Abstract
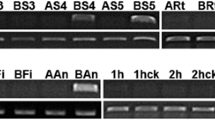
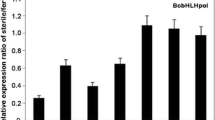
A putative RALF (rapid alkalinization factor)-like gene (GenBank accession number EF523517), named BcMF14, was isolated from Chinese cabbage (Brassica campestris L. ssp. chinensis Makino, syn. B. rapa ssp. chinensis) by rapid amplification of cDNA ends (RACE) based on a cDNA-AFLP differential fragment exclusively expressed in fertile line. Semi-quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) discovered that BcMF14 was prominently expressed in stage four and five flower buds of fertile line, no expression in vegetative structures or in sterility line. Detailed RT-PCR illuminated its strong expression in stamens. Successful suppression of BcMF14 gene expression greatly reduced the normal pollen grains. The frequency of abnormal pollen grains was 48.95% in the mutant with many shriveled pollen grains with irregular shape and some larger ones with deep hollows along the germination ditch. Pollen germination was stopped because of the severely twisted pollen tubes. These results demonstrate a potential role of the BcMF14 gene in the development of male gametogenesis in Chinese cabbage.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pearce G, Strydom D, Johnson S, Ryan CA (1991) A polypeptide from tomato leaves induces wound-inducible proteinase inhibitor proteins. Science 253:895–898
Matsubayashi Y, Sakagami Y (1996) Phytosulfokine, sulfated peptides that induce the proliferation of single mesophyll cells of Asparagus officinalis L. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:7623–7627
Martin DC, Jurkevitch E, Poiret M, d’Aubenton-Carafa Y, Petrovics G, Kondorosi E, Kondorosi A (1994) enod40, A gene expressed during nodule organogenesis, codes for a non-translatable RNA involved in plant growth. EMBO J 13:5099–5112
Clark SE, Running MP, Meyerowitz EM (1993) CLAVATA1, a regulator of meristem and flower development in Arabidopsis. Development 119:397–418
Clark SE, Running MP, Meyerowitz EM (1995) CLAVATA3 is a specific regulator of shoot and floral meristem development affecting the same processes as CLAVATA1. Development 121:2057–2067
Christel RS, Nasrallah ME, Nasrallah JB (1999) The male determinant of self-incompatibility in Brassica. Science 5445:1697–1700
Pearce G, Moura DS, Stratmann J, Ryan CA (2001) RALF, a 5-kDa ubiquitous polypeptide in plants, arrests root growth and development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:12843–12847
Matsubayashi Y, Yang H, Sakagami Y (2001) Peptide signals and their receptors in higher plants. Trends Plant Sci 6:573–577
Franssen HJ, Bisseling T (2001) Peptide signaling in plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:12855–12856
Ryan CA, Pearce G (2003) Systemins: a functionally defined family of peptide signals that regulate defensive genes in Solanaceae species. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:14577–14580
Ryan CA, Pearce G (1998) Systemin: a polypeptide signal for plant defensive genes. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 14:1–17
Meindl T, Boller T, Felix G (1998) The plant wound hormone systemin binds with the N-terminal part to its receptor but needs the C-terminal part to activate it. Plant Cell 10:1561–1570
Schaller A, Oecking C (1999) Modulation of plasma membrane H-ATPase activity differentially activates wound and pathogen defense responses in tomato plants. Plant Cell 11:263–272
Bolwell JP (1995) Role of active oxygen species and NO in plant defence responses. Curr Opin Plant Biol 2:287–294
Haruta M, Constabel CP (2003) Rapid alkalinization factors in poplar cell cultures. Peptide isolation, cDNA cloning, and differential expression in leaves and methyl jasmonate-treated cells. Plant Physiol 131:814–823
Germain H, Chevalier E, Caron S, Matton DP (2005) Characterization of five RALF-like genes from Solanum chacoense provides support for a developmental role in plants. Planta 220:447–454
Olsen AN, Mundy J, Skriver K (2002) Peptomics, identification of novel cationic Arabidopsis peptides with conserved sequence motifs. In Silico Biol 2:177–180
Bedinger P, Parsons R, Clark M, Covey P, Arthur-Asmah R (2003) PEX proteins, pollen specific LRX (Leucine-Rich Repeat Extensin Chimera) proteins. In: Proceedings of the 7th international congress on plant molecular biology, Barcelona, Spain, pp S20–S69
Deng W, Zhou L, Zhou Y, Wang Y, Wang M, Zhao Y (2010) Isolation and characterization of three duplicated PISTILLATA genes in Brassica napus. Mol Biol Rep. doi:10.1007/s11033-010-9981-9
Gao Y, Zhao Y, Li T, Liu Y, Ren C, Wang M (2010) Molecular cloning and expression analysis of an F-box protein gene responsive to plant hormones in Brassica napus. Mol Biol Rep 37(2):1037–1044
Zhuang J, Xiong AS, Peng RH, Gao F, Zhu B, Zhang J, Fu XY, Jin XF, Chen JM, Zhang Z, Qiao YS, Yao QH (2009) Analysis of Brassica rapa ESTs: gene discovery and expression patterns of AP2/ERF family genes. Mol Biol Rep 37(5):2485–2492
