Abstract
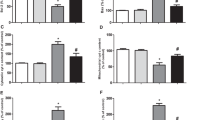
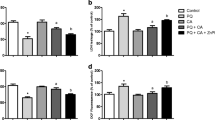
Propyl gallate (PG) as a synthetic antioxidant exerts a variety of effects on tissue and cell functions. Here, we investigated the effects of MAPK (MEK, JNK and p38) inhibitors on PG-treated HeLa cells in relation to cell death, ROS and GSH levels. PG induced cell growth inhibition and apoptosis in HeLa cells, which was accompanied by the loss of mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP; ΔΨm). ROS levels were increased or decreased in PG-treated HeLa cells depending on the incubation times. PG also increased GSH depleted cell numbers in HeLa cells. All the MAPK inhibitors slightly enhanced cell growth inhibition, death and MMP (ΔΨm) loss, and increased ROS levels in PG-treated HeLa cells. However, MAPK inhibitors did not significantly affect GSH depletion in PG-treated cells. In conclusion, the enhanced effect of MAPK inhibitors on PG-induced HeLa cell death was accompanied by increasing ROS levels but the effect was not related to changes of GSH level.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PG:
-
Propyl gallate
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- MEK:
-
MAP kinase or ERK kinase
- ERK:
-
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase
- JNK:
-
c-Jun N-terminal kinase
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- MMP (ΔΨm):
-
Mitochondrial membrane potential
- FBS:
-
Fetal bovine serum
- PI:
-
Propidium iodide
- FITC:
-
Fluorescein isothiocyanate
- H2DCFDA:
-
2′,7′-Dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate
- DHE:
-
Dihydroethidium
- GSH:
-
Glutathione
- CMFDA:
-
5-Chloromethylfluorescein diacetate
References
Daniel JW (1986) Metabolic aspects of antioxidants and preservatives. Xenobiot; Fate Foreign Compd Biol Syst 16:1073–1078
Dacre JC (1974) Long-term toxicity study of n-propyl gallate in mice. Food Cosmet Toxicol 12:125–129
Wu TW, Fung KP, Zeng LH, Wu J, Nakamura H (1994) Propyl gallate as a hepatoprotector in vitro and in vivo. Biochem Pharmacol 48:419–422
Rosin MP, Stich HF (1980) Enhancing and inhibiting effects of propyl gallate on carcinogen-induced mutagenesis. J Environ Pathol Toxicol 4:159–167
Abdo KM, Huff JE, Haseman JK, Alden CJ (1986) No evidence of carcinogenicity of d-mannitol and propyl gallate in F344 rats or B6C3F1 mice. Food Chem Toxicol 24:1091–1097
Reddan JR, Giblin FJ, Sevilla M, Padgaonkar V, Dziedzic DC, Leverenz VR et al (2003) Propyl gallate is a superoxide dismutase mimic and protects cultured lens epithelial cells from H2O2 insult. Exp Eye Res 76:49–59
Chen CH, Liu TZ, Chen CH, Wong CH, Chen CH, Lu FJ et al (2007) The efficacy of protective effects of tannic acid, gallic acid, ellagic acid, and propyl gallate against hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress and DNA damages in IMR-90 cells. Mol Nutr Food Res 51:962–968
Hirose M, Yada H, Hakoi K, Takahashi S, Ito N (1993) Modification of carcinogenesis by alpha-tocopherol, t-butylhydroquinone, propyl gallate and butylated hydroxytoluene in a rat multi-organ carcinogenesis model. Carcinogenesis 14:2359–2364
Kobayashi H, Oikawa S, Hirakawa K, Kawanishi S (2004) Metal-mediated oxidative damage to cellular and isolated DNA by gallic acid, a metabolite of antioxidant propyl gallate. Mutat Res 558:111–120
Kawanishi S, Oikawa S, Murata M (2005) Evaluation for safety of antioxidant chemopreventive agents. Antioxid Redox Signal 7:1728–1739
Nakagawa Y, Nakajima K, Tayama S, Moldeus P (1995) Metabolism and cytotoxicity of propyl gallate in isolated rat hepatocytes: effects of a thiol reductant and an esterase inhibitor. Mol Pharmacol 47:1021–1027
Boyd I, Beveridge EG (1979) Relationship between the antibacterial activity towards Escherichia coli NCTC 5933 and the physico-chemical properties of some esters of 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoic acid (gallic acid). Microbios 24:173–184
Miller C, Castonguay A, Teel RW (1996) Modulation of the mutagenicity and metabolism of the tobacco-specific nitrosamine 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone (NNK) by phenolic compounds. Mutat Res 368:221–233
Jacobi H, Eicke B, Witte I (1998) DNA strand break induction and enhanced cytotoxicity of propyl gallate in the presence of copper(II). Free Radic Biol Med 24:972–978
Blenis J (1993) Signal transduction via the MAP kinases: proceed at your own RSK. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:5889–5892
Genestra M (2007) Oxyl radicals, redox-sensitive signalling cascades and antioxidants. Cell Signal 19:1807–1819
