Abstract
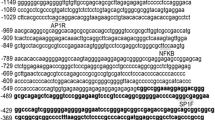
Tumor Suppressor in Lung Cancer-1 (TSLC1) expression is repressed in many different cancers. Hypermethylation of six CpG sites upstream of the TSLC1 coding region is correlated with TSLC1 repression. However, the functional elements of the TSLC1 promoter have not been examined. In this study, the transcription start site was identified as being 67 or 62 bp upstream of the translational start site by primer extension and bioinformatics analysis of expressed sequence tags (ESTs), respectively. Two promoter regions that regulate TSLC1 expression were identified. One, a small region of 170 bp, including 107 bp upstream of the transcription initiation site, is sufficient to generate maximal TSLC1 promoter activity. This minimal promoter does not contain the CpG sites that are hypermethylated in repressed TSLC1 promoters. Two, the maximal activity of the TSLC1 promoter is dampened by an inhibitory region that resides upstream of the minimal promoter.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Murakami Y (2005) Involvement of a cell adhesion molecule, TSLC1/IGSF4, in human oncogenesis. Cancer Sci 96(9):543–552. doi:10.1111/j.1349-7006.2005.00089.x
Yamada D et al (2006) Disruption of spermatogenic cell adhesion and male infertility in mice lacking TSLC1/IGSF4, an immunoglobulin superfamily cell adhesion molecule. Mol Cell Biol 26(9):3610–3624. doi:10.1128/MCB.26.9.3610-3624.2006
van der Weyden L et al (2006) Loss of TSLC1 causes male infertility due to a defect at the spermatid stage of spermatogenesis. Mol Cell Biol 26(9):3595–3609. doi:10.1128/MCB.26.9.3595-3609.2006
Kuramochi M et al (2001) TSLC1 is a tumor-suppressor gene in human non-small-cell lung cancer. Nat Genet 27(4):427–430. doi:10.1038/86934
Ito A et al (2008) Expression of cell adhesion molecule 1 in malignant pleural mesothelioma as a cause of efficient adhesion and growth on mesothelium. Lab Invest 88(5):504–514. doi:10.1038/labinvest.2008.15
Koma Y et al (2008) Cell adhesion molecule 1 is a novel pancreatic-islet cell adhesion molecule that mediates nerve-islet cell interactions. Gastroenterology 134(5):1544–1554. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2008.01.081
Gomyo H et al (1999) A 2-Mb sequence-ready contig map and a novel immunoglobulin superfamily gene IGSF4 in the LOH region of chromosome 11q23.2. Genomics 62(2):139–146. doi:10.1006/geno.1999.6001
Fujita E, Soyama A, Momoi T (2003) RA175, which is the mouse ortholog of TSLC1, a tumor suppressor gene in human lung cancer, is a cell adhesion molecule. Exp Cell Res 287(1):57–66. doi:10.1016/S0014-4827(03)00095-8
Watabe K et al (2003) IGSF4: a new intercellular adhesion molecule that is called by three names, TSLC1, SgIGSF and SynCAM, by virtue of its diverse function. Histol Histopathol 18(4):1321–1329
Shingai T et al (2003) Implications of nectin-like molecule-2/IGSF4/RA175/SgIGSF/TSLC1/SynCAM1 in cell–cell adhesion and transmembrane protein localization in epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 278(37):35421–35427. doi:10.1074/jbc.M305387200
Uchino K et al (2003) Clinical implication and prognostic significance of the tumor suppressor TSLC1 gene detected in adenocarcinoma of the lung. Cancer 98(5):1002–1007. doi:10.1002/cncr.11599
Lung HL et al (2004) Fine mapping of the 11q22–23 tumor suppressive region and involvement of TSLC1 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int J Cancer 112(4):628–635. doi:10.1002/ijc.20454
Steenbergen RD et al (2004) TSLC1 gene silencing in cervical cancer cell lines and cervical neoplasia. J Natl Cancer Inst 96(4):294–305
Surace EI et al (2004) Loss of tumor suppressor in lung cancer-1 (TSLC1) expression in meningioma correlates with increased malignancy grade and reduced patient survival. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 63(10):1015–1027
Sasaki H et al (2005) Overexpression of a cell adhesion molecule, TSLC1, as a possible molecular marker for acute-type adult T-cell leukemia. Blood 105(3):1204–1213. doi:10.1182/blood-2004-03-1222
Kitamura Y et al (2009) Frequent overexpression of CADM1/IGSF4 in lung adenocarcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 383(4):480–484. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.04.039
Fukami T et al (2003) Promoter methylation of the TSLC1 gene in advanced lung tumors and various cancer cell lines. Int J Cancer 107(1):53–59. doi:10.1002/ijc.11348
Tamura G (2004) Promoter methylation status of tumor suppressor and tumor-related genes in neoplastic and non-neoplastic gastric epithelia. Histol Histopathol 19(1):221–228
Lindsey JC et al (2004) Identification of tumour-specific epigenetic events in medulloblastoma development by hypermethylation profiling. Carcinogenesis 25(5):661–668. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgh055
Hui AB et al (2003) Epigenetic inactivation of TSLC1 gene in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Mol Carcinog 38(4):170–178. doi:10.1002/mc.10156
Honda T et al (2002) Hypermethylation of the TSLC1 gene promoter in primary gastric cancers and gastric cancer cell lines. Jpn J Cancer Res 93(8):857–860
Jansen M et al (2002) Aberrant methylation of the 5′ CpG island of TSLC1 is common in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and is first manifest in high-grade PanlNs. Cancer Biol Ther 1(3):293–296
Fukuhara H et al (2002) Promoter methylation of TSLC1 and tumor suppression by its gene product in human prostate cancer. Jpn J Cancer Res 93(6):605–609
Carey M, Smale S (2000) Transcriptional regulation in eukaryotes: concepts, strategies, techniques. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (eds) (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Planview
Lo K, Smale ST (1996) Generality of a functional initiator consensus sequence. Gene 182(1–2):13–22. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(96)00438-6
Crosby ME, Almasan A (2004) Opposing roles of E2Fs in cell proliferation and death. Cancer Biol Ther 3(12):1208–1211. doi:10.4161/cbt.3.12.1494
Acknowledgments
This work has been supported by a grant from Department of Energy/University of Tennessee Cancer Institute to RH.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hori, R.T. The minimal Tumor Suppressor in Lung Cancer-1 promoter is restrained by an inhibitory region. Mol Biol Rep 37, 1979–1985 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-009-9646-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-009-9646-8