Abstract
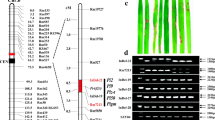
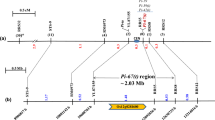
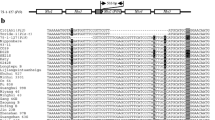
The Pi20(t) gene was determined to confer a broad-spectrum resistance against diverse blast pathotypes (races) in China based on inoculation experiments utilizing 160 Chinese Magnaporthe oryzae (formerly Magnaporthe grisea) isolates, among which isolate 98095 can specifically differentiate the Pi20(t) gene present in cv. IR24. Two flanking and three co-segregating simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers for Pi20(t), located near the centromere region of chromosome 12, were identified using 526 extremely susceptible F2 plants derived from a cross of Asominori, an extremely susceptible cultivar, with resistant cultivar IR24. The SSR OSR32 was mapped at a distance of 0.2 cM from Pi20(t), and the SSR RM28050 was mapped to the other side of Pi20(t) at a distance of 0.4 cM. The other three SSR markers, RM1337, RM5364 and RM7102, co-segregated with Pi20(t). RM1337 and RM5364 were found to be reliable markers of resistance conditioned by Pi20(t) in a wide range of elite rice germplasm in China. As such, they are useful tags in marker-assisted rice breeding programs aimed at incorporating Pi20(t) into advanced rice breeding lines and, ultimately, at obtaining a durable and broad spectrum of resistance to M. oryaze.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akagi H, Yokozeki Y, Inagaki A, Fujimura T (1996) Microsatellite DNA markers for rice chromosomes. Theor Appl Genet 93:1071–1077
Bonman JM, Dedios TIV, Khin MM (1986) Physiological specialization of Pyricularia oryzae in the Philippines. Plant Dis 70:767–769
Bryan GT, Wu K, Farrall L, Jia Y, Hershey HP, McAdams S, Tarchini R, Donaldson G, Faulk K, Valent B (2000) A single amino acid difference distinguishes resistant and susceptible alleles of the rice blast resistance gene Pi-ta. Plant Cell 12:2033–2045
Chen D, Zeigler RS, Ahn SW, Nelson RJ (1996) Phenotypic characterization of the rice blast resistance gene Pi2(t). Plant Dis 80:52–56
Chen M, Presting G, Barbazuk WB, Goicocchca JL, Blackmon B, Fang G, Kim H, Frisch D, Yu Y, Sun S, Higingbottom S, Phimphilai D, Thurmond S, Gaudettem B, Li P, Liu J, Hatfield J, Main D, Farrar K, Henderson C, Barnett L, Costa R, Williams B, Walser S, Atkins M, Hall C, Budiman MA, Tomkins JP, Luo M, Bancroft I, Salse J, Rcgad F, Mohapatra T, Singh NK, Tyagi AK, Soderlund C, Dean RA, Wing RA (2002) An integrated physical and genetic map of the rice genome. Plant Cell 14:537–545
Chen S, Wang L, Que Z, Pan R, Pan Q (2005) Genetic and physical mapping of Pi37(t), a new gene conferring resistance to rice blast in the famous cultivar St. No. 1. Theor Appl Genet 111:1563–1570
Chen X, Li S, Ma Y, Li H, Zhou K, Zhu L (2004) Marker-assisted selection and pyramiding for three blast resistance genes, Pid(t)1, Pib, Pita2, in Rice. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology 20:708–714 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Conaway-Bormans CA, Marchetti MA, Johnson CW, McClung AM, Park WD (2003) Molecular markers linked to the blast resistance gene Pi-z in rice for use in marker-assisted selection. Theor Appl Genet 107:1014–1020
Deng Y, Zhu X, Shen Y, He Z (2006) Genetic characterization and fine mapping of the blast resistance locus Pigm(t) tightly linked to Pi2 and Pi9 in a broad-spectrum resistant Chinese variety. Theor Appl Genet 113:705–713
