Abstract
Membranous nephropathy, a disease characterized by an accumulation of immune deposits on the outer aspect of the glomerular basement membrane, is the most common cause of idiopathic nephrotic syndrome in white adults. In the rat model of Heymann nephritis, the target antigen of antibodies is megalin, a multiligand receptor expressed at the podocyte cell surface. This review summarizes key findings provided by this experimental model and by our discovery of neutral endopeptidase being the alloantigen involved in neonatal cases of membranous nephropathy. We discuss the role of alloimmunization as a new mechanism of renal disease and the approach that we use to identify new podocyte antigens. We also summarize current knowledge on the mechanism of proteinuria, with special emphasis on the role of complement. In conclusion, substantial progresses have been made in understanding molecular mechanisms of membranous nephropathy, which should lead to novel therapeutic approaches.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wasserstein AG (1997) Membranous glomerulonephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol 8:664–674
Glassock RJ (2003) Diagnosis and natural course of membranous nephropathy. Semin Nephrol 23:324–332
Glassock RJ (2004) The treatment of idiopathic membranous nephropathy: a dilemma or a conundrum? Am J Kidney Dis 44:562–566
Perna A, Schieppati A, Zamora J, Giuliano GA et al (2004) Immunosuppressive treatment for idiopathic membranous nephropathy: a systematic review. Am J Kidney Dis 44:385–401
Ruggenenti P, Chiurchiu C, Brusegan V, Abbate M, Perna A, Filippi C, Remuzzi G (2003) Rituximab in idiopathic membranous nephropathy: a one-year prospective study. J Am Soc Nephrol 14:1851–1857
Cunningham PN, Quigg RJ (2005) Contrasting roles of complement activation and its regulation in membranous nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 16:1214–1222
Imai H, Hamai K, Komatsuda A, Ohtani H, Miura AB (1997) IgG subclasses in patients with membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis, membranous nephropathy, and lupus nephritis. Kidney Int 51:270–276
Noel LH, Aucouturier P, Monteiro RC, Preud’Homme JL, Lesavre P (1988) Glomerular and serum immunoglobulin G subclasses in membranous nephropathy and anti-glomerular basement membrane nephritis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 46:186–194
Heymann W, Hackel DB, Harwood S, Wilson SGF, Hunter JL (1959) Production of nephrotic syndrome in rats by Freund’s adjuvants and rat kidney suspension. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 100:660–664
Van Damme BJ, Fleuren GJ, Bakker WW, Vernier RL, Hoedemaeker PJ (1978) Experimental glomerulonephritis in the rat induced by antibodies directed against tubular antigens. V. Fixed glomerular antigens in the pathogenesis of heterologous immune complex glomerulonephritis. Lab Invest 38:502–510
Couser WG, Steinmuller DR, Stilmant MM, Salant DJ, Lowenstein LM (1978) Experimental glomerulonephritis in the isolated perfused rat kidney. J Clin Invest 62:1275–1287
Kerjaschki D, Farquhar MG (1982) The pathogenic antigen of Heymann nephritis is a membrane glycoprotein of the renal proximal tubule brush border. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 79:5557–5561
Kerjaschki D, Farquhar MG (1983) Immunocytochemical localization of the Heymann nephritis antigen (gp330) in glomerular epithelial cells of normal Lewis rats. J Exp Med 157:667–686
Allegri L, Brianti E, Chatelet F, Manara GC, Ronco P, Verroust P (1986) Polyvalent antigen-antibody interactions are required for the formation of electron-dense immune deposits in passive Heymann’s nephritis. Am J Pathol 125:1–6
