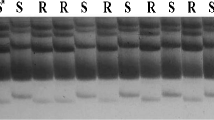
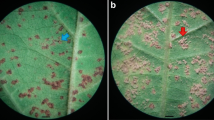
Abstract
Frogeye leaf spot is a yield-reducing disease of soybean caused by the pathogen Cercospora sojina. Rcs3 has provided durable resistance to all known races of C. sojina since its discovery in the cultivar Davis during the 1980s. Using a recombinant inbred line population derived from a cross between Davis and the susceptible cultivar Forrest, Rcs3 was fine-mapped to a 1.15 Mb interval on chromosome 16. This single locus was confirmed by tracing Rcs3 in resistant and susceptible progeny derived from Davis, as well as three near-isogenic lines. Haplotype analysis in the ancestors of Davis indicated that Davis has the same haplotype at the Rcs3 locus as susceptible cultivars in its paternal lineage. On the basis of these results, it is hypothesized that the resistance allele in Davis resulted from a mutation of a susceptibility allele. Tightly linked SNP markers at the Rcs3 locus identified in this research can be used for effective marker-assisted selection.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files or are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Andersson DI, Jerlström-Hultqvist J, Näsvall J (2015) Evolution of new functions de novo and from preexisting genes. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 7:a017996. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a017996
Andrews S (2010) FastQC: A quality control tool for high quality sequence data. https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/. Accessed June 29, 2022
Arias CAA, Yorinori JT, Ferraz De Toledo JF, Kiihl RAS (1996) Inheritance of resistance of soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merrill] to races 4 and 15 of frogeye leaf spot fungus (Cercospora sojina Hara). Braz J Genet 19:295–304
Athow K, Probst AH (1952) The inheritance of resistance to frog-eye leaf spot on soybeans. Phytopathology 42:660–662
Athow KL, Probst AH, Kurtzman CP, Laviolette FA (1962) A newly identified physiological race of Cercospora sojina on soybean. Phytopathology 52:712–714
Baker WA, Weaver DB, Qiu J, Pace PF (1999) Genetic analysis of frogeye leaf spot resistance in PI54610 and Peking soybean. Crop Sci 39:1021–1025. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci1999.0011183X003900040010x
Boerma HR, Hussey RS, Phillips DV, Wood ED, Finnerty SL (1992) Registration of ‘Cook’ soybean. Crop Sci 32:497. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci1992.0011183X003200020048x
Bolger AM, Lohse M, Usadel B (2014) Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 30:2114–2120. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu170
Bradley C, Allen T, Mueller D, Tenuta A, Mehl K, Sisson A (2022) Soybean Disease Loss Estimates from the United States and Ontario, Canada — 2021. Crop Protection Network CPN-1018–21. https://doi.org/10.31274/cpn-20220413-0
Burton JW, Brim CA, Young MF (1987) Registration of ‘Young’ soybean. Crop Sci 27:1093. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci1987.0011183X002700050071x
Caviness CE, Walters HJ (1966) Registration of ‘Davis’ soybeans. Crop Sci 6:502. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci1966.502areg3
Cook DE, Lee TG, Guo X, Melito S, Wang K et al (2012) Copy number variation of multiple genes at Rhg1 mediates nematode resistance in soybean. Science 338:1206–1209. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1228746
Cordeiro ACC, Sediyama T, Gomes JLL, Sediyama CS, Reis MS (1992) Heranca da Resistencia da Soja a Cercospora Sojina Hara, Isolado de Sao Gotardo, Minas Gerais. Pesqui Agropecu Bras 27:1035–1042
Cruz CD, Dorrance AE (2009) Characterization and survival of Cercospora sojina in Ohio. Plant Health Prog 10. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHP-2009-0512-03-RS
Danecek P, Bonfield JK, Liddle J, Marshall J, Ohan V, Pollard MO, et al (2021) Twelve years of SAMtools and BCFtools. Gigascience 10. https://doi.org/10.1093/gigascience/giab008
Dorrance AE, Cruz C, Mills D, Bender R, Koenig M, et al (2010) Effects of foliar fungicide and insecticide applications on soybean in Ohio. Plant Health Progress 11. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHP-2010-0122-01-RS
Filho SM, Sediyama CS, Moreira MA, Gonçalves de Barros E (2002) RAPD and SCAR markers linked to resistance to frogeye leaf spot in soybean. Genet Mol Biol 25:317–321. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1415-47572002000300012
Friedrich L, Lawton K, Dietrich R, Willits M, Cade R, Ryals J (2001) NIM1 Overexpression in Arabidopsis potentiates plant disease resistance and results in enhanced effectiveness of fungicides. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 14:1114–1124. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI.2001.14.9.1114
Gizlice Z, Carter TE, Burton JW (1994) Genetic base for North American public soybean cultivars released between 1947 and 1988. Crop Sci 34:1143. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci1994.0011183X003400050001x
Grant D, Nelson RT, Cannon SB, Shoemaker RC (2009) SoyBase, the USDA-ARS soybean genetics and genomics database. Nucleic Acids Res 38:D843–D846. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkp798
