Abstract
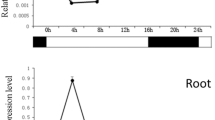
G protein plays an important role in signal pathways and involved in various signal transduction systems in plant. A full-length cDNA encoding a putative G protein α subunit (Gα), designated as BnGA1, was isolated from Brassica napus. The expression of BnGA1 in different B. napus tissues and developmental stags was analyzed using real-time PCR. The results showed that BnGA1 expressed was high in root, cotyledon and shoot apex. Stage expression pattern analysis revealed that BnGA1 expressed strongly at the 7th day, the bolting stage and fruiting stage. In addition, the expression of BnGA1 was analyzed under different concentrations of four plant hormones. The expression of BnGA1 was significantly induced by the high concentrations of abscisic acid (ABA) and brassinosteroid (BR). The expression of BnGA1 was also induced by low gibberellins acid 3 (GA3) concentrations and higher GA3 concentrations inhibit the expression of BnGA1. However, the expression of BnGA1 did not significantly regulated by exogenous indole-3-acetic acid (IAA). Moreover, the expression of BnGA1 under different abiotic stresses was analyzed at different time points. The BnGA1 was up-regulated in salt and drought stress and down-regulated in heat and cold stress. These expression results suggested that BnGA1 play an important role in plant hormones signal pathways and BnGA1 may be involved in plant defense system against environmental stresses in B. napus.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- G protein:
-
Heterotrimeric GTP-binding proteins
- Gα:
-
G proteins α subunit
- ORF:
-
Open reading frame
- ABA:
-
Abscisic acid
- GA:
-
Gibberellins
- BR:
-
Brassinosteroid
- IAA:
-
Indole-3-acetic acid
- PEG:
-
Polyetheleneglycol
- RGS:
-
Regulator of G-protein signaling proteins
- GPCR:
-
G protein-coupled receptor
References
Neer EJ (1995) Heterotrimeric G proteins: organizers of transmembrane signals. Cell 80:249–257
Offermanns S (2000) Mammalian G-protein function in vivo: new insights through altered gene expression. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol 140:63–133
Ma H, Yanofsky MF, Meyerowitz EM (1990) Molecular cloning and characterization of GPA1, a G protein α subunit gene from Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:3821–3825
Ishikawa A, Tsubouchi H, Iwasaki Y, Asahi T (1995) Molecular cloning and characterization of a cDNA for the alpha subunit of a G protein from rice. Plant Cell Physiol 36:353–359
Ishikawa A, Isasaki Y, Asahi T (1996) Molecular cloning and characterization of a cDNA for the beta subunit of a G protein from rice. Plant Cell Physiol 37:223–228
Assmann SM (2002) Heterotrimeric and unconventional GTP binding proteins in plant cell signaling. Plant Cell 14:S355–S373
Weiss CA, Garnaat CW, Mukai K, Hu Y, Ma H (1994) Isolation of cDNAs encoding guanine nucleotide-binding protein β-subunit homologues from maize (ZGB1) and Arabidopsis (AGB1). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:9554–9558
Kaul S, Koo HL, Jenkins J, Rizzo M, Rooney T, Tallon LJ et al (2000) Analysis of the genome sequence of the flowering plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature 408:796–815
Mason MG, Botella JR (2001) Isolation of a novel G-protein gamma-subunit from Arabidopsis thaliana and its interaction with G beta. Biochim Biophys Acta 1520:147–153
Marsh JF, Kaufmann LS (1999) Cloning and characterisation of PGA1 and PGA2: two G protein alpha-subunits from pea that promote growth in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Plant J 19:237–247
Liu XG, Yue YL, Li B, Nie YL, Li W, Wu WH, Ma LG (2007) A G protein-coupled receptor is a plasma membrane receptor for the plant hormone abscisic acid. Science 315:1712–1716
Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Fujisawa Y, Kobayashi M, Ashikari M, Iwasaki Y, Kitano H, Matsuoka M (2000) Rice dwarf mutant d1, which is defective in the α subunit of the heterotrimeric G protein, affects gibberellin signal transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:11638–11643
Ullah H, Chen JG, Wang SC, Jones AM (2002) Role of a heterotrimeric G protein in regulation of Arabidopsis seed germination. Plant Physiol 129:897–907
Oki K, Inaba N, Kitagawa K, Fujioka S, Kitano H, Fujisawa Y, Kato H, Iwasaki Y (2009) Function of the alpha subunit of rice heterotrimeric G protein in brassinosteroid signaling. Plant Cell Physiol 50:161–172
Ullah H, Chen JG, Temple B, Boyes DC, Alonso JM, Davis KR, Ecker JR, Jones AM (2003) The beta-subunit of the Arabidopsis G protein negatively regulates auxin-induced cell division and affects multiple developmental processes. Plant Cell 15:393–409