Christensen EI, Birn H (2002) Megalin and cubilin: multifunctional endocytic receptors. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3:256–266
Makker SP, Tramontano A (2006) Differential capacity of anti-RAP and anti-megalin antibodies to produce progressive passive Heymann nephritis-implications for the pathogenesis of idiopathic human membranous glomerulonephritis. J Pathol 210:282–287
Saito A, Pietromonaco S, Loo AKC, Farquhar MG (1994) Complete cloning and sequencing of rat gp330/“megalin,” a distinctive member of the low density lipoprotein receptor family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 91:9725–9729
Raychowdhury R, Zheng G, Brown D, McCluskey RT (1996) Induction of Heymann nephritis with a gp330/megalin fusion protein. Am J Pathol 148:1613–1623
Saito A, Yamazaki H, Rader K, Nakatani A, Ullrich R, Kerjaschki D, Orlando RA, Farquhar MG (1996) Mapping rat megalin: the second cluster of ligand binding repeats contains a 46-amino acid pathogenic epitope involved in the formation of immune deposits in Heymann nephritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93:8601–8605
Yamazaki H, Ullrich R, Exner M, Saito A, Orlando RA, Kerjaschki D, Farquhar MG (1998) All four putative ligand-binding domains in megalin contain pathogenic epitopes capable of inducing passive Heymann nephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol 9:1638–1644
Oleinikov AV, Feliz BJ, Makker SP (2000) A small N-terminal 60-kD fragment of gp600 (megalin), the major autoantigen of active Heymann nephritis, can induce a full-blown disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 11:57–64
Tramontano A, Knight T, Vizzuso D, Makker SP (2006) Nested N-terminal megalin fragments induce high-titer autoantibody and attenuated Heymann nephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol 17:1979–1985
Tramontano A, Makker SP (2004) Conformation and glycosylation of a megalin fragment correlate with nephritogenicity in Heymann nephritis. J Immunol 172:2367–2373
Shah P, Tramontano A, Makker SP (2007) Intramolecular spreading in Heymann nephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol (in press)
Ronco P, Allegri L, Melcion C, Pirotsky E, Appay MD, Bariety J, Pontillon F, Verroust P (1984) A monoclonal antibody to brush border and passive Heymann nephritis. Clin Exp Immunol 55:319–332
Ronco P, Allegri L, Brianti E, Chatelet F, Van Leer EHG, Verroust P (1989) Antigenic targets in epimembranous glomerulonephritis. Experimental data and potential application in human pathology. Appl Pathol 7:85–98
Assmann KJ, van Son JP, Dijkman HB, Koene RA (1992) A nephritogenic rat monoclonal antibody to mouse aminopeptidase A. Induction of massive albuminuria after a single intravenous injection. J Exp Med 175:623–635
Chatelet F, Brianti E, Ronco P, Roland J, Verroust P (1986) Ultrastructural localization by monoclonal antibodies of brush border antigens expressed by glomeruli. I. Renal distribution. Am J Pathol 122:500–511
Chatelet F, Brianti E, Ronco P, Roland J, Verroust P (1986) Ultrastructural localization by monoclonal antibodies of brush border antigens expressed by glomeruli. II. Extrarenal distribution. Am J Pathol 122:512–519
Assmann KJ, Tangelder MM, Lange WP, Tadema TM, Koene RA (1983) Membranous glomerulonephritis in the mouse. Kidney Int 24:303–312
Assmann KJ, Ronco P, Tangelder MM, Lange WP, Verroust P, Koene RA (1985) Comparison of antigenic targets involved in antibody-mediated membranous glomerulonephritis in the mouse and rat. Am J Pathol 121:112–122
Matsuo S, Fukatsu A, Taub ML, Caldwell PR, Brentjens JR, Andres G (1987) Glomerulonephritis induced in the rabbit by antiendothelial antibodies. J Clin Invest 79:1798–1811
