insulin under the control of the glucagon-like peptide-1 promoter for diabetes treatment. BMC Biotechnol 11:99
Scougall KT, Maltin CA, Shaw JA (2003) Tetracycline-regulated secretion of human insulin in a transfected non-endocrine cell line. J Mol Endocrinol 30(3):331–346
Schagger H, von Jagow G (1987) Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal Biochem 166(2):368–379
Lu YC, Sternini C, Rozengurt E, Zhukova E (2005) Release of transgenic human insulin from gastric g cells: a novel approach for the amelioration of diabetes. Endocrinology 146(6):2610–2619
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Grant BT/PR15035/AAQ/01/462/2011 from the Department of Biotechnology, Government of India, New Delhi, India. Author’s thanks to Ms. Neha Saini and Dr. Prashant Kadam for providing language help.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11033_2014_3464_MOESM1_ESM.eps
Fig.S1. Schematic representation of the strategy used to mutate the human proinsulin cDNA. The primers INSF1, H10A1 and CA2, INSR2 were used for preparation of INS-1 and INS-4, fragments. The primes INSF1, BC1 and BC2, CA1 were used for preparation of INS-2 and INS-3 fragments. The fragment INS5 was obtained after INS-2+3 fragment ligation by overlapping extension PCR and was then ligated between INS-1 and INS-4 by overlapping extension PCR. The resulting fragment INS6 contained the entire mutated cDNA. ∆ indicates mutation at the His-10 site; □ indicates mutations at the junction of the B and C peptides; * indicates mutation at the junction of the C and A peptides. (EPS 298 kb)
11033_2014_3464_MOESM2_ESM.tif
Fig.S2. PCR amplification of all inserted fragments in pAcISUBC vector by different combination of primers: Lane 1- buBLG promoters (BLGP3F & BLGP3R primer), Lane 2- buBLG promoter + insulin fragment (BLGL1 & INSR primer). Lane 3- Human insulin gene, (INSF1 & INSR2 primer). Lane 4- Insulin + SV40polyA (INSF1 & SVR primer). Lane 5- Insulin + BLG 3’UTR fragment (INSF1 & UTRR primer). Lane 6- BLG 3’UTR (UTRF & UTRR primer). Lane 7- BLG3’UTR + CMV promoter (UTRF & CMV R primer). Lane 8- CMV promoter (CMVF & CMVR primer). (TIFF 233 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaushik, R., Singh, K.P., Kumari, A. et al. Construction of a recombinant human insulin expression vector for mammary gland-specific expression in buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) mammary epithelial cell line. Mol Biol Rep 41, 5891–5902 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-014-3464-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-014-3464-3