Abstract
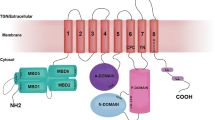
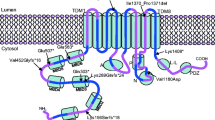
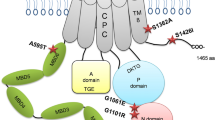
Copper-transporting ATPase 1 and 2 (ATP7A and ATP7B) are two highly homologous P-type copper ATPase exporters. Mutations in ATP7A can lead to Menkes disease which is an X-linked disorder of copper deficiency. Mutations in ATP7B can cause Wilson disease which is an autosomal recessive disorder of copper toxicity. In this study, we attempt to build a quantitative relationship between mutated ATPase and Menkes/Wilson disease. First, we use the amino-acid distribution probability as a measure to quantify the difference in ATPase before and after mutation. Second, we use the cross-impact analysis to define the quantitative relationship between mutant ATPase protein and Menkes/Wilson disease, and compute various probabilities. Finally, we use the Bayesian equation to determine the probability that Menkes/Wilson disease is diagnosed under a mutation. The results show (i) the vast majority of mutations lead to the amino-acid distribution probability increase in mutant ATP7As and decrease in ATP7Bs, and (ii) the probability that a mutation causes Menkes/Wilson disease is about nine tenth. Thus we provide a way to use the descriptively probabilistic method to couple the mutation with its clinical outcome after quantifying mutations in proteins.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
González-Díaz H, González-Díaz Y, Santana L, Ubeira FM, Uriarte E (2008) Proteomics, networks and connectivity indices. Proteomics 8: 750–778. doi:10.1002/pmic.200700638
González-Díaz H, Vilar S, Santana L, Uriarte E (2007) Medicinal chemistry and bioinformatics–current trends in drugs discovery with networks topological indices. Curr Top Med Chem 7: 1015–1029. doi:10.2174/156802607780906771
González-Díaz H, Pérez-Castillo Y, Podda G, Uriarte E (2007) Computational chemistry comparison of stable/nonstable protein mutants classification models based on 3D and topological indices. J Comput Chem 28: 1990–1995. doi:10.1002/jcc.20700
González-Díaz H, Uriarte E (2005) Proteins QSAR with Markov average electrostatic potentials. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 15: 5088–5094. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2005.07.056
González-Díaz H, Molina R, Uriarte E (2005) Recognition of stable protein mutants with 3D stochastic average electrostaticpotentials. FEBS Lett 579: 4297–4301. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2005.06.065
González-Díaz H, Uriarte E, Ramosde Armas R (2005) Predicting stability of Arc repressor mutants with protein stochastic moments. Bioorg Med Chem 13: 323–331. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2004.10.024
Marrero-Ponce Y, Medina-Marrero R, Castillo-Garit JA, Romero-Zaldivar V, Torrens F, Castro EA (2005) Protein linear indices of the macromolecular pseudograph alpha-carbon atomadjacency matrix’ in bioinformatics. Part 1: prediction of protein stability effects of a complete set of alanine substitutions in Arc repressor. BioorgMed Chem 13: 3003–3015. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2005.01.062
Fernández M, Caballero J, Fernández L, Abreu JI, Acosta G (2008) Classification of conformational stability of protein mutants from 3Dpseudo-folding graph representation of protein sequences using support vector machines. Proteins 70: 167–175. doi:10.1002/prot.21524
Fernández L, Caballero J, Abreu JI, Fernández M (2007) Amino acid sequence autocorrelation vectors and Bayesian-regularized geneticneural networks for modeling protein conformational stability: gene V protein mutants. Proteins 67: 834–852. doi:10.1002/prot.21349
Caballero J, Fernández L, Garriga M, Abreu JI, Collina S, Fernández M (2007) Proteometric study of ghrelin receptor function variations upon mutations using amino acid sequence autocorrelation vectors and genetic algorithm-based least square support vector machines. J Mol Graph Model 26: 166–178. doi:10.1016/j.jmgm.2006.11.002
Wu G, Yan S (2002) Randomness in the primary structure of protein: methods and implications. Mol Biol Today 3: 55–69
Wu G, Yan S (2006) Mutation trend of hemagglutinin of influenza A virus: a review from computational mutation viewpoint. Acta Pharmacol Sin 27: 513–526. doi:10.1111/j.1745-7254.2006.00329.x