Ronco P, Ardaillou N, Verroust P, Lelongt B (1994) Pathophysiology of the podocyte: A target and a major player in glomerulonephritis. Adv Nephrol Necker Hosp 23:91–131
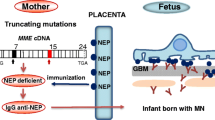
Debiec H, Guigonis V, Mougenot B, Decobert F, Haymann JP, Bensman A, Deschenes G, Ronco P (2002) Antenatal membranous glomerulonephritis due to anti-neutral endopeptidase antibodies. N Engl J Med 346:2053–2060
Debiec H, Nauta J, Coulet F, van der Burg M, Guigonis V, Schumans T, de Heer E, Soubrier F, Janssen F, ronco P (2004) Role of truncating mutations in MME gene in feto-maternal allo-immunization and neonatal glomerulopathies. Lancet 364:1252–1259
Nauta J, de Heer E, Baldwin WM 3rd, ten Kate FJ, v d Heijden AJ, Wolff ED (1990) Transplacental induction of membranous nephropathy in a neonate. Pediatr Nephrol 4:111–116
Tauc M, Châtelet F, Verroust P, Vandewalle A, Poujeol P, Ronco P (1988) Characterization of monoclonal antibodies specific for rabbit renal brush-border hydrolases: application to immunohistological localization. J Histochem Cytochem 36:523–532
Matsuo S, Caldwell PRB, Brentjens JR, Andres G (1985) In vivo interactions of antibodies with cell surface antigens. A mechanism responsible for in situ formation of immune deposits in the zona pellucida of rabbit oocytes. J Clin Invest 75:1369–1380
Lu B, Figini M, Emanueli C, Geppetti P, Grady EF, Gerard NP, Ansell J, Payan DG, Gerard C, Bunnett N (1997) The control of microvascular permeability and blood pressure by neutral endopeptidase. Nat Med 3:904–907
Ikeda K, Emoto N, Raharjo SB, Nurhantari Y, Saiki K, Yokoyama M, Matsuo M (1999) Molecular identification and characterization of novel membrane-bound metalloprotease, the soluble secreted form of which hydrolyzes a variety of vasoactive peptides. J Biol Chem 274:32469–32477
Bonvouloir N, Lemieux N, Crine P, Boileau G, DesGroseillers L (2001) Molecular cloning, tissue distribution, and chromosomal localization of MMEL2, a gene coding for a novel human member of the neutral endopeptidase-24.11 family. DNA Cell Biol 20:493–498
Gough J, Yilmaz A, Yilmaz S, Benediktsson H (2005) Recurrent and de novo glomerular immune-complex deposits in renal transplant biopsies. Arch Pathol Lab Med 129:231–233
Lin J et al (2001) Membranous glomerulopathy associated with graft-versus-host disease following allogeneic stem cell transplantation: report of 2 cases and review of the literature. Am J Nephrol 21:351–356
Rossi L et al (2001) Membranous glomerulonephritis after haematopoietic cell transplantation for multiple myeloma. Nephron 88:260–263
Miyazaki Y et al (2003) Membranous nephropathy associated with donor lymphocyte infusion following allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Int J Hematol 78:262–265
Tsutsumi C et al (2004) Membranous nephropathy after allogeneic stem cell transplantation: report of 2 cases. Int J Hematol 79:193–197
Stevenson WS et al (2005) Nephrotic syndrome after stem cell transplantation. Clin Transplant 19:141–144
Ikee R et al (2004) Recurrent nephrotic syndrome associated with graft-versus-host disease. Bone Marrow Transplant 34:1005–1006
Bruijn JA et al (1988) Murine chronic graft-versus-host disease as a model for lupus nephritis. Am J Pathol 130:639–641
Bianchi DW et al (1996) Male fetal progenitor cells persist in maternal blood for as long as 27 years postpartum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93:705–708
Maloney S et al (1999) Microchimerism of maternal origin persists into adult life. J Clin Invest 104:41–47
