Abstract
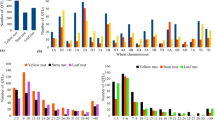
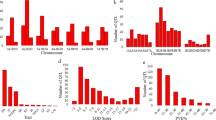
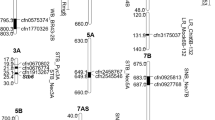
In wheat, meta-QTLs (MQTLs) and candidate genes (CGs) were identified for multiple disease resistance (MDR). For this purpose, information was collected from 58 studies for mapping QTLs for resistance to one or more of the five diseases. As many as 493 QTLs were available from these studies, which were distributed in five diseases as follows: septoria tritici blotch (STB) 126 QTLs; septoria nodorum blotch (SNB), 103 QTLs; fusarium head blight (FHB), 184 QTLs; karnal bunt (KB), 66 QTLs; and loose smut (LS), 14 QTLs. Of these 493 QTLs, only 291 QTLs could be projected onto a consensus genetic map, giving 63 MQTLs. The CI of the MQTLs ranged from 0.04 to 15.31 cM with an average of 3.09 cM per MQTL. This is a ~ 4.39 fold reduction from the CI of QTLs, which ranged from 0 to 197.6 cM, with a mean of 13.57 cM. Of 63 MQTLs, 60 were anchored to the reference physical map of wheat (the physical interval of these MQTLs ranged from 0.30 to 726.01 Mb with an average of 74.09 Mb). Thirty-eight (38) of these MQTLs were verified using marker–trait associations (MTAs) derived from genome-wide association studies. As many as 874 CGs were also identified which were further investigated for differential expression using data from five transcriptome studies, resulting in 194 differentially expressed candidate genes (DECGs). Among the DECGs, 85 genes had functions previously reported to be associated with disease resistance. These results should prove useful for fine mapping and cloning of MDR genes and marker-assisted breeding.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article (and its Supplementary Material).
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
AbuQamar S, Chai MF, Luo H, Song F, Mengiste T (2008) Tomato protein kinase 1b mediates signaling of plant responses to necrotrophic fungi and insect herbivory. Plant Cell 20:1964–1983. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.108.059477
Aduragbemi A, Soriano JM (2021) Unravelling consensus genomic regions conferring leaf rust resistance in wheat via meta-QTL analysis. Plant Genome. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.05.11.443557
Akhunova AR, Matniyazov RT, Liang H, Akhunov ED (2010) Homoeolog-specific transcriptional bias in allopolyploid wheat. BMC Genomics 11:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-11-505
Akio Amorim LL, da Fonseca dos Santos R, Pacifico Bezerra Neto J, Guida-Santos M, Crovella S, Maria Benko-Iseppon A (2017) Transcription factors involved in plant resistance to pathogens. Curr Protein Pept Sci 18:335-351
Alemu A, Brazauskas G, Gaikpa DS, Henriksson T, Islamov B, JØrgensen LN, Koppel M, Koppel R, Liatukas Ž, Svensson JT and Chawade A (2021) Genome-wide association analysis and genomic prediction for adult-plant resistance to Septoria tritici blotch and powdery mildew in winter wheat. Front Genet 12:661742https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2021.661742
Ali F, Pan Q, Chen G, Zahid KR, Yan J, (2013) Evidence of multiple disease resistance (MDR) and implication of meta-analysis in marker assisted selection. PLoS One 8:pe68150. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0068150
AlTameemi R, Gill HS, Ali S et al (2021) Genome-wide association analysis permits characterization of Stagonospora nodorum blotch (SNB) resistance in hard winter wheat. Sci Rep 11:12570. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-91515-6
Andersen EJ, Nepal MP, Purintun JM, Nelson D, Mermigka G, Sarris PF (2020) Wheat disease resistance genes and their diversification through integrated domain fusions. Front Genet 11:p898. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2020.00898
Arcade A, Labourdette A, Falque M, Mangin B, Chardon F, Charcosset A, Joets J (2004) BioMercator: integrating genetic maps and QTL towards discovery of candidate genes. Bioinformatics 20:2324–2326. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bth230
