Abstract
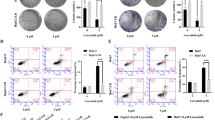
In this study, we investigate effect of PI3K gene silencing on growth, migration and related proteins expression of CD40 signal-mediated gastric cancer cells. We observed that combination of sCD40L with PI3K siRNA could significantly inhibit AGS cells growth, block cells in G1 phase, and promote tumour cells apoptosis after 24 h treatment. Transwell test showed that numbers of cells per visual field in group PI3K siRNA or group sCD40L (after 24 h PI3K siRNA or sCD40L alone treatment) were fewer than that (32.54 ± 4.22) in control group. Numbers of cells per visual field in (after 24 h combination treatment of PI3K siRNA with sCD40L) were significantly fewer than that in group PI3K siRNA or group sCD40L. Compared with group sCD40L, expression level of Fas protein in group sCD40L + PI3K siRNA was significantly increased. The findings suggest that PI3K siRNA may strengthen CD40-induced specific antitumour effect via blocking PI3K/Akt signal pathway, resisting tumour immunoediting regulated by CD40 signal. Combination of sCD40L and PI3K siRNA is an important mechanism of gastric cancer therapy.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P (2005) Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin 55:74–108
Bray F, Sankila R, Ferlay J, Parkin DM (2002) Estimates of cancer incidence and mortality in Europe in 1995. Eur J Cancer 38:99–166
Nguyen VT, Benveniste EN (2000) Involvement of STAT-1 and ets family members in interferon-gamma induction of CD40 transcription in microglia/macrophages. J Biol Chem 275:23674–23684
Krzesz R, Wagner AH, Cattaruzza M, Hecker M (1999) Cytokine-inducible CD40 gene expression in vascular smooth muscle cells is mediated by nuclear factor kappaB and signal transducer and activation of transcription-1. FEBS Lett 453:191–196
Schonbeck U, Libby P (2001) The CD40/CD154 receptor/ligand dyad. Cell Mol Life Sci 58:4–43
Reinders ME, Sho M, Robertson SW, Geehan CS, Briscoe DM (2003) Proangiogenic function of CD40 ligand-CD40 interactions. J Immunol 171:1534–1541
Tai YT, Podar K, Mitsiades N, Lin B, Mitsiades C, Gupta D, Akiyama M, Catley L, Hideshima T, Munshi NC, Treon SP, Anderson KC (2003) CD40 induces human multiple myeloma cell migration via phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT/NF-kappa B signaling. Blood 101(7):2762–2769
Deregibus MC, Buttiglieri S, Russo S, Bussolati B, Camussi G (2003) CD40-dependent activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway mediates endothelial cell survival and in vitro angiogenesis. J Biol Chem 278(20):18008–18014
Cai AQ, Landman KA, Hughes BD (2007) Multi-scale modeling of a wound-healing cell migration assay. J Theor Biol 245:576–594
Debeir O, Mégalizzi V, Warzée N, Kiss R, Decaestecker C (2008) Videomicroscopic extraction of specific information on cell proliferation and migration in vitro. Exp Cell Res 314:2985–2998
Vonderheide RH (2007) Prospect of targeting the CD40 pathway for cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res 13:1083–1088
Gallagher NJ, Eliopoulos AG, Agathangelo A, Oates J, Crocker J, Young LS (2002) CD40 activation in epithelial ovarian carcinoma cells modulates growth, apoptosis, and cytokine secretion. Mol Pathol 55:110–120
Davies CC, Mason J, Wakelam MJ, Young LS, Eliopoulos AG (2004) Inhibition of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase- and ERK MAPK-regulated protein synthesis reveals the pro-apoptotic properties of CD40 ligation in carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem 279:1010–1019
Baxendale AJ, Dawson CW, Stewart SE, Mudaliar V, Reynolds G, Gordon J, Murray PG, Young LS, Eliopoulos AG (2005) Constitutive activation of the CD40 pathway promotes cell transformation and neoplastic growth. Oncogene 24:7913–7923
Sbih-Lammali F, Clausse B, Ardila-Osorio H, Guerry R, Talbot M, Havouis S, Ferradini L, Bosq J, Tursz T, Busson P (1999) Control of apoptosis in Epstein Barr virus-positive nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells: opposite effects of CD95 and CD40 stimulation. Cancer Res 59:924–930