Adams KM, Nelson JL (2004) Microchimerism: an investigative frontier in autoimmunity and transplantation. JAMA 291:1127–1131
Khosrotehrani K, Bianchi DW (2003) Fetal cell microchimerism: helpful or harmful to the parous woman? Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol 15:195–199
Nagahama K et al (2005) Possible role of autoantibodies against nephrin in an experimental model of chronic graft-versus-host disease. Clin Exp Immunol 141:215–222
Ronco PM (1999) Paraneoplastic glomerulopathies: New insights into an old entity (clinical conference). Kidney Int 56:355–377
Hörl WH, Kerjaschki D (2000) Membranous glomerulonephritis (MGN). J Nephrol 13:291–316
Winfield JB, Faiferman I, Koffler D (1977) Avidity of anti-DNA antibodies in serum and IgG glomerular eluates from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Association of high avidity antinative DNA antibody with glomerulonephritis. J Clin Invest 59:90–96
van Bruggen MC, Kramers C, Walgreen B, Elema JD, Kallenberg CG, van den Born J, Smeenk RJ, Assmann KJ, Muller S, Monestier M, Berden JH (1997) Nucleosomes and histones are present in glomerular deposits in human lupus nephritis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 12:57–66
Jordan SC, Buckingham B, Sakai R, Olson D (1991) Studies of immune-complex glomerulonephritis mediated by human thyroglobulin. N Engl J Med 304:1212–1215
Takekoshi Y, Tanaka M, Miyakawa Y, Yoshizawa H, Takahashi K, Mayumi M (1979) Free “small” and IgG-associated “large” hepatitis B e antigen in the serum and glomerular capillary walls of two patients with membranous glomerulonephritis. N Engl J Med 300:814–819
Lai KN, Li PK, Lui SF, Au TC, Tam JS, Tong KL, Lai FM (1991) Membranous nephropathy related to hepatitis B virus in adults. N Engl J Med 324:1457–1463
Gamble CN, Reardan JB (1975) Immunopathogenesis of syphilitic glomerulonephritis. Elution of antitreponemal antibody from glomerular immune-complex deposits. N Engl J Med 292:449–454
Nagashima R, Maeda K, Yuda F, Kudo K, Saitoh M, Takahashi T (1997) Helicobacter pylori antigen in the glomeruli of patients with membranous nephropathy. Virchows Arch 431:235–239
Chen JS, Chen A, Chang LC, Chang WS, Lee HS, Lin SH, Lin YF (2004) Mouse model of membranous nephropathy induced by cationic bovine serum albumin: antigen dose-response relations and strain differences. Nephrol Dial Transplant 19:2721–2728
Naruse T, Kitamura D, Miyakawa Y, Shibata S (1973) Deposition of renal tubular epithelial antigens along the renal glomerular capillary walls of patients with membranous glomerulonephritis. J Immunol 110:1163–1169
Douglas MFS, Rabideau DP, Schwartz MM, Lewis EJ (1981) Evidence of autologous immune complex nephritis. N Engl J Med 305:1326–1329
Zanetti M, Mandet C, Duboust A, Bedrossian J, Bariety J (1981) Demonstration of a passive Heymann-nephritis like mechanism in human kidney transplants. Clin Nephrol 15:272–288
Ivanyi B, Haszon I, Endreffy E, Szenohradszky P, Petri IB, Kalmar T, Butkowski RJ, Charonis AS, Turi S (1998) Childhood membranous nephropathy, circulating antibodies to the 58-kD TIN antigen, and anti-tubular basement membrane nephritis: an 11-year follow-up. Am J Kidney Dis 32:1068–1074
Nelson TR, Charonis AS, McIvor RS, Butkowski RJ (1995) Identification of a cDNA encoding tubulointerstitial nephritis antigen. J Biol Chem 270:16265–16270
Butkowski RJ, Kleppel MM, Katz A, Michael AF, Fish AJ (1991) Distribution of tubulointerstitial nephritis antigen and evidence for multiple forms. Kidney Int 40:838–846
Habib R, Beziau A, Goulet O, Blanche S, Niaudet P (1993) Renal involvement in autoimmune enteropathies. Ann Pediatr 40:103–107
Couser WG, Salant DJ (1980) In situ immune complex formation and glomerular injury. Kidney Int 17:1–13
