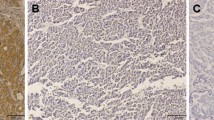
Abstract
Purpose
Whereas some studies have indicated that the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) was correlated to some apoptosis and angiogenesis factors: p53, survivin, matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs, including MMP-2 and MMP-9) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), other studies have failed to confirm this. The aim of the present study is to investigate the expression of p53, survivin, MMPs and VEGF in HCC and the relationship between these factors and the prognosis of HCC patients.
Methods
The expression of p53, survivin, MMP-2, MMP-9 and VEGF was measured by immunohistochemical assays in the liver resection specimens of 90 patients with HCC.
Results
The positive rate of p53, survivin, MMP-2, MMP-9 and VEGF was 33.3, 51.1, 60.0, 37.8 and 76.7%, respectively. The expression of MMP-2, MMP-9 and VEGF was correlated to the recurrence of HCC patients, respectively (P < 0.01). No correlation was found between the expression of apoptosis factors (p53 and survivin) and the recurrence of HCC patients, respectively (P > 0.05). The positive correlations were found between MMP-2 and VEGF (r = 0.32, P < 0.01), MMP-9 and VEGF (r = 0.24, P < 0.05). Significant differences of disease-free survival rates occurred among subgroups according to the expression of MMP-2, MMP-9 and VEGF (P < 0.01). Multivariate analysis revealed that macroscopically disseminated nodules, tumor micrometastasis, high serum alpha-fetoprotein level, positive expression of MMP-9 and VEGF were independent recurrence risk factors.
Conclusions
Our investigation revealed that p53 and survivin could not estimate the prognosis of HCC patients. Angiogenesis factors (MMPs and VEGF) positively correlated to the prognosis of HCC patients. The expression of MMPs and VEGF in HCC tissues could be regarded as a valuable indicator in estimating the prognosis of HCC patients.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arii S, Yamaoka Y, Futagawa S, Inoue K, Kobayashi K, Kojiro M, Makuuchi M, Nakamura Y, Okita K, Yamada R (2000) Results of surgical and nonsurgical treatment for small-sized hepatocellular carcinomas: a retrospective and nationwide survey in Japan. Hepatology 32:1224–1229
Bergers G, Brekken R, McMahon G, Vu TH, Itoh T, Tamaki K, Tanzawa K, Thorpe P, Itohara S, Werb Z, Hanahan D (2000) Matrix metalloproteinase-9 triggers the angiogenic switch during carcinogenesis. Nat Cell Biol 2:737–744
Chao Y, Li CP, Chau GY, Chen CP, King KL, Lui WY, Yen SH, Chang FY, Chan WK, Lee SD (2003) Prognostic significance of vascular endothelial growth factor, basic fibroblast growth factor, and angiogenin in patients with respectable hepatocellular carcinoma after surgery. Ann Surg Oncol 10:355–362
Edmondson HA, Steiner PE (1954) Primary carcinoma of the liver: a study of 100 cases among 48900 necropsies. Cancer 7:462–503
Farges O, Regimbeau JM, Belghiti J (1998) Aggressive management of recurrence following surgical resection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatogastroenterology 45(s):1275–1280
Garzetti GG, Ciavattini A, Lucarini G, Pugnaloni A, De Nictolis M, Amati S, Romanini C, Biagini G (1999) Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor related to 72-kilodalton metalloproteinase immunostaining in patients with serous ovarian tumors. Cancer 85:2219–2225
Gorog D, Regoly Merei J, Paku S, Kopper L, Nagy P (2005) Alpha-fetoprotein expression is a potential prognostic marker in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 11:5015–5018
Hayashi H, Sugio K, Matsumata T, Adachi E, Takenaka K, Sugimachi K (1995) The clinical significance of p53 gene mutation in hepatocellular carcinoma from Japan. Hepatology 22:1702–1707
Hermanek P, Hutter RV, Sobin LH, Wittekind C (1999) Classification of isolated tumor cells and micrometastasis. Cancer 86:2668–2673
Hsu HC, Tseng HJ, Lai PL, Lee PH, Peng SY (1993) Expression of p53 gene in 184 unifocal hepatocellular carcinomas: association with tumor growth and invasiveness. Cancer Res 53:4691–4694
Ikeguchi M, Hirooka Y, Kaibara N (2002a) Quantitative analysis of apoptosis-related gene expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer 95:1938–1945
Ikeguchi M, Ueda T, Sakatani T, Hirooka Y, Kaibara N (2002b) Expression of survivin messenger RNA correlates with poor prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Diagn Mol Pathol 11:33–40
Ishii Y, Nakasato Y, Kobayashi S, Yamazaki Y, Aoki T (2003) A study on angiogenesis-related matrix metalloproteinase networks in primary hepatocellular carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 22:461–470
Ito T, Shiraki K, Sugimoto K, Yamanaka T, Fujikawa K, Ito M, Takase K, Moriyama M, Kawano H, Hayashida M, Nakano T, Suzuki A (2000) Survivin promotes cell proliferation in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 31:1080–1085
Jeng KS, Sheen IS, Chen BF, Wu JY (2000) Is the p53 gene mutation of prognostic value in hepatocellular carcinoma after resection? Arch Surg 135:1329–1333
