Abstract
Neutral endopeptidase (NEP) is the first podocytic antigen responsible for human membranous nephropathy (MN). Besides the prevailing pathogenetic mechanism of immune complex, NEP is also involved in the metabolism of natriuretic peptides (NP). The identification of anti-NEP antibodies in human MN suggests that the decreased circulating NEP may down-regulate the NP catabolism. In this context, we hypothesize that NP disarrangement secondary to anti-NEP antibodies may account, in part, for the onset of proteinuria in MN. Whereas the pathways for the onset of proteinuria caused by elevated NP level are still obscure. The data presented in this review focus on those which support this hypothesis with regards to evidence from the glomerular haemodynamic changes, endothelial permeability, glomerular basement membrane disruption, and podocyte detachment.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cybulsky AV (2011) Membranous nephropathy. Contrib Nephrol 169:107–125
Heymann W, Hackel DB, Harwood S, Wilson SG, Hunter JL (1959) Production of nephrotic syndrome in rats by Freund’s adjuvants and rat kidney suspensions. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 100:660–664
Ronco P, Debiec H (2007) Target antigens and nephritogenic antibodies in membranous nephropathy: of rats and men. Semin Immunopathol 29:445–458
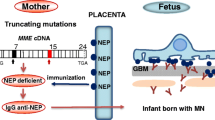
Debiec H, Guigonis V, Mougenot B, Decobert F, Haymann JP, Bensman A, Deschênes G, Ronco PM (2002) Antenatal membranous glomerulonephritis due to anti-neutral endopeptidase antibodies. N Engl J Med 346:2053–2060
Jalal F, Lemay G, Zollinger M, Berteloot A, Boileau G, Crine P (1991) Neutral endopeptidase, a major brush border protein of the kidney proximal nephron, is directly targeted to the apical domain when expressed in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. J Biol Chem 266:19826–19832
Ebihara F, Di Marco GS, Juliano MA, Casarini DE (2003) Neutral endopeptidase expression in mesangial cells. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst 4:228–233
Hashimoto S, Amaya F, Oh-Hashi K, Kiuchi K, Hashimoto S (2010) Expression of neutral endopeptidase activity during clinical and experimental acute lung injury. Respir Res 11:164
Debiec H, Guigonis V, Mougenot B, Haymann JP, Bensman A, Deschênes G, Ronco PM (2003) Antenatal membranous glomerulonephritis with vascular injury induced by anti-neutral endopeptidase antibodies: toward new concepts in the pathogenesis of glomerular diseases. J Am Soc Nephrol 14:S27–S32
Prunotto M, Carnevali ML, Candiano G, Murtas C, Bruschi M, Corradini E, Trivelli A, Magnasco A, Petretto A, Santucci L, Mattei S, Gatti R, Scolari F, Kador P, Allegri L, Ghiggeri GM (2010) Autoimmunity in membranous nephropathy targets aldose reductase and SOD2. J Am Soc Nephrol 21:507–519
Nangaku M, Shankland SJ, Couser WG (2005) Cellular response to injury in membranous nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 16:1195–1204
Hong Y, Turner AJ (2007) Old enzyme with new interest: review of newly understood NEP functions and its potential regulators. Chin J Biochem Mol Biol 23:85–92
Baxter GF (2004) The natriuretic peptides. Basic Res Cardiol 99:71–75
Woodard GE, Rosado JA (2007) Recent advances in natriuretic peptide research. J Cell Mol Med 11:1263–1271
Kuhn M (2004) Molecular physiology of natriuretic peptide signalling. Basic Res Cardiol 99:76–82
Hu P, Lu L, Hu B, Qin YH (2010) Renal action of C-type natriuretic peptide: advocating the isolated perfused rat kidney model. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl 21:613–620
Marumo F, Sakamoto H, Ando K, Ishigami T (1990) Concentrations of atrial natriuretic peptide in plasma and urine of kidney disease patients. Clin Chem 36:1650–1653
Shin SJ, Wen JD, Lee YJ, Chen IH, Tsai JH (1998) Increased C-type natriuretic peptide mRNA expression in the kidney of diabetic rats. J Endocrinol 158:35–42
Cataliotti A, Malatino LS, Jougasaki M, Zoccali C, Castellino P, Giacone G, Bellanuova I, Tripepi R, Seminara G, Parlongo S, Stancanelli B, Bonanno G, Fatuzzo P, Rapisarda F, Belluardo P, Signorelli SS, Heublein DM, Lainchbury JG, Leskinen HK, Bailey KR, Redfield MM, Burnett JC Jr (2001) Circulating natriuretic peptide concentrations in patients with end-stage renal disease: role of brain natriuretic peptide as a biomarker for ventricular remodeling. Mayo Clin Proc 76:1111–1119
Hu P, Wang J, Zhao XQ, Hu B, Lu L, Qin YH (2012) Overexpressed C-type natriuretic peptide serves as an early compensatory response to counteract extracellular matrix remodeling in unilateral ureteral obstruction rats. Mol Biol Rep. doi:10.1007/s11033-012-2186-7
Cataliotti A, Giordano M, De Pascale E, Giordano G, Castellino P, Jougasaki M, Costello LC, Boerrigter G, Tsuruda T, Belluardo P, Lee SC, Huntley B, Sandberg S, Malatino LS, Burnett JC Jr (2002) CNP production in the kidney and effects of protein intake restriction in nephrotic syndrome. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 283:F464–F472
Hu P, Wang J, Hu B, Lu L, Xuan Q, Qin YH (2012) Increased urinary C-type natriuretic peptide excretion may be an early marker of renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis. Peptides 37:98–105