Ashfield T, Egan AN, Pfeil BE et al (2012) Evolution of a complex disease resistance gene cluster in diploid Phaseolus and tetraploid Glycine. Plant Physiol 159:336–354. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.112.195040
Breia R, Conde A, Badim H, Fortes AM, Gerós H, Granell A (2021) Plant SWEETs: from sugar transport to plant–pathogen interaction and more unexpected physiological roles. Plant Physiol 186:836–852. https://doi.org/10.1093/plphys/kiab127
Buhrow LM, Cram D, Tulpan D, Foroud NA, Loewen MC (2016) Exogenous abscisic acid and gibberellic acid elicit opposing effects on Fusarium graminearum infection in wheat. Phytopathology 106:986–996. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHYTO-01-16-0033-R
Cavanagh CR, Chao S, Wang S et al (2013) Genome-wide comparative diversity uncovers multiple targets of selection for improvement in hexaploid wheat landraces and cultivars. Proc Natl Acad Sci 110:8057–8062. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1217133110
Chardon F, Virlon B, Moreau L et al (2004) Genetic architecture of flowering time in maize as inferred from quantitative trait loci meta-analysis and synteny conservation with the rice genome. Genetics 168:2169–2185. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.104.032375
Chen C, Chen H, Zhang Y, Thomas HR, Frank MH, He Y, Xia R (2020) TBtools: an integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol Plant 13:1194–1202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2020.06.009
Clavijo BJ, Venturini L, Schudoma C, Accinelli GG, Kaithakottil G, Wright J, Borrill P, Kettleborough G, Heavens D, Chapman H, Lipscombe J (2017) An improved assembly and annotation of the allohexaploid wheat genome identifies complete families of agronomic genes and provides genomic evidence for chromosomal translocations. Genome Res 27:885–896. http://www.genome.org/cgi/doi/10.1101/gr.217117.116
Cooley MB, Pathirana S, Wu HJ, Kachroo P, Klessig DF (2000) Members of the Arabidopsis HRT/RPP8 family of resistance genes confer resistance to both viral and oomycete pathogens. Plant Cell 12:663–676. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.12.5.663
Cuthbert PA, Somers DJ, Brulé-Babel A (2007) Mapping of Fhb2 on chromosome 6BS: a gene controlling Fusarium head blight field resistance in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L). Theor Appl Genet 114:429–437. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-006-0439-3
Dang PM, Lamb MC, Bowen KL, Chen CY (2019) Identification of expressed R-genes associated with leaf spot diseases in cultivated peanut. Mol Biol Rep 46:225–239. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-018-4464-5
Darvasi A, Soller M (1997) A simple method to calculate resolving power and confidence interval of QTL map location. Behav Genet 27:125–132. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025685324830
de Toledo Thomazella DP, Brail Q, Dahlbeck D, Staskawicz B (2016) CRISPR-Cas9 mediated mutagenesis of a DMR6 ortholog in tomato confers broad-spectrum disease resistance. BioRxiv p064824 https://doi.org/10.1101/064824
Deppe JP, Rabbat R, Hörtensteiner S, Keller B, Martinoia E, Lopéz-Marqués RL (2018) The wheat ABC transporter Lr34 modifies the lipid environment at the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem 293:18667–18679. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA118.002532
Dutta A, Croll D, McDonald BA et al (2021) Genome-wide association study for septoria tritici blotch resistance reveals the occurrence and distribution of Stb6 in a historic Swiss landrace collection. Euphytica 217:108. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-021-02843-7
Duveiller E, Singh RP, Nicol JM (2007) The challenges of maintaining wheat productivity: pests diseases and potential epidemics. Euphytica 157:417–430. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-007-9380-z
Emebiri L, Singh S, Tan MK et al (2019) Unravelling the complex genetics of Karnal bunt (Tilletia indica) resistance in common wheat (Triticum aestivum) by genetic linkage and genome-wide association analyses. G3: Genes Genom Genet 9:1437–1447. https://doi.org/10.1534/g3.119.400103
Endelman JB, Plomion C (2014) LPmerge: an R package for merging genetic maps by linear programming. Bioinformatics 30:1623–1624. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu091