Kallakury BV, Karikehalli S, Haholu A, Sheehan CE, Azumi N, Ross JS (2001) Increased expression of matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9 and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases 1 and 2 correlate with poor prognostic variables in renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 7:3113–3119
Kannangai R, Wang J, Liu QZ, Sahin F, Torbenson M (2005) Survivin overexpression in hepatocellular carcinoma is associated with p53 dysregulation. Int J Gastrointest Cancer 35:53–60
Kawakita N, Seki S, Sakaguchi H, Yanai A, Kuroki T, Mizoguchi Y, Kobayashi K, Monna T (1992) Analysis of proliferating hepatocytes using a monoclonal antibody against proliferating cell nuclear antigen/cyclin in embedded tissues from various liver diseases fixed in formaldehyde. Am J Pathol 140:513–520
Maatta M, Soini Y, Liakka A, Autio-Harmainen H (2000) Differential expression of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2, MMP-9, and membrane type 1-MMP in hepatocellular and pancreatic adenocarcinoma: implications for tumor progression and clinical prognosis. Clin Cancer Res 6:2726–2734
Mise K, Tashiro S, Yogita S, Wada D, Harada M, Fukuda Y, Miyake H, Isikawa M, Izumi K, Sano N (1998) Assessment of the biological malignancy of hepatocellular carcinoma: relationship to clinicopathological factors and prognosis. Clin Cancer Res 4:1475–1482
Moon WS, Rhyu KH, Kang MJ, Lee DG, Yu HC, Yeum JH, Koh GY, Tarnawski AS (2003) Overexpression of VEGF and angioproietin 2: a key to high vascularity of hepatocellular carcinoma? Mod Pathol 16:552–557
Morinaga S, Nakamura Y, Ishiwa N, Yoshikawa T, Noguchi Y, Yamamoto Y, Rino Y, Imada T, Takanashi Y, Akaike M, Sugimasa Y, Takemiya S (2004) Expression of survivin mRNA associates with apoptosis, proliferation and histologically aggressive features in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Rep 12:1189–1194
Nakanishi K, Sakamoto M, Yamasaki S, Todo S, Hirohashi S (2005) Akt phosphorylation is a risk factor for early disease recurrence and poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer 103:307–312
Nakano S, Haratake J, Okamoto K, Takeda S (1994) Investigation of resected multinodular hepatocellular carcinoma: assessment of unicentric or multicentric genesis from histological and prognosis viewpoint. Am J Gastroenterol 89:189–193
Nanashima A, Yano H, Yamaguchi H, Tanaka K, Shibasaki S, Sumida Y, Sawai T, Shindou H, Nakagoe T (2004) Immunohistochemical analysis of tumor biological factors in hepatocellular carcinoma: relationship to clinicopathological factors and prognosis after hepatic resection. J Gastroenterol 39:148–154
Ng IO, Lai EC, Chan AS, So MK (1995) Overexpression of p53 in hepatocellular carcinomas: a clinicopathological and prognostic correlation. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 10:250–255
Poon RT, Fan ST, Lo CM, Liu CL, Wong J (1999) Intrahepatic recurrence after curative resection of hepatocellular carcinoma: long-term results of treatment and prognostic factors. Ann Surg 229:216–222
Pugh RN, Murray-Lyon IM, Dawson JL, Pietroni MC, Williams R (1973) Transection of the oesophagus for bleeding oesophageal varices. Br J Surg 60:646–649
Qin LX, Tang ZY (2004) Recent progress in predictive biomarkers for metastatic recurrence of human hepatocellular carcinoma: a review of the literature. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 130:497–513
Saffroy R, Lelong JC, Azoulay D, Salvucci M, Reynes M, Bismuth H, Debuire B, Lemoine A (1999) Clinical significance of circulating anti-p53 antibodies in European patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Br J Cancer 79:604–610
Shi M, Zhang CQ, Zhang YQ, Liang XM, Li JQ (2004) Micrometastases of solitary hepatocellular carcinoma and appropriate resection margin. World J Surg 28:376–381
Tanaka S, Toh Y, Adachi E, Matsumata T, Mori R, Sugimachi K (1993) Tumor progression in hepatocellular carcinoma may be mediated by p53 mutation. Cancer Res 53:2884–2887
The Liver Cancer Study Group of Japan (1990) Primary liver cancer in Japan. Clinicopathologic features and results of surgical treatment. Ann Surg 211:277–287
Unemori EN, Ferrara N, Bauer EA, Amento EP (1992) Vascular endothelial growth factor induces interstitial collagenase expression in human endothelial cells. J Cell Physiol 153:557–562
Yamaguchi R, Yano H, Iemura A, Ogasawara S, Haramaki M, Kojiro M (1998) Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 28:68–77
Yamanaka N, Okamoto E, Toyosaka A, Mitunobu M, Fujihara S, Kato T, Fujimoto J, Oriyama T, Furukawa K, Kawamura E (1990) Prognostic factors after hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinomas. A univariate and multivariate analysis. Cancer 65:1104–1110
Acknowledgments
We thank Kai-Tao Feng and Jin-Hui Hou for their technical assistance. Grants: National Science and Technology Key Project, PR China (No. 2001BA703B054); Science and Technology Project of Guangdong Province (No. 2002254); Science and Technology Project of Guangzhou City (No. 2005Z3-E0111).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, RP., Zhong, C., Shi, M. et al. Clinical value of apoptosis and angiogenesis factors in estimating the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 132, 547–555 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-006-0097-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-006-0097-5