Warpeha KM, Hamm HE, Rasenick MM, Kaufman LS (1991) A blue-light activated GTP-binding protein in the plasma membrane of etiolated peas. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:8925–8929
Wang YJ, Cheng H, Edwards RL, An ZS, Wu JY, Shen CC, Dorale JA (2001) A high-resolution absolute-dated Late Pleistocene monsoon record from Hulu Cave, China. Science 294:2345–2348
Coursol S, Fan LM, Le Stunff H, Spiegel S, Gilroy S, Assmann SM (2003) Sphingolipid signalling in Arabidopsis guard cells involves heterotrimeric G proteins. Nature 423:651–654
Fujisawa Y, Kato H, Iwasaki Y (2001) Structure and function of heterotrimeric G-protein in plants. Plant Cell Physiol 42:789–794
Mishra G, Zhang W, Deng F, Zhao J, Wang X (2006) A bifurcating pathway directs abscisic acid effects on stomatal closure and opening in Arabidopsis. Science 312:264–266
Perfus-Barbeoch L, Jones AM, Assmann SM (2004) Plant heterotrimeric G protein function: insights from Arabidopsis and rice mutants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 7:719–731
Gudermann T, Schoneberg T, Schultz G (1997) Functional and structural complexity of signal transduction via G-protein-coupled receptors. Annu Rev Neurosci 20:399–427
Morris AJ, Malbon CC (1999) Physiological regulation of G protein-linked signaling. Physiol Rev 79:1373–1430
Jones AM (2002) G-protein-coupled signaling in Arabidopsis. Curr Opin Plant Biol 5:402–407
Jones AM, Assmann SM (2004) Plants: the latest model system for G-protein research. EMBO Rep 5:572–578
Okamoto H, Gobel C, Capper RG, Saunders N, Feussner I, Knight MR (2009) The alpha-subunit of the heterotrimeric G-protein affects jasmonate responses in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Exp Bot 60:1991–2003
Deng W, Zhou L, Zhou Y, Wang Y, Wang M, Zhao Y (2010) Isolation and characterization of three duplicated PISTILLATA genes in Brassica napus. Mol Biol Rep. doi:10.1007/s11033-010-9981-9
Gao Y, Zhao Y, Li T, Liu Y, Ren C, Wang M (2010) Molecular cloning and expression analysis of an F-box protein gene responsive to plant hormones in Brassica napus. Mol Biol Rep 37:1037–1044
Fu SX, Cheng H, Qi C (2261) Microarray analysis of gene expression in seeds of Brassica napus planted in Nanjing (altitude: 8.9 m), Xining (altitude: 2261.2 m) and Lhasa (altitude: 3658 m) with different oil content. Mol Biol Rep 36:2375–2386
Zhao Y, Wang ML, Zhang YZ, Du LF, Pan T (2000) A chlorophyll-reduced seedling mutant in oilseed rape, Brassica napus, for utilization in F-1 hybrid production. Plant Breed 119:131–135
Xu BB, Li JN, Zhang XK, Wang R, Xie LL, Chai YR (2007) Cloning and molecular characterization of a functional flavonoid 3′-hydroxylase gene from Brassica napus. J Plant Physiol 164:350–363
Yu X, Lu H, Lu G, Chen Z, Cao J, Hirata Y (2010) Analysis of genetic diversity in cytoplasmic male sterility, and association of mitochondrial genes with petaloid-type cytoplasmic male sterility in tuber mustard (Brassica juncea var. tumida Tsen et Lee). Mol Biol Rep 37:1059–1067
Zhuang J, Xiong AS, Peng RH, Gao F, Zhu B, Zhang J, Fu XY, Jin XF, Chen JM, Zhang Z, Qiao YS, Yao QH (2009) Analysis of Brassica rapa ESTs: gene discovery and expression patterns of AP2/ERF family genes. Mol Biol Rep. doi:10.1007/s11033-009-9763-4
Temple BRS, Jones AM (2007) The plant heterotrimeric G-protein complex. Annu Rev Plant Biol 58:249–266
Wang HX, Weerasinghe RR, Perdue TD, Cakmakci NG, Taylor JP, Marzluff WF, Jones AM (2006) A golgi-localized hexose transporter is involved in heterotrimeric G protein-mediated early development in Arabidopsis. Mol Biol Cell 17:4257–4269
Ullah H, Chen JG, Young JC, Im KH, Sussman MR, Jones AM (2001) Modulation of cell proliferation by heterotrimeric G protein in Arabidopsis. Science 292:2066–2069
Chen JG, Gao YJ, Jones AM (2006) Differential roles of Arabidopsis heterotrimeric G-protein subunits in modulating cell division in roots. Plant Physiol 141:887–897
Chen JG, Pandey S, Huang JR, Alonso JM, Ecker JR, Assmann SM, Jones AM (2004) GCR1 acts independently of heterotrimeric G protein in response to brassinosteroids and gibberellins in Arabidopsis seed germination. Plant Physiol 135:907–915
Koornneef M, Bentsink L, Hilhorst H (2002) Seed dormancy and germination. Curr Opin Plant Biol 5:33–36
Bishopp A, Mahonen AP, Helariutta Y (2006) Signs of change: hormone receptors that regulate plant development. Development 133:1857–1869