Figlan S, Ntushelo K, Mwadzingeni L, Terefe T, Tsilo TJ, Shimelis H (2020) Breeding wheat for durable leaf rust resistance in Southern Africa: variability distribution current control strategies challenges and future prospects. Front Plant Sci 11:549. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.00549
Flemmig EL (2012) Molecular markers to deploy and characterize stem rust resistance in wheat MS Thesis N C State Univ Raleigh
Friesen TL, Xu SS, Harris MO (2008) Stem rust, tan spot, Stagonosporanodorum blotch, and Hessian fl y resistance in Langdon durum-Aegilops tauschii synthetic hexaploid wheat lines. Crop Sci 48:1062–1070. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2007.08.0463
Gassmann W, Hinsch ME, Staskawicz BJ (1999) The Arabidopsis RPS4 bacterial-resistance gene is a member of the TIR-NBS-LRR family of disease-resistance genes. Plant J 20:265–277. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313X.1999.00600.x
Gerard GS, Börner A, Lohwasser U et al (2017) Genome-wide association mapping of genetic factors controlling Septoria tritici blotch resistance and their associations with plant height and heading date in wheat. Euphytica 213:27. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-016-1820-1
Gillies SA, Futardo A, Henry RJ (2012) Gene expression in the developing aleurone and starchy endosperm of wheat. Plant Biotechnol J10:668–679. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-7652.2012.00705.x
Goffinet B, Gerber S (2000) Quantitative trait loci: a meta-analysis. Genetics 155:463–473. https://doi.org/10.1093/genetics/155.1.463
Gou L, Hattori J, Fedak G, Balcerzak M, Sharpe A, Visendi P, Edwards D, Tinker N, Wei YM, Chen GY, Ouellet T (2016) Development and validation of Thinopyrum elongatum–expressed molecular markers specific for the long arm of chromosome 7E. Crop Sci 56:354–364. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2015.03.0184
Goudemand E, Laurent V, Duchalais L, Ghaffary SMT, Kema GH, Lonnet P, Margalé E, Robert O (2013) Association mapping and meta-analysis: two complementary approaches for the detection of reliable Septoria tritici blotch quantitative resistance in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L). Mol Breed 32:563–584. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-013-9890-4
Gullner G, Komives T, Király L, Schröder P (2018) Glutathione S-transferase enzymes in plant-pathogen interactions. Front Plant Sci 9:1836. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.01836
Gunupuru LR, Arunachalam C, Malla KB, Kahla A, Perochon A, Jia J, Thapa G, Doohan FM (2018) A wheat cytochrome P450 enhances both resistance to deoxynivalenol and grain yield. PLoS ONE 13:0204992. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0204992
Guo B, Sleper DA, Lu P, Shannon JG, Nguyen HT, Arelli PR (2006) QTLs associated with resistance to soybean cyst nematode in soybean: meta-analysis of QTL locations. Crop Sci 46:595. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2005.04-0036-2
Gupta PK, Balyan HS, Chhuneja P et al (2021a) Pyramiding of genes for grain protein content, grain quality and rust resistance in eleven Indian bread wheat cultivars: a multi-institutional effort. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-637558/v1
Gupta PK, Vasistha NK, Singh PK (2021b) Sensitivity genes in wheat and corresponding effector genes in necrotrophs exhibiting inverse gene-for-gene relationship. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-223024/v1
Gupta V, He X, Kumar N et al (2019) Genome wide association study of karnal bunt resistance in a wheat germplasm collection from Afghanistan. Int J Mol Sci 20:3124. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20133124
Gurung S, Bonman JM, Ali S, Patel J, Myrfield M, Mergoum M, Singh PK, Adhikari TB (2009) New and diverse sources of multiple disease resistance in wheat. Crop Sci 49:1655–1666. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2008.10.0633
Hernandez MV, Crossa J, Singh PK, Bains NS, Singh K, Sharma I (2012) Multi-trait and multi-environment QTL analyses for resistance to wheat diseases. PLoS One 7:pe38008. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0038008