Salant DJ, Belok S, Madaio MP, Couser WG (1980) A new role for complement in experimental membranous nephropathy in rats. J Clin Invest 66:1339–1350
Baker PJ, Ochi RF, Schulze M, Johnson RJ, Campbell C, Couser WG (1989) Depletion of C6 prevents development of proteinuria in experimental membranous nephropathy in rats. Am J Pathol 135:185–194
Cybulsky AV, Quigg RJ, Salant DJ (1986) The membrane attack complex in complement-mediated glomerular epithelial cell injury: formation and stability of C5b-9 and C5b-7 in rat membranous nephropathy. J Immunol 137:1511–1516
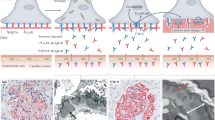
Ronco P, Debiec H (2005) Molecular pathomechanisms of membranous nephropathy: from Heymann nephritis to alloimmunization. J Am Soc Nephrol 16:1205–1213
Noble B, Van Liew JB, Andres GA, Brentjens JR (1984) Factors influencing susceptibility of LEW rats to Heymann nephritis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 30:241–254
Doi T, Mayumi M, Kanatsu K, Suehiro F, Hamashima Y (1984) Distribution of IgG subclasses in membranous nephropathy. Clin Exp Immunol 58:57–62
Haas M (1994) IgG subclass deposits in glomeruli of lupus and nonlupus membranous nephropathies. Am J Kidney Dis 23:358–364
Doi T, Kanatsu K, Nagai H, Suehiro F, Kuwahara T, Hamashima Y (1984) Demonstration of C3d deposits in membranous nephropathy. Nephron 37:232–235
Moll S, Miot S, Sadallah S, Gudat F, Mihatsch MJ, Schifferli JA (2001) No complement receptor 1 stumps on podocytes in human glomerulopathies. Kidney Int 59:160–168
Neale TJ, Ullrich R, Ojha P, Poczewski H, Verhoeven AJ, Kerjaschki D (1993) Reactive oxygen species and neutrophil respiratory burst cytochrome b558 are produced by kidney glomerular cells in passive Heymann nephritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 90:3645–3649
Neale TJ, Ojha PP, Exner M, Poczewski H, Ruger B, Witztum JL, Davis P, Kerjaschki D (1994) Proteinuria in passive Heymann nephritis is associated with lipid peroxidation and formation of adducts on type IV collagen. J Clin Invest 94:1577–1584
Kerjaschki D (2004) Pathomechanisms and molecular basis of membranous glomerulopathy. Lancet 364:1194–1196
Urushihara M, Kagami S, Kuhara T, Tamaki T, Kuroda Y (2002) Glomerular distribution and gelatinolytic activity of matrix metalloproteinases in human glomerulonephritis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 17:1189–1196
McMillan JI, Riordan JW, Couser WG, Pollock AS, Lovett DH (1996) Characterization of a glomerular epithelial cell metalloproteinase as matrix metalloproteinase-9 with enhanced expression in a model of membranous nephropathy. J Clin Invest 97:1094–1101
Saran AM, Yuan H, Takeuchi E, McLaughlin M, Salant DJ (2003) Complement mediates nephrin redistribution and actin dissociation in experimental membranous nephropathy. Kidney Int 64:2072–2078
Doublier S, Ruotsalainen V, Salvidio G, Lupia E, Biancone L, Conaldi PG, Reponen P, Tryggvason K, Camussi G (2001) Nephrin redistribution on podocytes is a potential mechanism for proteinuria in patients with primary acquired nephrotic syndrome. Am J Pathol 158:1723–1731
Ronco P (2007) Proteinuria: is it all in the foot? J Clin Invest 117:2079–2082
Topham PS, Haydar SA, Kuphal R, Lightfoot JD, Salant DJ (1999) Complement-mediated injury reversibly disrupts glomerular epithelial cell actin microfilaments and focal adhesions. Kidney Int 55:1763–1775
Yuan H, Takeuchi E, Taylor GA, McLaughlin M, Brown D, Salant DJ (2002) Nephrin dissociates from actin, and its expression is reduced in early experimental membranous nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 13:946–956