Hsin YH, Chen CF, Huang S, Shih TS, Lai PS, Chueh PJ (2008) The apoptotic effect of nanosilver is mediated by a ROS- and JNK-dependent mechanism involving the mitochondrial pathway in NIH3T3 cells. Toxicol Lett 179:130–139
Mao X, Yu CR, Li WH, Li WX (2008) Induction of apoptosis by shikonin through a ROS/JNK-mediated process in Bcr/Abl-positive chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) cells. Cell Res 18:879–888
Gomez-Lazaro M, Galindo MF, Melero-Fernandez de Mera RM, Fernandez-Gomez FJ, Concannon CG, Segura MF et al (2007) Reactive oxygen species and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activate Bax to induce mitochondrial cytochrome c release and apoptosis in response to malonate. Mol Pharmacol 71:736–743
Guyton KZ, Liu Y, Gorospe M, Xu Q, Holbrook NJ (1996) Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase by H2O2. Role in cell survival following oxidant injury. J Biol Chem 271:4138–4142
Liu Y, Borchert GL, Surazynski A, Hu CA, Phang JM (2006) Proline oxidase activates both intrinsic and extrinsic pathways for apoptosis: the role of ROS/superoxides, NFAT and MEK/ERK signaling. Oncogene 25:5640–5647
Henson ES, Gibson SB (2006) Surviving cell death through epidermal growth factor (EGF) signal transduction pathways: implications for cancer therapy. Cell Signal 18:2089–2097
Han YH, Park WH (2009) Propyl gallate inhibits the growth of HeLa cells via regulating intracellular GSH level. Food Chem Toxicol 47:2531–2538
Han YH, Moon HJ, You BR, Park WH (2009) The anti-apoptotic effects of caspase inhibitors on propyl gallate-treated HeLa cells in relation to reactive oxygen species and glutathione levels. Arch Toxicol 83:825–833
Han YH, Moon HJ, You BR, Kim SZ, Kim SH, Park WH (2009) JNK and p38 inhibitors increase and decrease apoptosis, respectively, in pyrogallol-treated calf pulmonary arterial endothelial cells. Int J Mol Med 24:717–722
Park WH, Seol JG, Kim ES, Hyun JM, Jung CW, Lee CC et al (2000) Arsenic trioxide-mediated growth inhibition in MC/CAR myeloma cells via cell cycle arrest in association with induction of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, p21, and apoptosis. Cancer Res 60:3065–3071
Han YH, Kim SZ, Kim SH, Park WH (2008) Arsenic trioxide inhibits the growth of Calu-6 cells via inducing a G2 arrest of the cell cycle and apoptosis accompanied with the depletion of GSH. Cancer Lett 270:40–55
Han YH, Kim SZ, Kim SH, Park WH (2008) Apoptosis in pyrogallol-treated Calu-6 cells is correlated with the changes of intracellular GSH levels rather than ROS levels. Lung Cancer 59:301–314
Han YH, Kim SZ, Kim SH, Park WH (2007) Arsenic trioxide inhibits growth of As4.1 juxtaglomerular cells via cell cycle arrest and caspase-independent apoptosis. Am J Physiol 293:F511–F520
Han YH, Kim SH, Kim SZ, Park WH (2008) Caspase inhibitor decreases apoptosis in pyrogallol-treated lung cancer Calu-6 cells via the prevention of GSH depletion. Int J Oncol 33:1099–1105
Yang J, Liu X, Bhalla K, Kim CN, Ibrado AM, Cai J et al (1997) Prevention of apoptosis by Bcl-2: release of cytochrome c from mitochondria blocked. Science 275:1129–1132
Marshall NJ, Goodwin CJ, Holt SJ (1995) A critical assessment of the use of microculture tetrazolium assays to measure cell growth and function. Growth Regul 5:69–84
Raghavan S, Hultin HO (2005) Model system for testing the efficacy of antioxidants in muscle foods. J Agric Food Chem 53:4572–4577
Wilcox CS (2002) Reactive oxygen species: roles in blood pressure and kidney function. Curr Hypertens Rep 4:160–166
Nakagawa Y, Tayama S (1995) Cytotoxicity of propyl gallate and related compounds in rat hepatocytes. Arch Toxicol 69:204–208
Rygiel TP, Mertens AE, Strumane K, van der Kammen R, Collard JG (2008) The Rac activator Tiam1 prevents keratinocyte apoptosis by controlling ROS-mediated ERK phosphorylation. J Cell Sci 121:1183–1192
Higuchi Y (2004) Glutathione depletion-induced chromosomal DNA fragmentation associated with apoptosis and necrosis. J Cell Mol Med 8:455–464
Park WH, Han YW, Kim SH, Kim SZ (2007) A superoxide anion generator, pyrogallol induces apoptosis in As4.1 cells through the depletion of intracellular GSH content. Mutat Res 619:81–92
Acknowledgments
The work was supported by a grant 15 from Kye-Nam, Kim Jae Jung Memorial Fund.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
You, B.R., Park, W.H. The enhancement of propyl gallate-induced HeLa cell death by MAPK inhibitors is accompanied by increasing ROS levels. Mol Biol Rep 38, 2349–2358 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-010-0368-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-010-0368-8