Abstract
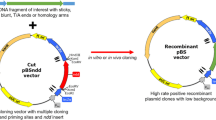
A novel vector for direct PCR fragments cloning by positive selection, pBN, was constructed based on the lethal barnase from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. Barnase was modified by inserting an additional insert at a pivotal Ile-54 site, which could take crucial affect on protein structure and absolute activity. The lacZ’ expressing cassette of pUC19 was replaced by the modified barnase under the NptIII promoter. This novel vector could exist in large quantities as pUC19 in E. coli hosts. For the direct cloning PCR fragments, the positive selective vector was prepared by linearizing pBN with EcoRV to cut off the additional insert. PCR fragments with different length were prepared to verify this vector by ligation with this vector. The results showed that this positive selective vector for PCR fragment cloning was higher efficient and more convenient in manipulation than previous positive vectors.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schlieper D, von Wilcken-Bergmann B, Schmidt M, Sobek H, Muller-Hill B (1998) A positive selection vector for cloning of long polymerase chain reaction fragments based on a lethal mutant of the crp gene of Escherichia coli. Anal Biochem 257(2):203–209. doi:10.1006/abio.1997.2558
Chan RY, Palfree RG, Congote LF, Solomon S (1994) Development of a novel type of cloning vector for suicide selection of recombinants. DNA Cell Biol 13(3):311–319
Trudel P, Provost S, Massie B, Chartrand P, Wall L (1996) pGATA: a positive selection vector based on the toxicity of the transcription factor GATA-1 to bacteria. Biotechniques 20(4):684–693
Hagan CE, Warren GJ (1982) Lethality of palindromic DNA and its use in selection of recombinant plasmids. Gene 19(1):147–151. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(82)90199-8
Kast P (1994) pKSS—a second-generation general purpose cloning vector for efficient positive selection of recombinant clones. Gene 138(1–2):109–114. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(94)90790-0
Gossen JA, Molijn AC, Douglas GR, Vijg J (1992) Application of galactose-sensitive E. coli strains as selective hosts for LacZ- plasmids. Nucleic Acids Res 20(12):3254. doi:10.1093/nar/20.12.3254
Bernard P (1995) New ccdB positive-selection cloning vectors with kanamycin or chloramphenicol selectable markers. Gene 162(1):159–160. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(95)00314-V
Mongkolsuk S, Rabibhadana S, Vattanaviboon P, Loprasert S (1994) Generalized and mobilizable positive-selection cloning vectors. Gene 143(1):145–146. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(94)90620-3
Messing J, Gronenborn B, Müller-Hill B, Hans Hopschneider P (1977) Filamentous coliphage M13 as a cloning vehicle: insertion of a HindII fragment of the lac regulatory region in M13 replicative form in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74(9):3642–3646. doi:10.1073/pnas.74.9.3642
Ullmann A (1992) Complementation in beta-galactosidase: from protein structure to genetic engineering. Bioessays 14(3):201–205. doi:10.1002/bies.950140311
Yazynin SA, Deyev SM, Jucovic M, Hartley RW (1997) A plasmid vector with positive selection and directional cloning based on a conditionally lethal gene. Gene 169:131–132. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(95)00814-4
Yazynin S, Lange H, Mokros T, Deyev S, Lemke H (1999) A new phagemid vector for positive selection of recombinants based on a conditionally lethal barnase gene. FEBS Lett 452(3):351–354. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(99)00661-4
Hajdukiewicz P, Svab Z, Maliga P (1994) The small, versatile pPZP family of Agrobacterium binary vectors for plant transformation. Plant Mol Biol 25(6):989–994. doi:10.1007/BF00014672
Schwede T, Kopp J, Guex N, Peitsch MC (2003) SWISS-MODEL: An automated protein homology-modeling server. Nucleic Acids Res 31(13):3381–3385. doi:10.1093/nar/gkg520
Guex N, Peitsch MC (1997) SWISS-MODEL and the Swiss-PdbViewer: an environment for comparative protein modeling. Electrophoresis 18(15):2714–2723. doi:10.1002/elps.1150181505
Salvatella X, Dobson CM, Fersht AR, Vendruscolo M (2005) Determination of the folding transition states of barnase by using -value-restrained simulations validated by double mutant PhiIJ-values. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(35):12389–12394. doi:10.1073/pnas.0408226102
Mauguen Y, Hartley RW, Dodson EJ, Dodson GG, Bricogne G, Chothia C, Jack A (1982) Molecular structure of a new family of ribonucleases. Nature 297(5862):162–164. doi:10.1038/297162a0
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
You, L., Weng, H., Chen, Z. et al. A novel vector for direct cloning PCR fragments by positive selection based on the lethal barnase . Mol Biol Rep 36, 1793–1798 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-008-9382-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-008-9382-5