Sever S et al (2007) Proteolytic processing of dynamin by cytoplasmic cathepsin L defines a mechanism for proteinuric kidney disease. J Clin Invest 117:2095–2104
Takano T, Cybulsky AV (2000) Complement C5b-9-mediated arachidonic acid metabolism in glomerular epithelial cells: role of cyclooxygenase-1 and -2. Am J Pathol 156:2091–2101
Torbohm I, Schonermark M, Wingen AM, Berger B, Rother K, Hansch GM (1990) C5b-8 and C5b-9 modulate the collagen release of human glomerular epithelial cells. Kidney Int 37:1098–1104
Kuroki A, Shibata T, Honda H, Totsuka D, Kobayashi K, Sugisaki T (2002) Glomerular and serum IgG subclasses in diffuse proliferative lupus nephritis, membranous lupus nephritis, and idiopathic membranous nephropathy. Intern Med 41:936–942
Ohtani H, Wakui H, Komatsuda A, Okuyama S, Masai R, Maki N, Kigawa A, Sawada K, Imai H (2004) Distribution of glomerular IgG subclass deposits in malignancy-associated membranous nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant 19:574–579
Simister NE, Story CM (1997) Human placental Fc receptors and the transmission of antibodies from mother to fetus. J Reprod Immunol 37:1–23
Clark MR (1997) IgG effect or mechanisms. Chem Immunol 65:88–110
Lucisano YM, Lachmann PJ (1991) The effect of antibody isotype and antigenic epitope density on the complement-fixing activity of immune-complexes: a systematic study using chimeric anti-NIP antibodies with human Fc regions. Clin Exp Immunol 84:1–8
Kerjaschki D, Exner M, Ullrich R, Susani M, Curtiss LK, Witztum JL, Farquhar MG, Orlando RA (1997) Pathogenic antibodies inhibit the binding of apolipoproteins to megalin/gp330 in passive Heymann nephritis. J Clin Invest 100:2303–2309
Dussaule JC, Stefanski A, Bea ML, Ronco P, Ardaillou R (1993) Characterization of neutral endopeptidase in vascular smooth muscle cells of rabbit renal cortex. Am J Physiol 264:F45–F52
Sumimoto M, Shen R, Nanus DM (2005) Involvement of neutral endopeptidase in neoplastic progression. Biochim Biophys Acta 1751:52–59
Terawaki SI, Kitano K, Hakoshima T (2007) Structural basis for type II membrane protein binding by ERM proteins revealed by the radixin-neutral endopeptidase 24–11 (NEP) complex. J Biol Chem 282:19854–19862
Reynolds J, Prodromidi EI, Juggapah JK, Abbott DS, Holthaus KA, Kalluri R, Pusey CD (2005) Nasal administration of recombinant rat alpha3(IV)NC1 prevents the development of experimental autoimmune glomerulonephritis in the WKY rat. J Am Soc Nephrol 16:1350–1359
Debiec H, Luimula P, Lefeu F, Nortier JL, Ronco P (2006) Identification of B-cell epitopes on neutral endopeptidase in feto-maternal allo-immunization with antenatal glomerulopathies. J Am Soc Nephrol 17:F–PO065 (abstract)
Nortier JL, Debiec H, Tournay Y, Mougenot B, Noël JC, Deschodt-Lanckman MM, Janssen F, Ronco P (2005) Neonatal Disease in neutral endopeptidase alloimmunization: lessons for pregnancy management and Immunological monitoring. Pediatric Nephrol 21:1399–1405
Acknowledgment
The research of the authors is funded by grants from GIS-Institut des Maladies Rares, Agence de la Biomédecine, Programme Hospitalier de Recherche Clinique, INSERM, Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale, AURA (Association pour l’Utilisation du Rein Artificiel), AMGEN France, and Genzyme Renal Innovations Program (GRIP). We thank Christine Vial for assistance in editing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ronco, P., Debiec, H. Target antigens and nephritogenic antibodies in membranous nephropathy: of rats and men. Semin Immunopathol 29, 445–458 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00281-007-0091-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00281-007-0091-2