Herrera-Foessel SA, Singh RP, Lillemo M, Huerta-Espino J, Bhavani S, Singh S, Lan C, Calvo-Salazar V, Lagudah ES (2014) Lr67/Yr46 confers adult plant resistance to stem rust and powdery mildew in wheat. Theor Appl Genet 127:781–789. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-013-2256-9
Holder A (2018) A Genome wide association study for Fusarium head blight resistance in southern soft red winter wheat. Graduate theses and dissertations Retrieved from https://scholarworks.uark.edu/etd/2636
Hou W, Mu J, Li A, Wang H, Kong L (2015) Identification of a wheat polygalacturonase-inhibiting protein involved in Fusarium head blight resistance. Eur J Plant Pathol 141:731–745. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-014-0574-7
Hu W, Gao D, Wu H et al (2020) Genome-wide association mapping revealed syntenic loci QFhb-4AL and QFhb-5DL for Fusarium head blight resistance in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). BMC Plant Biol 20:29. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-019-2177-0
Huerta-Espino J, Singh R, Crespo-Herrera LA, Villaseñor-Mir HE, Rodriguez-Garcia MF, Dreisigacker S, Barcenas-Santana D, Lagudah E (2020) Adult plant slow rusting genes confer high levels of resistance to rusts in bread wheat cultivars from Mexico. Front Plant Sci 11:824. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.00824
Hulbert SH, Webb CA, Smith SM, Sun Q (2001) Resistance gene complexes: evolution and utilization. Annu Rev Phytopathol 39:285–312. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.phyto.39.1.285
Huo N, Zhang S, Zhu T, Dong L, Wang Y, Mohr T, Hu T, Liu Z, Dvorak J, Luo MC, Wang D (2018) Gene duplication and evolution dynamics in the homeologous regions harboring multiple prolamin and resistance gene families in hexaploid wheat. Front Plant Sci 9:673. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.00673
Jan I, Saripalli G, Kumar K et al (2021) Meta-QTL Analysis for Stripe Rust Resistance in Wheat. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-380807/v1
Jighly A, Alagu M, Makdis F, Singh M, Singh S, Emebiri LC, Ogbonnaya FC (2016) Genomic regions conferring resistance to multiple fungal pathogens in synthetic hexaploid wheat. Mol Breed 36:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-016-0541-4
Juery C, Concia L, De Oliveira R, Papon N, Ramírez-González R, Benhamed M, Uauy C, Choulet F, Paux E (2021) New insights into homoeologous copy number variations in the hexaploid wheat genome. Plant Genome. https://doi.org/10.1002/tpg2.20069
Kaur B, Bhatia D, Mavi GS (2021a) Eighty years of gene-for-gene relationship and its applications in identification and utilization of R genes. J Genet 100:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-021-01300-7
Kaur B, Sandhu KS, Kamal R, Kaur K, Singh J, Röder MS, Muqaddasi QH (2021b) Omics for the improvement of abiotic, biotic, and agronomic traits in major cereal crops: applications, challenges, and prospects. Plants 10:1989. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10101989
Kidane YG, Hailemariam BN, Mengistu DK, Fadda C, Pè ME and Dell'Acqua M (2017) Genome-wide association study of Septoria tritici blotch resistance in Ethiopian durum wheat landraces. Front Plant Sci 8:1586 https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.01586
Knox RE, Campbell HL, Clarke FR et al (2014) Quantitative trait loci for resistance in wheat (Triticum aestivum) to Ustilago tritici. Can J Plant Pathol 36:187–201. https://doi.org/10.1080/07060661.2014.905497
Kou Y, Wang S (2010) Broad-spectrum and durability: understanding of quantitative disease resistance. Curr Opin Plant Biol 13:181–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2009.12.010
Krattinger SG, Lagudah ES, Spielmeyer W, Singh RP, Huerta-Espino J, McFadden H, Bossolini E, Selter LL, Keller B (2009) A putative ABC transporter confers durable resistance to multiple fungal pathogens in wheat. Science 323:1360–1363. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1166453