Ha BK, Boerma HR (2008) High-throughput SNP genotyping by melting curve analysis for resistance to southern root-knot nematode and frogeye leaf spot in soybean. J Crop Sci Biotechnol 11:91–100
Hannan Parker A, Wilkinson SW, Ton J (2022) Epigenetics: a catalyst of plant immunity against pathogens. New Phytol 233:66–83. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.17699
Harrelson BC, Kemerait RC, Culbreath AK, Ghimire B, Li Z et al (2021) Assessment of quinone outside inhibitor sensitivity and frogeye leaf spot race of Cercospora sojina in Georgia soybean. Plant Dis 105:2946–2954. https://doi.org/10.1094/pdis-02-21-0236-re
Hartwig EE, Epps JM (1973) Registration of ‘Forrest’ soybeans. Crop Sci 13:287. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci1973.0011183X001300020047x
He P, Warren RF, Zhao T, Shan L, Zhu L et al (2001) Overexpression of Pti5 in tomato potentiates pathogen-induced defense gene expression and enhances disease resistance to Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 14:1453–1457. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI.2001.14.12.1453
Keim P, Olson TC, Shoemaker RC (1988) A rapid protocol for isolating soybean DNA. Soyb Genet Newsl 15:150–152
Langmead B, Salzberg SL (2012) Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat Methods 9:357–359. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1923
Li H, Handsaker B, Wysoker A, Fennell T, Ruan J et al (2009) The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 25:2078–2079. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp352
Lucena JAM, Gastal MFDC, Casela CR, Vernetti FJ (1982) Herança da resisténcia à raça 4 de Cercospora sojina Hara em soja 1. Pesqui Agropecu Bras 17:1751–1755
Mathew FM, Byamukama E, Neves DL, Bradley CA (2019) Resistance to quinone outside inhibitor fungicides conferred by the G143A mutation in Cercospora sojina (causal agent of frogeye leaf spot) isolates from South Dakota soybean fields. Plant Health Progress 20(2):104–105. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHP-02-19-0014-BR
McDonald SC, Buck J, Li Z (2022) Automated, image-based disease measurement for phenotyping resistance to soybean frogeye leaf spot. Plant Methods 18:103. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13007-022-00934-7
McDonald SC, Buck J, Song Q, Li Z (2023) Genome-wide association study reveals novel loci and a candidate gene for resistance to frogeye leaf spot (Cercospora sojina) in soybean. Mol Genet Genomics 298:441–454. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-022-01986-z
Mian MAR, Boerma HR, Phillips DV, Kenty MM, Shannon G, Shipe ER et al (1998) Performance of frogeye leaf spot-resistant and-susceptible near-isolines of soybean. Plant Dis 82:1017–1021
Mian MAR, Wang T, Phillips DV, Alvernaz J, Boerma HR (1999) Molecular mapping of the Rcs3 gene for Resistance to Frogeye Leaf Spot in Soybean. Crop Sci 39:1687. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci1999.3961687x
Mian MAR, Missaoui AM, Walker DR, Phillips DV, Boerma HR (2008) Frogeye leaf spot of soybean: A review and proposed race designations for isolates of Cercospora sojina Hara. Crop Sci 48:14–24. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2007.08.0432
Milne I, Shaw P, Stephen G, Bayer M, Cardle L, Thomas WTB et al (2010) Flapjack-Graphical Genotype Visualization Bioinformatics Applications Note 26:3133–3134. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btq580
Missaoui AM, Ha BK, Phillips DV, Boerma HR (2007a) Single nucleotide polymorphism detection of the Rcs3 gene for resistance to frogeye leaf spot in soybean. Crop Sci 47:1681–1690. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2006.11.0711
Missaoui AM, Phillips DV, Boerma HR (2007b) DNA marker analysis of “Davis” soybean and its descendants for the Rcs3 gene conferring resistance to Cercospora sojina. Crop Sci 47:1263–1270. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2006.07.0472
Neves DL, Chilvers MI, Jackson-Ziems TA, Malvick DK, Bradley CA (2020) Resistance to quinone outside inhibitor fungicides conferred by the G143A mutation in Cercospora sojina (causal agent of frogeye leaf spot) isolates from Michigan, Minnesota, and Nebraska soybean fields. Plant Health Progress 21:230–231. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHP-06-20-0052-BR
Neves DL, Berguis BG, Halvorson JM, Hansen BC, Markell SG et al (2022a) First detection of frogeye leaf spot in soybean fields in North Datkora and the G143A mucation in the cytochrome b gene of Cercospora sojina. Plant Health Progress 23:269–271. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHP-10-21-0132-BR
Neves DL, Webster RW, Smith DL, Bradley CA (2022b) The G143A mutation in the cytochrome b gene is associated with quinone outside inhibitor fungicide resistance in Cercospora sojina from soybean fields in Wisconsin. Plant Health Progress 23(241):242. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHP-09-21-0115-BR
Pham AT, Harris DK, Buck J, Hoskins A, Serrano J, Abdel-Haleem H, Cregan P, Song Q, Boerma HR, Li Z (2015) Fine mapping and characterization of candidate genes that control resistance to Cercospora sojina K. Hara in two soybean germplasm accessions. PLoSONE 10(5):e0126753. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0126753