Ebron LA, Fukuta Y, Imbe T, Kato H, Yanoria JMT, Tsunematsu H, Khush GS, Yokoo M (2004) Estimation of genes in blast resistance in elite indica-type rice (Oryza sativa L.) varieties-bred at the international rice research institute. Breed Sci 54:381–387
Fjellstrom R, Conaway-Bormans CA, McClung AM, Marchetti MA, Shank AR, Park WD (2004) Development of DNA markers suitable for marker assisted selection of three Pi genes conferring resistance to multiple Pyricularia grisea pathotypes. Crop Sci 44:1790–1798
Fjellstrom R, McClung AM, Shank AR (2006) SSR markers closely linked to the Pi-z locus are useful for selection of blast resistance in a broad array of rice germplasm. Mol Breed 17:149–157
Fukuta Y, Araki E, Yanoria MJT, Imbe T, Tsunematsu H, Kato H, Ebron LA, Mercado-Escueta D, Khush GS (2004) Development of varieties for blast resistance in IRRI-Japan collaborative research project. In: Kawasaki S (ed) Rice blast interaction with rice and control. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 229–233
Hayashi K, Yoshida H, Ashikawa I (2006) Development of PCR-based allele-specific and InDel marker sets for nine rice blast resistance genes. Theor Appl Genet 113:251–260
Hittalmani S, Parco A, Mew TV, Zeigler RS, Huang N (2000) Fine mapping and DNA marker-assisted pyramiding of the three major genes for blast resistance in rice. Theor Appl Genet 100:1121–1128
Imbe T, Ora S, Yanoria MJT, Tsunematsu H (1997) A new gene for blast resistance in rice cultivar, IR24. Rice Genet Newsl 14:60–62
International Rice Genome Sequencing Project (IRGSP) (2005) The map-based sequence of the rice genome. Nature 436:793–800
Jia Y (2003) Marker assisted selection for the control of rice blast disease. Pestic Outlook 14:150–152
Jia Y, Wang Z, Singh P (2002) Development of dominant rice blast Pi-ta resistance gene markers. Crop Sci 42:2145–2149
Jia Y, Wang Z, Fjellstrom RG, Moldenhauer KAK, Azam MA, Correll J, Lee FN, Xia Y, Rutger JN (2004) Rice Pi-ta gene confers resistance to the major pathotypes of the rice blast fungus in the US. Phytopathology 96:296–301
Kinoshita T (1998) Linkage mapping using mutant genes in rice. Rice Genet Newsl 15:13–74
Kiyosawa S (1982) Genetics and epidemical modeling of breakdown of plant disease resistance. Annu Rev Phytopathol 20:93–117
Kiyosawa S, Ikehashi H, Kato H, Ling Z (1981) Pathogenicity tests of Philippine isolates of blast fungus using two sets rice varieties. Jpn J Breed 31:367–376
Kosambi D (1944) The estimation of map distance from recombination values. Ann Eugen 12:172–175
Lander ESP, Green J, Abhrahamson A, Barlow MJ (1987) MAPMAKER: an interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics 1:174–181
Lei C, Wang J, Mao S, Jiang W, Zhu L, Ling Z (1996) Genetic analysis of blast resistance in indica variety Zhaiyeqing 8 (ZYQ8). Chin J Genet 23:287–293
Lei C, Wang J, Jiang W, Ling Z (2000) Study on pathologic races and virulence of blast fungus and their movement in japonica rice-growing region of northern China (in Chinese with English abstract). Acta Agron Sin 26:769–776
Liu XQ, Wang L, Chen S, Lin F, Pan QH (2005) Genetic and physical mapping of Pi36(t), a novel rice blast resistance gene located on rice chromosome 8. Mol Gen Genomics 274:394–401
McCouch SR, Teytelman L, Xu Y, Lobos KB, Clare K, Walton M, Fu B, Maghirang R, Li Z, Xing Y, Zhang Q, Kono I, Yano M, Fjellstrom R, DeClerck G, Schneider D, Cartinhour S, Ware D, Stein L (2002) Development and mapping of 2240 new SSR markers for rice (Oryza sativa L.). DNA Res 9[Suppl]:257–279