Kugler KG, Siegwart G, Nussbaumer T et al (2013) Quantitative trait loci-dependent analysis of a gene co-expression network associated with Fusarium head blight resistance in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L). BMC Genomics 14:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-14-728
Kumar IS, Nadarajah K (2020) A meta-analysis of quantitative trait loci associated with multiple disease resistance in rice (Oryza sativa L). Plants 9:1491. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9111491
Kumar S, Singh VP, Saini DK, Sharma H, Saripalli G, Kumar S, Balyan HS, Gupta PK (2021) Meta-QTLs, ortho-MQTLs, and candidate genes for thermotolerance in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Mol Breed 41:1–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-021-01264-7
Larkin DL, Holder AL, Mason RE et al (2020) Genome-wide analysis and prediction of Fusarium head blight resistance in soft red winter wheat. Crop Sci 60:2882–2900. https://doi.org/10.1002/csc2.20273
Leach LJ, Belfield EJ, Jiang C, Brown C, Mithani A, Harberd NP (2014) Patterns of homoeologous gene expression shown by RNA sequencing in hexaploid bread wheat. BMC Genomics 15:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-15-276
Li HZ, Gao X, Li XY, Chen QJ, Dong J, Zhao WC (2013) Evaluation of assembly strategies using RNA-seq data associated with grain development of wheat (Triticum aestivum L). PlOS one 8:pe83530. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0083530
Liu N, Sun Y, Pei Y, Zhang X, Wang P, Li X, Li F, Hou Y (2018) A pectin methylesterase inhibitor enhances resistance to Verticillium wilt. Plant Physiol 176:2202–2220. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.17.01399
Liu Y, Salsman E, Wang R, Galagedara N, Zhang Q, Fiedler JD, Liu Z, Xu S, Faris J, Li X (2020) Meta-QTL analysis of tan spot resistance in wheat. Theor Appl Genet 133:2363–2375. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-020-03604-1
Lv T, Li X, Fan T, Luo H, Xie C, Zhou Y, Tian CE (2019) The calmodulin-binding protein IQM1 interacts with CATALASE2 to affect pathogen defense. Plant Physiol 181:1314–1327. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.19.01060
Mago R, Tabe L, McIntosh RA, Pretorius Z et al (2011) A multiple resistance locus on chromosome arm 3BS in wheat confers resistance to stem rust (Sr2) leaf rust (Lr27) and powdery mildew. Theor Appl Genet 123:615–623. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-011-1611-y
Mahboubi M, Talebi R, Mehrabi R et al (2021) Genome-wide association mapping in wheat reveals novel QTLs and potential candidate genes involved in resistance to septoria tritici blotch. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-486336/v1
Manosalva PM, Davidson RM, Liu B, Zhu X, Hulbert SH, Leung H, Leach JE (2009) A germin-like protein gene family functions as a complex quantitative trait locus conferring broad-spectrum disease resistance in rice. Plant Physiol 149:286–296. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.108.128348
Marone D, Russo MA, Laidò G, De Vita P, Papa R, Blanco A, Gadaleta A, Rubiales D, Mastrangelo AM (2013) Genetic basis of qualitative and quantitative resistance to powdery mildew in wheat: from consensus regions to candidate genes. BMC Genomics 14:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-14-562
McHale L, Tan X, Koehl P, Michelmore RW (2006) Plant NBS-LRR proteins: adaptable guards. Genome Biol 7:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2006-7-4-212
Meng X, Zhang S (2013) MAPK cascades in plant disease resistance signalling. Annu Rev Phytopathol 51:245–266. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-phyto-082712-102314
Michelmore RW, Meyers BC (1998) Clusters of resistance genes in plants evolve by divergent selection and a birth-and-death process. Genome Res 8:1113–1130. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.8.11.1113
Miedaner T, Akel W, Flath K, Jacobi A, Taylor M, Longin F, Würschum T (2020) Molecular tracking of multiple disease resistance in a winter wheat diversity panel. Theor Appl Genet 133:419–431. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-019-03472-4