Wu G, Yan S (2008) Lecture notes on computational mutation. Nova Science Publishers, New York
Wu G, Yan S (2006) Prediction of possible mutations in H5N1 hemagglutinins of influenza A virus by means of logistic regression. Comp Clin Pathol 15: 255–261. doi:10.1007/s00580-006-0638-y
Wu G, Yan S (2006) Prediction of mutations in H5N1 hemagglutinins from influenza A virus. Protein Pept Lett 13: 971–976. doi:10.2174/092986606778777533
Wu G, Yan S (2007) Improvement of model for prediction of hemagglutinin mutations in H5N1 influenza viruses with distinguishing of arginine, leucine and serine. Protein Pept Lett 14: 191–196. doi:10.2174/092986607779816032
Wu G, Yan S (2007) Improvement of prediction of mutation positions in H5N1 hemagglutinins of influenza A virus using neural network with distinguishing of arginine, leucine and serine. Protein Pept Lett 14: 465–470. doi:10.2174/092986607780782713
Wu G, Yan S (2008) Prediction of mutations initiated by internal power in H3N2 hemagglutinins of influenza A virus from North America. Int J Pept Res Ther 14: 41–51. doi:10.1007/s10989-007-9104-1
Wu G, Yan S (2008) Prediction of mutations in H1 neuraminidases from North America influenza A virus engineered by internal randomness. Mol Divers 11: 131–140. doi:10.1007/s11030-008-9067-y
Wu G, Yan S (2008) Prediction of mutations engineered by randomness in H5N1 neuraminidases from influenza A virus. Amino Acids 34: 81–90. doi:10.1007/s00726-007-0579-z
Wu G, Yan S (2008) Prediction of mutation in H3N2 hemagglutinins of influenza A virus from North America based on different datasets. Protein Pept Lett 15: 144–152
Wu G, Yan S (2008) Prediction of mutations engineered by randomness in H5N1 hemagglutinins of influenza A virus. Amino Acids. doi:10.1007/s00726-007-0602-4
Wu G, Yan S (2008) Three sampling strategies to predict mutations in H5N1 hemagglutinins from influenza A virus. Protein Pept Lett http://www.bentham.org/ppl/CurrentIssue.htm
Wu G, Yan S (2005) Timing of mutation in hemagglutinins from influenza A virus by means of unpredictable portion of amino-acid pair and fast Fourier transform. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 333: 70–78. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.05.094
Wu G, Yan S (2006) Timing of mutation in hemagglutinins from influenza A virus by means of amino-acid distribution rank and fast Fourier transform. Protein Pept Lett 13: 143–148. doi:10.2174/092986606775101616
Linder MC (1991) Biochemistry of copper. Plenum Press, New York
Pardo CA, Xu Z, Borchelt DR, Price DL, Sisodia SS, Cleveland DW (1995) Superoxide dismutase is an abundant component of cell bodies, dendrites and axons of motor neurons and in a subset of other neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92: 954–958. doi:10.1073/pnas.92.4.954
Rolfs A, Hediger MA (1999) Metal ion transporters in mammals: structure, function and pathological implications. J Physiol 518: 1–12. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7793.1999.0001r.x
Tanzi RE, Petrukhin K, Chernov I, Pellequer JL, Wasco W, Ross B et al (1993) The Wilson disease gene is a copper transporting ATPase with homology to the Menkes disease gene. Nat Genet 5: 344–350. doi:10.1038/ng1293-344
Terada K, Kawarada Y, Miura N, Yasui O, Koyama K, Sugiyama T (1995) Copper incorporation into ceruloplasmin in rat livers. Biochim Biophys Acta 1270: 58–62
Yoshida K, Furihata K, Takeda S, Nakamura A, Yamamoto K, Morita H et al (1995) A mutation in the ceruloplasmin gene is associated with systemic hemosiderosis in humans. Nat Genet 9: 267–272. doi:10.1038/ng0395-267
Terada K, Nakako T, Yang XL, Iida M, Aiba N, Minamiya Y et al (1998) Restoration of holoceruloplasmin synthesis in LEC rat after infusion of recombinant adenovirus bearing WND cDNA. J Biol Chem 273: 1815–1820. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.3.1815
Camakaris J, Voskoboinik I, Mercer JFB (1999) Molecular mechanisms of copper homeostasis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 261: 225–232. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1999.1073
Peña MMO, Lee J, Thiele DJ (1999) A delicate balance: homeostatic control of copper uptake and distribution. J Nutr 129: 1251–1260