Fu SX, Cheng H, Qi C (2009) Microarray analysis of gene expression in seeds of Brassica napus planted in Nanjing (altitude: 8.9 m), Xining (altitude: 2261.2 m), Lhasa (altitude: 3658 m) with different oil content. Mol Biol Rep 36(8):2375–2386
Yan F, Peng J, Lu Y, Lin L, Zheng H, Chen H, Chen J, Adams MJ (2009) Molecular cloning and characterization of the Dicer-like 2 gene from Brassica rapa. Mol Biol Rep 36(6):1283–1289
Sambrook J, Russell DW, Russell D (2000) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 3rd edn. Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Cao JS, Yu XL, Ye WZ, Lu G, Xiang X (2006) Functional analysis of a novel male fertility CYP86MF gene in Chinese cabbage (Brassica campestris L. ssp. Chinensis makino). Plant Cell Rep 24:715–723
Boisson B, Giglione C, Meinnel T (2003) Unexpected protein families including cell defense components feature in the N-myristoylome of a higher eukaryote. J Biol Chem 278:4341–43429
Ye WZ, Cao JS, Xiang X, Zeng GW (2003) Molecular cloning and characterization of the genic male sterility related gene CYP86MF in Chinese cabbage (Brassica campestris L.ssp. chinensis Makinovar. communis Tsenet Lee). J Hort Sci Biotechnol 78:319–323
Yu XL, Cao JS, Ye WZ, Wang YQ (2004) Construction of an antisense CYP86MF gene plasmid vector and production of a male-sterile Chinese cabbage transformant by the pollen-tube method. J Hort Sci Biotechnol 79:833–839
Wang YQ, Ye WZ, Cao JS, Yu XL, Xiang X, Lu G (2005) Cloning and characterization of the microspore development related gene BcMF2 in Chinese cabbage pak-choi (Brassica campestris L. ssp. chinensis Makino). J Integr Plant Biol 47:863–872
Mascarenhas JP (1990) Gene activity during pollen development. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 41:317–338
Foster GD, Robinson SW, Blundell RP, Roberts MR, Hodge R, Draper J, Scott RJ (1992) A Brassica napus mRNA encoding a protein homologous to phospholipid transfer proteins is expressed specifically in the tapetum and developing microspores. Plant Sci 84:187–192
Albani D, Sardana R, Robert LS, Altosaar I, Arnison PG, Fabijanski SF (1992) A Brassica napus gene family which shows sequence similarity to ascorbate oxidase is expressed in developing pollen. Molecular characterization and analysis of promoter activity in transgenic tobacco plants. Plant J 2:331–342
McCormick S (1993) Male gametophyte development. Plant Cell 5:1265–1275
Li Y, Cao J (2009) Morphological and functional characterization of BcMF13 in the antisense-silenced plants of Brassica campestris ssp. chinensis. var. parachinensis. Mol Biol Rep 36(5):929–937
Li Y, Cao J, Huang L, Yu X, Xiang X (2008) BcMF13, a new reproductive organ-specific gene from Brassica rapa. ssp. chinensis, affects pollen development. Mol Biol Rep 35(2):207–214
Song J, Zhang L, Cao J (2009) Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel pollen predominantly membrane protein gene BcMF12 from Brassica campestris ssp. chinensis. Mol Biol Rep 36(8):2307–2314
Tian A, Cao J, Huang L, Yu X, Ye W (2009) Characterization of a male sterile related gene BcMF15 from Brassica campestris ssp. chinensis. Mol Biol Rep 36(2):307–314
Zhang Q, Liu H, Cao J (2008) Identification and preliminary analysis of a new PCP promoter from Brassica rapa ssp. chinensis. Mol Biol Rep 35(4):685–691
Huang L, Cao JS, Zhang AH, Ye YQ (2008) Characterization of a putative pollen-specific arabinogalactan protein gene, BcMF8, from Brassica campestris ssp. chinensis. Mol Biol Rep 35(4):631–639
Jiang M, Cao J (2008) Sequence variation of chalcone synthase gene in a spontaneous white-flower mutant of Chinese cabbage-pak-choi. Mol Biol Rep 35(4):507–512
Park BS, Park YD, Kim HU, Jin YM, Kim HI (2002) BAN103, a pollen-preferential gene, from Chinese cabbage and its promoter activity. Mol Cell 14:150–157
Liu Q, Guo Z (2009) Molecular cloning and characterization of a profilin gene BnPFN from Brassica nigra that expressing in a pollen-specific manner. Mol Biol Rep 36(1):135–139
Yang JH, Zhang MF, Yu JQ (2007) Mitochondrial nad2 gene is co-transcripted with CMS-associated orfB gene in cytoplasmic male-sterile stem mustard (Brassica juncea). Mol Biol Rep 36(2):345–351
Scheer JM, Pearce G, Ryan CA (2005) LeRALF, a plant peptide that regulates root growth and development, specifically binds to 25 and 120 kDa cell surface membrane proteins of Lycopersicon peruvianum. Planta 221:667–674
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31000132) and the Key Sci-technology Project of Zhejiang Province, China (No. 2005C12019-02).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Nie, C. & Cao, J. Isolation and characterization of a novel BcMF14 gene from Brassica campestris ssp. chinensis . Mol Biol Rep 38, 1821–1829 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-010-0298-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-010-0298-5