Moore JW, Herrera-Foessel S, Lan C et al (2015) A recently evolved hexose transporter variant confers resistance to multiple pathogens in wheat. Nat Genet 47:1494–1498. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3439
Muqaddasi QH, Zhao Y, Rodemann B, Plieske J, Ganal MW, Röder MS (2019) Genome-wide association mapping and prediction of adult stage Septoria tritici blotch infection in European winter wheat via high-density marker arrays. Plant Genome 12:180029. https://doi.org/10.3835/plantgenome2018.05.0029
N’Diaye A, Haile JK, Cory AT, Clarke FR, Clarke JM, Knox RE, Pozniak CJ (2017) Single marker and haplotype-based association analysis of semolina and pasta colour in elite durum wheat breeding lines using a high-density consensus map. PLoS One 12:e0170941. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0170941
Narusaka Y, Narusaka M, Park P et al (2004) RCH1 a locus in Arabidopsis that confers resistance to the hemibiotrophic fungal pathogen Colletotrichum higginsianum. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 17:749–762. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI.2004.17.7.749
Nene YL (1988) Multiple-disease resistance in grain legumes. Annu Rev Phytopathol 26:203–217. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.py.26.090188.001223
Pal N, Saini DK, Kumar S (2021) Meta-QTLs, ortho-MQTLs and candidate genes for the traits contributing to salinity stress tolerance in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Physiol Mol Biol Plants 1–20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-021-01112-0
Paudel B, Zhuang Y, Galla A, Dahal S, Qiu Y, Ma A, Raihan T, Yen Y (2020) WFhb1-1 plays an important role in resistance against Fusarium head blight in wheat. Sci Rep 10:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-64777-9
Perochon A, Kahla A, Vranić M, Jia J, Malla KB, Craze M, Wallington E, Doohan FM (2019) A wheat NAC interacts with an orphan protein and enhances resistance to Fusarium head blight disease. Plant Biotechnol J 17:1892–1904. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.13105
Pfeifer M, Kugler KG, Sandve SR, Zhan B, Rudi H, Hvidsten TR, Mayer KF, Olsen OA (2014) Genome interplay in the grain transcriptome of hexaploid bread wheat. Science 345:1250091. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1250091
Phan HTT, Rybak K, Bertazzoni S et al (2018) Novel sources of resistance to Septoria nodorum blotch in the Vavilov wheat collection identified by genome-wide association studies. Theor Appl Genet 131:1223–1238. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-018-3073-y
Pooja S, Sharma RB, Singh AK, Rakesh S, Sundeep K (2014) Multiple disease resistance in wheat: need of today. Wheat Information Service 118:7–16
Ramírez-González RH, Borrill P, Lang D et al (2018) The transcriptional landscape of polyploid wheat. Science 361:6403. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aar6089
Rana M, Kaldate R, Nabi SU, Wani SH, Khan H (2021) Marker-assisted breeding for resistance against wheat rusts. In physiological molecular and genetic perspectives of wheat improvement (pp 229–262) Springer Cham https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59577-7_11
Saini DK, Chopra Y, Pal N, Chahal A, Srivastava P, Gupta PK (2021) Meta-QTLs, ortho-MQTLs and candidate genes for nitrogen use efficiency and root system architecture in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Physiol Mol Biol Plants 27:2245–2267. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-021-01085-0
Saini DK, Chopra Y, Singh J, Sandhu KS, Kumar A, Bazzer S, Srivastava P (2022a) Comprehensive evaluation of mapping complex traits in wheat using genome-wide association studies. Mol Breed 42:1–52. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-021-01272-7
Saini DK, Srivastava P, Pal N, Gupta PK (2022b) Meta-QTLs, ortho-meta-QTLs and candidate genes for grain yield and associated traits in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Theor Appl Genet 1–33. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-021-04018-3
Sandhu KS, Merrick LF, Sankaran S, Zhang Z, Carter AH (2022) Prospectus of Genomic Selection and Phenomics in Cereal, Legume and Oilseed Breeding Programs. Front Genet 12:829131. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2021.829131