Yamaguchi H, Tanaka F, Sadanaga N, Ohta M, Inoue H, Mori M (2003) Stimulation of CD40 inhibits Fas- or chemotherapy-mediated apoptosis and increases cell motility in human gastric carcinoma cells. Int J Oncol 23:1697–1702
Peter ME, Budd RC, Desbarats J, Hedrick SM, Hueber AO, Newell MK, Owen LB, Pope RM, Tschopp J, Wajant H, Wallach D, Wiltrout RH, Zörnig M, Lynch DH (2007) The CD95 receptor: apoptosis revisited. Cell 129:447–450
Gregory MS, Hackett CG, Abernathy EF, Lee KS, Saff RR, Hohlbaum AM, Moody KS, Hobson MW, Jones A, Kolovou P, Karray S, Giani A, John SW, Chen DF, Marshak-Rothstein A, Ksander BR (2011) Opposing roles for membrane bound and soluble Fas ligand in glaucoma-associated retinal ganglion cell death. PLoS One 6(3):17659
Lasham A, Lindridge E, Rudert F, Onrust R, Watson J (2000) Regulation of the human fas promoter by YB-1, Puralpha and AP-1 transcription factors. Gene 252:1–13
Nakamura T, Imai Y, Matsumoto T, Sato S, Takeuchi K, Igarashi K, Harada Y, Azuma Y, Krust A, Yamamoto Y, Nishina H, Takeda S, Takayanagi H, Metzger D, Kanno J, Takaoka K, Martin TJ, Chambon P, Kato S (2007) Estrogen prevents bone loss via estrogen receptor alpha and induction of Fas ligand in osteoclasts. Cell 130:811–823
Folkman J (1990) What is the evidence that tumors are angiogenesis dependent? J Natl Cancer Inst 82:4–6
Bedoya F, Meneu JC, Macías MI, Moreno A, Enríquez-de-Salamanca R, Gonzalez EM, Vegh I (2009) Mutation in CNR1 gene and VEGF expression in esophageal cancer. Tumori 95:68–75
Inoue K, Ozeki Y, Suganuma Y, Sugiura Y, Tanaka S (1997) Vascular endothelial growth factor expression in primary esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: association with angiogenesis and tumor progression. Cancer 79:206–213
Bendardaf R, Buhmeida A, Hilska M, Laato M, Syrjänen S, Syrjänen K, Collan Y, Pyrhönen S (2008) VEGF-1 expression in colorectal cancer is associated with disease localization, stage, and longterm disease-specific survival. Anticancer Res 28:3865–3870
Li YJ, Deng YJ, Wen G, Zhang XL (2009) Evaluation of angiogenesis in the tumorigenesis and progression of breast cancer. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi 47:519–522
Bluff JE, Menakuru SR, Cross SS, Higham SE, Balasubramanian SP, Brown NJ, Reed MW, Staton CA (2009) Angiogenesis is associated with the onset of hyperplasia in human ductal breast disease. Br J Cancer 101:666–672
Gisterek I, Matkowki R, Lacko A, Sedlaczek P, Szewczyk K, Biecek P, Halon A, Staszek U, Szelachowska J, Pudelko M, Bebenek M, Harlozinska-Szmyrka A, Kornafel J (2010) Serum vascular endothelial growth factors A, C, and D in human breast tumors. Pathol Oncol Res 16:337–344
Mysliwiec P, Pawlak K, Kuklinski A, Kedra B (2008) Combined preoperative plasma endoglobin and VEGF-A assessment on colorectal cancer patients. Folia Histochem Cytobiol 46:487–492
Tang ZY, Ye SL, Liu YK, Qin LX, Sun HC, Ye QH, Wang L, Zhou J, Qiu SJ, Li Y, Ji XN, Liu H, Xia JL, Wu ZQ, Fan J, Ma ZC, Zhou XD, Lin ZY, Liu KD (2004) A decade’s studies on metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 130:187–196
Guo RP, Zhong C, Shi M, Zhang CQ, Wei W, Zhang YQ, Li JQ (2006) Clinical value of apoptosis and angiogenesis factors in estimating the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 132:547–555
Acknowledgments
The work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31270919) and the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK2010231).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, R., Chen, WC., Pang, XQ. et al. Effect of PI3K gene silencing on growth, migration and related proteins expression of CD40 signal-mediated gastric cancer cells. Mol Biol Rep 40, 999–1008 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-012-2141-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-012-2141-7