Ahluwalia A, MacAllister RJ, Hobbs AJ (2004) Vascular actions of natriuretic peptides. Cyclic GMP-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Basic Res Cardiol 99:83–89
Obineche EN, Adeghate E, Chandranath IS, Benedict S, Al Gafri LS, Adem A (2004) Alterations in atrial natriuretic peptide and its receptors in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat kidneys. Mol Cell Biochem 261:3–8
Fonteles MC, Greenberg RN, Monteiro HS, Currie MG, Forte LR (1998) Natriuretic and kaliuretic activities of guanylin and uroguanylin in the isolated perfused rat kidney. Am J Physiol 275:F191–F197
Huxley VH, Tucker VL, Verburg KM, Freeman RH (1987) Increased capillary hydraulic conductivity induced by atrial natriuretic peptide. Circ Res 60:304–307
Pham I, Sediame S, Maistre G, Roudot-Thoraval F, Chabrier PE, Carayon A, Adnot S (1997) Renal and vascular effects of C-type and atrial natriuretic peptides in humans. Am J Physiol 273:R1457–R1464
Kiemer AK, Fürst R, Vollmar AM (2005) Vasoprotective actions of the atrial natriuretic peptide. Curr Med Chem Cardiovasc Hematol Agents 3:11–21
Sarker MH, Fraser PA (2002) The role of guanylyl cyclases in the permeability response to inflammatory mediators in pial venular capillaries in the rat. J Physiol 540:209–218
van Hinsbergh WM (1997) Endothelial permeability for macromolecules. Mechanistic aspects of pathophysiological modulation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 17:1018–1023
Suenobu N, Shichiri M, Iwashina M, Marumo F, Hirata Y (1999) Natriuretic peptides and nitric oxide induce endothelial apoptosis via a cGMP-dependent mechanism. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 19:140–146
Fürst R, Brueckl C, Kuebler WM, Zahler S, Krötz F, Görlach A, Vollmar AM, Kiemer AK (2005) Atrial natriuretic peptide induces mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 in human endothelial cells via Rac1 and NAD(P)H oxidase/Nox2-activation. Circ Res 96:43–53
Llorens-Cortes C, Huang H, Vicart P, Gasc JM, Paulin D, Corvol P (1992) Identification and characterization of neutral endopeptidase in endothelial cells from venous or arterial origins. J Biol Chem 267:14012–14018
Levidiotis V, Power DA (2005) New insights into the molecular biology of the glomerular filtration barrier and associated disease. Nephrology (Carlton) 10:157–166
Cybulsky AV, Quigg RJ, Salant DJ (2005) Experimental membranous nephropathy redux. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 289:F660–F671
Minto AW, Kalluri R, Togawa M, Bergijk EC, Killen PD, Salant DJ (1998) Augmented expression of glomerular basement membrane specific type IV collagen isoforms (alpha3–alpha5) in experimental membranous nephropathy. Proc Assoc Am Physicians 110:207–217
Raats CJ, Luca ME, Bakker MA, Van Der Wal A, Heeringa P, Van Goor H, Van Den Born J, De Heer E, Berden JH (1999) Reduction in glomerular heparan sulfate correlates with complement deposition and albuminuria in active Heymann nephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol 10:1689–1699
McMillan JI, Riordan JW, Couser WG, Pollock AS, Lovett DH (1996) Characterization of a glomerular epithelial cell metalloproteinase as matrix metalloproteinase-9 with enhanced expression in a model of membranous nephropathy. J Clin Invest 97:1094–1101
Canaan-Kühl S, Ostendorf T, Zander K, Koch KM, Floege J (1998) C-type natriuretic peptide inhibits mesangial cell proliferation and matrix accumulation in vivo. Kidney Int 53:1143–1151
Osawa H, Yamabe H, Kaizuka M, Tamura N, Tsunoda S, Baba Y, Shirato K, Tateyama F, Okumura K (2000) C-Type natriuretic peptide inhibits proliferation and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 secretion in cultured human mesangial cells. Nephron 86:467–472
Liu S, Ding J, Fan Q, Zhang H (2010) The activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase is responsible for podocyte injury. Mol Biol Rep 37:2477–2484
Lewko B, Stepinski J (2002) Cyclic GMP signaling in podocytes. Microsc Res Tech 57:232–235
Rippe C, Rippe A, Larsson A, Asgeirsson D, Rippe B (2006) Nature of glomerular capillary permeability changes following acute renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 291:F1362–F1368
Friedrich C, Endlich N, Kriz W, Endlich K (2006) Podocytes are sensitive to fluid shear stress in vitro. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 291:F856–F865
Lewko B, Gołos M, Latawiec E, Angielski S, Stepinski J (2006) Regulation of cGMP synthesis in cultured podocytes by vasoactive hormones. J Physiol Pharmacol 57:599–610
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81000306) and the Post-Doctoral Foundation of Anhui Medical University (No. 2009KJ02).
Conflict of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, P., Xuan, Q., Hu, B. et al. Anti-neutral endopeptidase, natriuretic peptides disarrangement, and proteinuria onset in membranous nephropathy. Mol Biol Rep 40, 2963–2967 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-012-2367-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-012-2367-4