Abstract
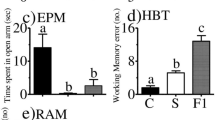
The aim of this study is to investigate whether ketamine, a noncompetitive N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) antagonist, had an influence on learning and memory in developing mice. Fifty Kunming mice aged 21 days were randomly divided into 5 subgroups (n = 10 for each) to receive intraperitoneal injection of equal volume of saline (S group) or ketamine (25, 50 or 100 mg/kg of body weight/day) for 7 consecutive days, or to be left untreated (C group). A step-down passive avoidance test was performed to evaluate learning and memory in these mice on days 8 and 9. Additionally, the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in the hippocampus was determined. Rats receiving saline or sub-anesthetic dose of ketamine (25 mg/kg) showed significantly decreased abilities of learning and memory and reduced expression of BDNF, compared to the normal controls (P < 0.05). In contrast, comparable abilities of learning and memory and expression of BDNF were found for anesthetic doses of ketamine (50 or 100 mg/kg)-treated rats and controls (P > 0.05). Repetitive mechanical stress impairs learning and memory performance in developing mice, which may be associated with decreased BDNF expression. The stress-induced learning and memory impairment can be prevented by anesthetic doses of ketamine.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Riedel G, Platt B, Micheau J (2003) Glutamate receptor function in learning and memory. Behav Brain Res 140(1–2):1–47
Li F, Tsien JZ (2009) Memory and the NMDA receptors. N Engl J Med 361(3):302–303
Malenka RC, Bear MF (2004) LTP and LTD: an embarrassment of riches. Neuron 44(1):5–21
Tsien JZ (2000) Linking Hebb’s coincidence-detection to memory formation. Curr Opin Neurobiol 10(2):266–273
Sakimura K, Kutsuwada T, Ito I, Manabe T, Takayama C, Kushiya E, Yagi T, Aizawa S, Inoue Y, Sugiyama H et al (1995) Reduced hippocampal LTP and spatial learning in mice lacking NMDA receptor epsilon 1 subunit. Nature 373(6510):151–155
Shimizu E, Tang YP, Rampon C, Tsien JZ (2000) NMDA receptor-dependent synaptic reinforcement as a crucial process for memory consolidation. Science 290(5494):1170–1174
Tang YP, Shimizu E, Dube GR, Rampon C, Kerchner GA, Zhuo M, Liu G, Tsien JZ (1999) Genetic enhancement of learning and memory in mice. Nature 401(6748):63–69
Tang YP, Wang H, Feng R, Kyin M, Tsien JZ (2001) Differential effects of enrichment on learning and memory function in NR2B transgenic mice. Neuropharmacology 41(6):779–790
Okon T (2007) Ketamine: an introduction for the pain and palliative medicine physician. Pain Physician 10(3):493–500
Hetem LA, Danion JM, Diemunsch P, Brandt C (2000) Effect of a subanesthetic dose of ketamine on memory and conscious awareness in healthy volunteers. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 152(3):283–288
Krystal JH, Bennett A, Abi-Saab D, Belger A, Karper LP, D’Souza DC, Lipschitz D, Abi-Dargham A, Charney DS (2000) Dissociation of ketamine effects on rule acquisition and rule implementation: possible relevance to NMDA receptor contributions to executive cognitive functions. Biol Psychiatry 47(2):137–143
Zhang DX, Levy WB (1992) Ketamine blocks the induction of LTP at the lateral entorhinal cortex-dentate gyrus synapses. Brain Res 593(1):124–127
Haugan F, Rygh LJ, Tjølsen A (2008) Ketamine blocks enhancement of spinal long-term potentiation in chronic opioid treated rats. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 52(5):681–687
Tsumoto T, Hagihara K, Sato H, Hata Y (1987) NMDA receptors in the visual cortex of young kittens are more effective than those of adult cats. Nature 327(6122):513–514
Miller KD, Chapman B, Stryker MP (1989) Visual responses in adult cat visual cortex depend on N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA 86(13):5183–5187
Yamada K, Nabeshima T (2003) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor/TrkB signaling in memory processes. J Pharmacol Sci 91(4):267–270
Mizuno M, Yamada K, He J, Nakajima A, Nabeshima T (2003) Involvement of BDNF receptor TrkB in spatial memory formation. Learn Mem 10(2):108–115
Bekinschtein P, Cammarota M, Katche C, Slipczuk L, Rossato JI, Goldin A, Izquierdo I, Medina JH (2008) BDNF is essential to promote persistence of long-term memory storage. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA 105(7):2711–2716
Bekinschtein P, Cammarota M, Igaz LM, Bevilaqua LR, Izquierdo I, Medina JH (2007) Persistence of long-term memory storage requires a late protein synthesis- and BDNF-dependent phase in the hippocampus. Neuron 53(2):261–277
Yang J, Zhao X, Zhou Q, Jiang Q (2003) Effects of nimodipine and fructose-1, 6-diphosphate on cerebral damage in carbon monoxide poisoning mice. Chin Med J (Engl) 116(12):1911–1915
Domino EF, Chodoff P, Corssen G (1965) Pharmacologic effects of ci-581, a new dissociative anesthetic, in man. Clin Pharmacol Ther 6:279–291
Bergman SA (1999) Ketamine: review of its pharmacology and its use in pediatric anesthesia. Anesth Prog 46(1):10–20
Glickman A (1995) Ketamine: the dissociative anesthetic and the development of a policy for its safe administration in the pediatric emergency department. J Emerg Nurs 21(2):116–124
Parwani A, Weiler MA, Blaxton TA, Warfel D, Hardin M, Frey K, Lahti AC (2005) The effects of a subanesthetic dose of ketamine on verbal memory in normal volunteers. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 183(3):265–274
Jeong YH, Park CH, Yoo J, Shin KY, Ahn SM, Kim HS, Lee SH, Emson PC, Suh YH (2006) Chronic stress accelerates learning and memory impairments and increases amyloid deposition in APPV717I-CT100 transgenic mice, an Alzheimer’s disease model. FASEB J 20(6):729–731
Li XH, Liu NB, Zhang MH, Zhou YL, Liao JW, Liu XQ, Chen HW (2007) Effects of chronic multiple stress on learning and memory and the expression of Fyn, BDNF, TrkB in the hippocampus of rats. Chin Med J (Engl) 120(8):669–674
Fujioka T, Fujioka A, Tan N, Chowdhury GM, Mouri H, Sakata Y, Nakamura S (2001) Mild prenatal stress enhances learning performance in the non-adopted rat offspring. Neuroscience 103(2):301–307
Garcia R (2001) Stress, hippocampal plasticity, and spatial learning. Synapse 40(3):180–183
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Medical Science Research Foundation of Jiangsu Province, China (Grant No. H200645) and Science Foundation of the Health Bureau of Wuxi City, China (Grant No. XM0805).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, S., Zhang, Y., Wang, H. et al. Anesthetic ketamine counteracts repetitive mechanical stress-induced learning and memory impairment in developing mice. Mol Biol Rep 38, 4347–4351 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-010-0561-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-010-0561-9