Phillips DV, Boerma HR (1981) Cercospora sojina race 5: a threat to soybeans in the Southeastern United States. Phytopathology 71:334–336
Phillips DV, Boerma HR (1982) Two genes for resistance to race 5 of Cercospora sojina in soybeans. Phytopathology 72:764–766
Piñeros-Guerrero N, Neves DL, Bradley CA, Darcy EP (2022) Determining the distribution of QoI fungicide-resistant Cercospora sojina on soybean from Indiana.https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-08-22-1744-SR
Probst AH, Athow KL, Laviolette FA (1965) Inheritance of resistance to race 2 of Cercospora sojina in soybeans. Crop Sci 5:332. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci1965.0011183X000500040013x
Ross JP (1968) Additional physiological races of Cercospora sojina on soybeans in North Carolina. Phytopathology 58:708–709
Shipe ER, Mueller JD, Lewis SA, Musen HL, Williams PF (1992) Registration of ‘Hagood’ soybean. Crop Sci 32:829–830
Shipe ER, Mueller JD, Lewis SA, Williams PF, Tomkins JP (1997) Registration of ‘Dillon’ soybean. Crop Sci 37:1983
Spearman C (1906) ‘Footrule’ for measuring correlation. Br J Psychol 2:89–108. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2044-8295.1906.tb00174.x
Standish JR, Tomaso-Peterson M, Allen TW, Sabanadzovic S, Aboughanem-Sabanadzovic N (2015) Occurrence of QoI fungicide resistance in Cercospora sojina from Mississippi soybean. Plant Dis 99(10):1347–1352. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-02-15-0157-RE
Steketee CJ, Schapaugh WT, Carter TE, Li Z (2020) Genome-wide association analyses reveal genomic regions controlling canopy wilting in soybean. G3: Genes. Genomes, Genetics 10:1413–1425. https://doi.org/10.1534/g3.119.401016
Stokes TL, Kunkel BN, Richards EJ (2002) Epigenetic variation in Arabidopsis disease resistance. Genes Dev 16:171–182. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.952102
van Ooijen JW (2006) JoinMap 4.0, software for the calculation of genetic linkage maps in experimental populations
Wang S, Basten CJ, Zeng, ZB (2012) Windows QTL Cartographer 2.5. Department of Statistics, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC. http://statgen.ncsu/qtlcart/WQTLCart.htm
Yang WB, Weaver DB, Nielsen BL, Qui J (2001) Molecular mapping of a new gene for resistance to frogeye leaf spot of soya bean in “Peking.” Plant Breeding 120:73–78
Yorinori JT (1992) Management of foliar fungal diseases in soybean in Brazil. In: Coping LG (ed.) Pest management in Soybean Springer Netherlands, pp 185–195. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-2870-4_18
Zhang GR, Newman MA, Bradley CA (2012a) First report of the soybean frogeye leaf spot fungus (Cercospora sojina) resistant to quinone outside inhibitor fungicides in North America. Plant Dis 96(5):767–767. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-10-11-0915-PDN
Zhang G, Pedersen DK, Phillips DV, Bradley CA (2012b) Sensitivity of Cercospora sojina isolates to quinone outside inhibitor fungicides. Crop Prot 40:63–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cropro.2012.04.025
Acknowledgements
A special thanks to: Dr. Qijian Song, Beltsville Agricultural Research Station, USDA-ARS, Beltsville, MD for genotyping the near isogenic lines; Carol Picard for providing support in growing plants, pathogen cultures, and phenotyping. Thanks also go to Nicole Bachleda and Tatyana Nienow for providing technical lab assistance, and to Dale Wood, Earl Baxter, Brice Wilson, Brian Little, and Greg Gokalp for their help with developing populations. SM appreciates the support provided by the Roger and Cindy Boerma Excellence in Plant Breeding Award.
Funding
Funding for this research was provided by the University of Georgia Research Foundation, Georgia Agricultural Commodity Commission for Soybeans, and Georgia Seed Development. This research was also supported by the funds allocated to the Georgia Agricultural Experiment Stations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SM conducted experiments, analyzed the data, interpreted results, and drafted the manuscript; JB oversaw phenotyping and edited the manuscript; ZL conceived the project, interpreted results, and edited the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Soybean Functional Genomics.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11032_2023_1397_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Supplementary file1 Comparison of the genomic region of Rcs3 among Wright-Rcs3, Thomas-Rcs3, Gordon-Rcs3, Dillon, Hagood, Cook, and Forrest × Davis RILs. Colored bars represent the region of Rcs3 based on that line/population. Scale bar at the bottom gives the physical position along chromosome 16 in the Williams82.a2 genome. (PDF 139 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
McDonald, S.C., Buck, J.W. & Li, Z. Pinpointing Rcs3 for frogeye leaf spot resistance and tracing its origin in soybean breeding. Mol Breeding 43, 49 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-023-01397-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-023-01397-x