Sandhu N, Pruthi G, Raigar P, Singh MP, Phagna K, Kumar A, Sethi M, Singh J, Ade PA, Saini DK (2021) Meta-QTL analysis in rice and cross-genome talk of the genomic regions controlling nitrogen use efficiency in cereal crops revealing phylogenetic relationship. Front Genet 12:807210–807210. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2021.807210
Schnippenkoetter W, Lo C, Liu G et al (2017) The wheat Lr34 multipathogen resistance gene confers resistance to anthracnose and rust in sorghum. Plant Biotechnol J 15:1387–1396. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12723
Schweiger W, Steiner B, Vautrin S et al (2016) Suppressed recombination and unique candidate genes in the divergent haplotype encoding Fhb1 a major Fusarium head blight resistance locus in wheat. Theor Appl Genet 129:1607–1623. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-016-2727-x
Schweizer P, Stein N (2011) Large-scale data integration reveals colocalization of gene functional groups with meta-QTL for multiple disease resistance in barley. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 24:1492–1501. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI-05-11-0107
Sharma A, Srivastava P, Mavi GS, Kaur S, Kaur J, Bala R, Sohu VS, Chhuneja P, Bains NS (2021) Resurrection of wheat cultivar ‘PBW343’using marker assisted gene pyramiding for rust resistance. Front Plant Sci 12:42. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2021.570408
Shi C, Geng J, Ren Y et al (2021) Genome-wide association study and QTL mapping revealed genetic loci for Fusarium head blight resistance in Chinese hexaploid wheat. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-335212/v1
Simón MR, Ayala FM, Cordo CA, Röder MS, Börner A (2004) Molecular mapping of quantitative trait loci determining resistance to septoria tritici blotch caused by Mycosphaerella graminicola in wheat. Euphytica 138:41–48. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:EUPH.0000047059.57839.98
Singh K, Batra R, Sharma S et al (2021) WheatQTLdb: a QTL database for wheat. Mol Genet Genom 1-6 10https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-021-01796-9
Singh S, Sehgal D, Kumar S et al (2020) GWAS revealed a novel resistance locus on chromosome 4D for the quarantine disease Karnal bunt in diverse wheat pre-breeding germplasm. Sci Rep 10:5999. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-62711-7
Somers DJ, Isaac P, Edwards K (2004) A high-density microsatellite consensus map for bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L). Theor Appl Genet 109:1105–1114
Soriano JM, Royo C (2015) Dissecting the genetic architecture of leaf rust resistance in wheat by QTL meta-analysis. Phytopathology 105:1585–1593. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHYTO-05-15-0130-R
Sosnowski O, Charcosset A, Joets J (2012) BioMercator V3: an upgrade of genetic map compilation and quantitative trait loci meta-analysis algorithms. Bioinformatics 28:2082–2083. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bts313
Takahagi K, Inoue K, Mochida K (2018) Gene co-expression network analysis suggests the existence of transcriptional modules containing a high proportion of transcriptionally differentiated homoeologs in hexaploid wheat. Front Plant Sci 9:1163. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.01163
Takahashi H, Miller J, Nozaki Y (2002) RCY1 an Arabidopsis thaliana RPP8/HRT family resistance gene conferring resistance to cucumber mosaic virus requires salicylic acid ethylene and a novel signal transduction mechanism. Plant J 32:655–667. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313X.2002.01453.x
Tessmann EW, Van Sanford DA (2018) GWAS for Fusarium head blight related traits in winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L) in an artificially warmed treatment. Agronomy 8:68. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy8050068
Venske E, Dos Santos RS, Farias DDR, Rother V, da Maia LC, Pegoraro C, Costa de Oliveira A (2019) Meta-analysis of the QTLome of Fusarium head blight resistance in bread wheat: refining the current puzzle. Front Plant Sci 10:727. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00727