Chelly J, Tumer Z, Tonnesen T, Petterson A, Ishikawa-Brush Y, Tommerup N et al (1993) Isolation of a candidate gene for Menkes disease that encodes a potential heavy metal binding protein. Nat Genet 3: 14–19. doi:10.1038/ng0193-14
Mercer JF, Livingston J, Hall B, Paynter JA, Begy C, Chandrasekharappa S et al (1993) Isolation of a partial candidate gene for Menkes disease by positional cloning. Nat Genet 3: 20–25. doi:10.1038/ng0193-20
Vulpe C, Levinson B, Whitney S, Packman S, Gitschier J (1993) Isolation of a candidate gene for Menkes disease and evidence that it encodes a copper-transporting ATPase. Nat Genet 3: 7–13. doi:10.1038/ng0193-7
Tuemer Z, Moeller LB, Horn N (1999) Mutation spectrum of ATP7A, the gene defective in Menkes disease. Adv Exp Med Biol 448: 83–95
Ambrosini L, Mercer JFB (1999) Defective copper-induced trafficking and localization of the Menkes protein in patients with mild and copper-treated classical Menkes disease. Hum Mol Genet 8: 1547–1555. doi:10.1093/hmg/8.8.1547
Ogawa A, Yamamoto S, Takayanagi M, Kogo T, Kanazawa M, Kohno Y (1999) Identification of three novel mutations in the MNK gene in three unrelated Japanese patients with classical Menkes disease. J Hum Genet 44: 206–209. doi:10.1007/s100380050144
Gu Y-H, Kodama H, Murata Y, Mochizuki D, Yanagawa Y, Ushijima H et al (2001) ATP7A gene mutations in 16 patients with Menkes disease and a patient with occipital horn syndrome. Am J Med Genet 99:217–222. doi:10.1002/1096-8628(2001)9999:9999<::AID-AJMG1167>3.0.CO;2-R
Turner Z, Horn N (1997) Menkes disease: recent advances and new aspects. J Med Genet 34: 265–274
Bull PC, Thomas GR, Rommens JM, Forbes JR, Cox DW (1993) The Wilson disease gene is a putative copper transporting P-type ATPase similar to the Menkes gene. Nat Genet 5: 327–337. doi:10.1038/ng1293-327
Yamaguchi Y, Heiny ME, Gitlin JD (1993) Isolation and characterization of a human liver cDNA as a candidate gene for Wilson disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 197: 271–277. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1993.2471
Petrukhin K, Lutsenko S, Chernov I, Ross BM, Kaplan JH, Gilliam TC (1994) Characterization of the Wilson disease gene encoding a P-type copper transporting ATPase: genomic organization, alternative splicing, and structureÏfunction predictions. Hum Mol Genet 3: 1647–1656. doi:10.1093/hmg/3.9.1647
Oh WJ, Kim EK, Park KD, Hahn SH, Yoo OJ (1999) Cloning and characterization of the promoter region of the Wilson disease gene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 259: 206–211. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1999.0732
Tao TY, Gitlin JD (2003) Hepatic copper metabolism: insights from genetic disease. Hepatology 37: 1241–1247. doi:10.1053/jhep.2003.50281
Linder MC, Wooten L, Cerveza P, Cotton S, Shulze R, Lomeli N (1998) Copper transport. Am J Clin Nutr 67(5 Suppl): 965S–971S
Schaefer M, Hopkins RG, Failla ML, Gitlin JD (1999) Hepatocyte-specific localization and copper-dependent trafficking of the Wilson’s disease protein in the liver. Am J Physiol 276: G639–G646
Terada K, Aiba N, Yang XL, Iida M, Nakai M, Miura N et al (1999) Biliary excretion of copper in LEC rat after introduction of copper transporting P-type ATPase, ATP7B. FEBS Lett 448: 53–56. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(99)00319-1
Roelofsen H, Wolters H, Van Luyn MJA, Miura N, Kuipers F, Vonk RJ (2000) Copper-induced apical trafficking of ATP7B in polarized hepatoma cells provides a mechanism for biliary copper excretion. Gastroenterology 119: 782–793. doi:10.1053/gast.2000.17834
Thomas GR, Forbes JR, Roberts EA, Walshe JM, Cox DW (1995) The Wilson disease gene: spectrum of mutations and their consequences. Nat Genet 9: 210–216. doi:10.1038/ng0295-210
Loudianos G, Dessi V, Angius A, Lovicu M, Loi A, Deiana M et al (1996) Wilson disease mutations associated with uncommon haplotypes in Mediterranean patients. Hum Genet 98: 640–642. doi:10.1007/s004390050275
Shah AB, Chernov I, Zhang HT, Ross BM, Das K, Lutsenko S et al (1997) Identification and analysis of mutations in the Wilson disease gene (ATP7B): population frequencies, genotype–phenotype correlation, and functional analyses. Am J Hum Genet 61: 317–328. doi:10.1086/514864