Zentella R, Zhang ZL, Park M, Thomas SG, Endo A, Murase K, Fleet CM, Jikumaru Y, Nambara E, Kamiya Y, Sun TP (2007) Global analysis of della direct targets in early gibberellin signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 19:3037–3057
Wang XF, Zhang DP (2008) Abscisic acid receptors: multiple signal-perception sites. Annu Bot 101:311–317
Shen YY, Wang XF, Wu FQ, Du SY, Cao Z, Shang Y, Wang XL, Peng CC, Yu XC, Zhu SY, Fan RC, Xu YH, Zhang DP (2006) The Mg-chelatase H subunit is an abscisic acid receptor. Nature 443:823–826
Gomez-Cadenas A, Zentella R, Walker-Simmons MK, Ho THD (2001) Gibberellin/abscisic acid antagonism in barley aleurone cells: site of action of the protein kinase PKABA1 in relation to gibberellin signaling molecules. Plant Cell 13:667–679
Gubler F, Hughes T, Waterhouse P, Jacobsen J (2008) Regulation of dormancy in barley by blue light and after-ripening: effects on abscisic acid and gibberellin metabolism. Plant Physiol 147:886–896
Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Nakajima M, Motoyuki A, Matsuoka M (2007) Gibberellin receptor and its role in gibberellin signaling in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 58:183–198
Yang GX, Matsuoka M, Iwasaki Y, Komatsu S (2003) A novel brassinolide-enhanced gene identified by cDNA microarray is involved in the growth of rice. Plant Mol Biol 52:843–854
Spartz AK, Gray WM (2008) Plant hormone receptors: new perceptions. Genes Dev 22:2139–2148
Asakura Y, Kurosaki F (2007) Cloning and expression of dcga gene encoding a subunit of GTP-Binding protein in carrot seedlings. Biol Pharm Bull 30:1800–1804
Misra S, Wu Y, Venkataraman G, Sopory SK, Tuteja N (2007) Heterotrimeric G-protein complex and G-protein-coupled receptor from a legume (Pisum sativum): role in salinity and heat stress and cross-talk with phospholipase C. Plant J 51:656–669
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National ‘863’ Programme (SN: 2001AA241104) and the 10th ‘five-year’ key task project in crop breeding of Sichuan Province (SN: 200107001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Yong Gao and Tingting Li contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11033_2010_54_MOESM1_ESM.jpg
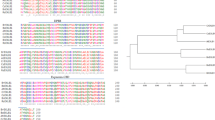
Fig. S1 Comparison of the putative amino acid sequences of BnGA1 with some representative Gα proteins. The identical amino acids were showed in white with black background and the conserved amino acids were showed in white with gray background. The specific sites for NTP binding, GTP hydrolysis, guanine recognition, two RGS-box interaction sites (RIS 1-2) and three binding to Gβγ–subunit complex (βγBS 1-3) were highly conserved in the listed Gα-subunits of plants. Putative sites for N-myristoylation (*) and ADP-ribosylation by cholera toxin (↓) were also presented. The aligned Gα subunit sequences were from Arabidopsis thaliana (GPA1, GenBank accession no. AT2G26300), Nicotiana tabacum (NtGA2, GenBank accession no. BAB84093), Pisum sativum (PGA2, GenBank accession no. AAB57826), Triticum aestivum (TaGA1, GenBank accession no. BAC10501) and Oryza sativa (Os05g0333200, GenBank accession no. AY792541)
11033_2010_54_MOESM2_ESM.jpg
Fig. S2 Phylogenetic tree analysis of BnGA1 from plants by MEGA version 3.1. The neighbor-joining method was used to construct the tree. Numbers on nodes indicate the bootstrap values after 1,000 replicates. The amino acids sequences used in phylogenetic tree analysis were from plants including Arabidopsis thaliana (GenBank accession no. AT2G26300), Daucus carota (GenBank accession no. ABK80761), Glycine max (GenBank accession no. X95582), Hordeum vulgare (GenBank accession no. AAF71788), Lotus japonicus (GenBank accession no. X77250), Lupinus luteus (GenBank accession no. X99485), Nicotiana tabacum (GenBank accession no. BAB84093), Oryza sativa (GenBank accession no. AY792541), Phaseolus lunatus (GenBank accession no. AB234091), Pisum sativum (GenBank accession no. AAB57826), Scoparia dulcis (GenBank accession no. EU489474), Solanum tuberosum (GenBank accession no. CAA61105), Sorghum bicolor (GenBank accession no. ABU48662), Spinacia oleracea (GenBank accession no. CAA76186), Triticum aestivum (GenBank accession no. BAC10501) and Vitis vinifera (GenBank accession no. CAO43897)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, Y., Li, T., Liu, Y. et al. Isolation and characterization of gene encoding G protein α subunit protein responsive to plant hormones and abiotic stresses in Brassica napus . Mol Biol Rep 37, 3957–3965 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-010-0054-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-010-0054-x