Veyrieras JB, Goffinet B, Charcosset A (2007) MetaQTL: a package of new computational methods for the meta-analysis of QTL mapping experiments. BMC Bioinformatics 8:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-8-49
Wang J, Wang J, Shang H, Chen X, Xu X, Hu X (2019) TaXa21, a leucine-rich repeat receptor–like kinase gene associated with TaWRKY76 and TaWRKY62, plays positive roles in wheat high-temperature seedling plant resistance to Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 32:1526–1535. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI-05-19-0137-R
Wang S, Wong D, Forrest K et al (2014) Characterization of polyploid wheat genomic diversity using a high-density 90 000 single nucleotide polymorphism array. Plant Biotechnol J 12:787–796. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12183
Wiesner-Hanks T, Nelson R (2016) Multiple disease resistance in plants. Annu Rev Phytopathol 54:229–252. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-phyto-080615-100037
Wisser RJ, Sun Q, Hulbert SH, Kresovich S, Nelson RJ (2005) Identification and characterization of regions of the rice genome associated with broad-spectrum quantitative disease resistance. Genetics 169:2277–2293. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.104.036327
Wormit A, Usadel B (2018) The multifaceted role of pectin methylesterase inhibitors (PMEIs). Int J Mol Sci 19:2878. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19102878
Xing L, Gao L, Chen Q, Pei H, Di Z, Xiao J, Wang H, Ma L, Chen P, Cao A, Wang X (2018) Over-expressing a UDP-glucosyltransferase gene (Ta-UGT 3) enhances Fusarium head blight resistance of wheat. Plant Growth Regul 84:561–571. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-017-0361-5
Yang F, Li W, Jørgensen HJ (2013) Transcriptional reprogramming of wheat and the hemibiotrophic pathogen Septoria tritici during two phases of the compatible interaction . PLoS One 8:pe81606. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0081606
Yang Y, Amo A, Wei D, Chai Y, Zheng J, Qiao P, Cui C, Lu S, Chen L, Hu YG (2021) Large-scale integration of meta-QTL and genome-wide association study discovers the genomic regions and candidate genes for yield and yield-related traits in bread wheat. Theor Appl Genet 1-27https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-021-03881-4
Zheng T, Hua C, Li L, Sun Z, Yuan M, Bai G, Humphreys G, Li T (2020) Integration of meta-QTL discovery with omics: Towards a Mol Breed platform for improving wheat resistance to Fusarium head blight. Crop J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cj.2020.10.006
Zwart RS, Thompson JP, Milgate AW, Bansal UK, Williamson PM, Raman H, Bariana HS (2010) QTL mapping of multiple foliar disease and root-lesion nematode resistances in wheat. Mol Breed 26:107–124. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-009-9381-9
Acknowledgements
The Department of Science and Technology (DST), New Delhi, India, provided DKS with an INSPIRE fellowship, while the Head, Department of Plant Breeding and Genetics, Punjab Agricultural University, Ludhiana, India, provided the necessary facilities.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PS and PKG conceived and planned the study. AC, DKS, and NP collected the literature and tabulated the data for meta-analysis. DKS conducted the analysis. DKS and AC interpreted the results and wrote the first draft of the manuscript. PKG and PS edited and finalized the manuscript with the help of DKS.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflicts of interest/Competing interests
There are no competing interests declared by the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saini, D.K., Chahal, A., Pal, N. et al. Meta-analysis reveals consensus genomic regions associated with multiple disease resistance in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Mol Breeding 42, 11 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-022-01282-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-022-01282-z