Kim EK, Yoo OJ, Song KY, Yoo HW, Choi SY, Cho SW et al (1998) Identification of three novel mutations and a high frequency of the Arg778Leu mutation in Korean patients with Wilson disease. Hum Mutat 11:275–278. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1098-1004(1998)11:4<275::AID-HUMU4>3.0.CO;2-L
Wilson SAK (1912) Progressive lenticular degeneration: a familial nervous disease associated with cirrhosis of the liver. Brain 34: 295–508. doi:10.1093/brain/34.4.295
Thomas GR, Forbes JR, Roberts EA, Walshe JM, Cox DW (1995) The Wilson disease gene: spectrum of mutations and their consequences. Nat Genet 9: 210–217. Erratum in Nat Genet 1995; 9:451. doi:10.1038/ng0295-210
Schilsky ML (1996) Wilson disease: genetic basis of copper toxicity and natural history. Semin Liver Dis 16: 83–95
Mercer JFB (2001) The molecular basis of copper transport diseases. Trends Mol Med 7: 64–69. doi:10.1016/S1471-4914(01)01920-7
Shim H, Harris ZL (2003) Genetic defects in copper metabolism. J Nutr 133: 1527S–1531S
Das SK, Ray K (2006) Wilson’s disease: an update. Nat Clin Pract Neurol 2: 482–493. doi:10.1038/ncpneuro0291
Brewer GJ, Yuzbasiyan-Gurkan V (1992) Wilson disease. Medicine 71: 139–164. doi:10.1097/00005792-199205000-00004
Moeller LB, Bukrinsky JT, Moelgaard A, Paulsen M, Lund C, Tuemer Z et al (2005) Identification and analysis of 21 novel disease-causing amino acid substitutions in the conserved part of ATP7A. Hum Mutat 26: 84–93. doi:10.1002/humu.20190
Loudianos G, Dessi V, Lovicu M, Angius A, Nurchi A, Sturniolo GC et al (1998) Further delineation of the molecular pathology of Wilson disease in the Mediterranean population. Hum Mutat 12:89–94. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1098-1004(1998)12:2<89::AID-HUMU3>3.0.CO;2-G
Loudianos G, Dessi V, Lovicu M, Angius A, Altuntas B, Giacchino R et al (1999) Mutation analysis in patients of Mediterranean descent with Wilson disease: identification of 19 novel mutations. J Med Genet 36: 833–836
Okada T, Shiono Y, Hayashi H, Satoh H, Sawada T, Suzuki A et al (2000) Mutational analysis of ATP7B and genotype–phenotype correlation in Japanese with Wilson’s disease. Hum Mutat 15:454–462. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1098-1004(200005)15:5<454::AID-HUMU7>3.0.CO;2-J
Caca K, Ferenci P, Kuehn H-J, Polli C, Willgerodt H, Kunath B et al (2001) High prevalence of the H1069Q mutation in East German patients with Wilson disease: rapid detection of mutations by limited sequencing and phenotype–genotype analysis. J Hepatol 35: 575–581. doi:10.1016/S0168-8278(01)00219-7
Gu Y-H, Kodama H, Du S-L, Gu Q-J, Sun H-J, Ushijima H (2003) Mutation spectrum and polymorphisms in ATP7B identified on direct sequencing of all exons in Chinese Han and Hui ethnic patients with Wilson’s disease. Clin Genet 64: 479–484. doi:10.1046/j.1399-0004.2003.00179.x
Margarit E, Bach V, Gomez D, Bruguera M, Jara P, Queralt R et al (2005) Mutation analysis of Wilson disease in the Spanish population-identification of a prevalent substitution and eight novel mutations in the ATP7B gene. Clin Genet 68: 61–68
Vrabelova S, Letocha O, Borsky M, Kozak L (2005) Mutation analysis of the ATP7B gene and genotype/phenotype correlation in 227 patients with Wilson disease. Mol Genet Metab 86: 277–285. doi:10.1016/j.ymgme.2005.05.004
Cox DW (1999) Disorders of copper transport. Br Med Bull 55: 544–555. doi:10.1258/0007142991902619
Wu G, Yan S (2000) Prediction of distributions of amino acids and amino acid pairs in human haemoglobin α-chain and its seven variants causing α-thalassemia from their occurrences according to the random mechanism. Comp Haematol Int 10: 80–84. doi:10.1007/s005800070012
Wu G, Yan S (2001) Analysis of distributions of amino acids, amino acid pairs and triplets in human insulin precursor and four variants from their occurrences according to the random mechanism. J Biochem Mol Biol Biophys 5: 293–300
Wu G, Yan S (2001) Analysis of distributions of amino acids and amino acid pairs in human tumor necrosis factor precursor and its eight variants according to random mechanism. J Mol Model 7: 318–323
Wu G, Yan S (2002) Random analysis of presence and absence of two- and three-amino-acid sequences and distributions of amino acids, two- and three-amino-acid sequences in bovine p53 protein. Mol Biol Today 3: 31–37