Murray MG, Thompson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of high-molecular-weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 8:4321–4325
Nguyen TTT, Koizumi S, La TN, Zenbayashi KS, Ashizawa T, Yasuda N, Imazaki I, Miyasaka A (2006) Pi35(t), a new gene conferring partial resistance to leaf blast in the rice cultivar Hokkai 188. Theor Appl Genet 113:697–704
Ou SH (1985) Rice diseases, 2nd edn. Commonwealth Mycology Institute Kew, The Cambridge News, Cambridge
Sallaud C, Lorieux M, Roumen E, Tharreau D, Berruyer R, Svestasrani P, Garsmeur O, Ghesquiere A, Notteghem JL (2003) Identification of five new blast resistance genes in the highly blast-resistant rice variety IR64 using a QTL mapping strategy. Theor Appl Genet 106:794–803
Sanguinetti CJ, Dias NE, Simpson AJG (1994) Rapid silver staining and recover of PCR products separated on polyarylamide gel. Biotechniques 17:915–919
Tabien RE, Li Z, Paterson AH, Marchetti MA, Stansel JW, Pinson SRM (2000) Mapping of four major rice blast resistance genes from ‘Lemont’ and ‘Teqing’ and evaluation of their combinatorial effect for field resistance. Theor Appl Genet 101:1215–1225
Tsunematsu H, Yoshimura A, Harushima Y, Nagamura Y, Kurata N, Yano M, Sasaki T, Iwata N (1996) RFLP framework map using recombinant inbred lines in rice. Breed Sci 46:279–284
Valent B, Farrall L, Chumley FG (1991) Magnaporthe grisea genes for pathogenicity and virulence identified through a series of backcrosses. Genetics 127:87–101
Wang ZX, Yano M, Yamanouchi U, Iwamoto M, Monna L, Hayasaka H, Katayose Y, Sasaki T (1999) The Pib gene for rice blast resistance belongs to the nucleotide binding and leucine rich repeat class of plant disease resistance genes. Plant J 19:55–64
Zhang X, Tai D (2001) Utilization of the IRRI-bred rice varieties in China (in Chinese with English abstract). J Plant Genet Resour 2:56–59
Zhou E, Jia Y, Singh P, Correll JC, Lee FN (2007) Instability of the Magnaporthe oryzae avirulence gene AVR-Pita alters virulence. Fungal Genet Biol 44:1024–1034
Zhu M, Wang L, Pan Q (2004a) Identification and characterization of a new blast resistance gene located on rice chromosome 1 through linkage and differential analyses. Phytopathology 94:515–519
Zhu X, Yang Q, Yang J, Lei C, Wang J, Ling Z (2004b) Differentiation ability of monogenic lines to Magnaporthe grisea in indica rice (in Chinese with English abstract). Acta Phytopathol Sin 34:361–368
Acknowledgements
We gratefully thank Dr. Y. Fukuta at the International Rice Research Institute for providing the rice mono-genic lines, Dr. Xinghua Wei at China National Rice Research Institute for providing some of the rice leading cultivars and Mr. Zhanling Liu and Mr. Ke Shi for their help in the inoculation experiments. This work was supported by grants from the 863 Program (Grant No. 2006AA100101), National Key Technology R&D Program (Grant no: 2006BAD13B01-3) the 948 Program (Grant No. 2006-G61) of China, and National Program 301 Component II (Genomic Characterization and Genetic Improvement) of Agriculture Research Service of the United States Department of Agriculture.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Wei Li and Cailin Lei contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, W., Lei, C., Cheng, Z. et al. Identification of SSR markers for a broad-spectrum blast resistance gene Pi20(t) for marker-assisted breeding. Mol Breeding 22, 141–149 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-008-9163-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-008-9163-9