Wu G, Yan S (2002) Analysis of distributions of amino acids in the primary structure of apoptosis regulator Bcl-2 family according to the random mechanism. J Biochem Mol Biol Biophys 6: 407–414. doi:10.1080/1025814021000036106
Wu G, Yan S (2002) Analysis of distributions of amino acids in the primary structure of tumor suppressor p53 family according to the random mechanism. J Mol Model 8: 191–198. doi:10.1007/s00894-002-0087-8
Wu G, Yan S (2004) Determination of sensitive positions to mutations in human p53 protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 321: 313–319. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.06.117
Wu G, Yan S (2005) Searching of main cause leading to severe influenza A virus mutations and consequently to influenza pandemics/epidemics. Am J Infect Dis 1: 116–123
Wu G, Yan S (2005) Prediction of mutation trend in hemagglutinins and neuraminidases from influenza A viruses by means of cross-impact analysis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 326: 475–482. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.11.052
Gao N, Yan S, Wu G (2006) Pattern of positions sensitive to mutations in human haemoglobin α-chain. Protein Pept Lett 13: 101–107. doi:10.2174/092986606774502090
Feller W (1968) An introduction to probability theory and its applications vol I, 3rd edn. Wiley, New York, pp 34–40
Butler P, McIntyre N, Mistry PK (2001) Molecular diagnosis of Wilson disease. Mol Genet Metab 72: 223–230. doi:10.1006/mgme.2000.3143
Enzer S (1970) Delphi and cross-impact techniques: an effective combination for systematic futures analysis. Futures 3: 48–61
Enzer S (1972) Cross-impact techniques in technology assessment. Futures 4: 30–51. doi:10.1016/0016-3287(72)90023-7
Gordon TG, Hayward H (1968) Initial experiments with the cross-impact matrix method of forecasting. Futures 1: 100–116. doi:10.1016/S0016-3287(68)80003-5
Gordon TG (1969) Cross-impact matrices—an illustration of their use for policy analysis. Futures 2: 527–531
Sage AP (1977) Methodology for Large-scale Systems. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 165–203
Wu G (2000) Application of cross-impact analysis to the relationship between aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 and flushing. Alcohol Alcohol 35: 55–59. doi:10.1093/alcalc/35.1.55
Wu G, Yan S (2008) Building quantitative relationship between changed sequence and changed oxygen affinity in human hemoglobin β-chain. Protein Pept Lett 15: 341–345. doi:10.2174/092986608784246498
Wikipedia—The free encyclopedia (2007) Bayes’ theorem. en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bayes’_theorem
Tanzi RE, Petrukhin K, Chernov I, Pellequer JL, Wasco W, Ross B et al (1993) The Wilson disease gene is a copper transporting ATPase with homology to the Menkes disease gene. Nat Genet 5: 344–350. doi:10.1038/ng1293-344
Forbes JR, Cox DW (2000) Copper-dependent trafficking of Wilson disease mutant ATP7B proteins. Hum Mol Genet 9: 1927–1935. doi:10.1093/hmg/9.13.1927
Mercer JFB, Llanos RM (2003) Molecular and cellular aspects of copper transport in developing mammals. J Nutr 133: 1481S–1484S
La Fontaine S, Theophilos MB, Firth SD, Gould R, Parton RG, Mercer JFB (2001) Effect of the toxic milk mutation (tx) on the function and intracellular localization of Wnd, the murine homologue of the Wilson copper ATPase. Hum Mol Genet 10: 361–370. doi:10.1093/hmg/10.4.361
Mercer JFB, Barnes N, Stevenson J, Strausak D, Llanos RM (2002) Copper-induced trafficking of the Cu-ATPases: a key mechanism for copper homeostasis. Biometals 16: 175–184. doi:10.1023/A:1020719016675
Hahn S, Cho K, Ryu K, Kim J, Pai K, Kim M et al (2001) Identification of four novel mutations in classical Menkes disease and successful prenatal DNA diagnosis. Mol Genet Metab 73: 86–90. doi:10.1006/mgme.2001.3169
Cox DW (1996) Molecular advances in Wilson disease. In: Boyer JL, Ockner RK (eds) Progress in liver diseases. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 245–264
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, S., Wu, G. Quantitative relationship between mutated amino-acid sequence of human copper-transporting ATPases and their related diseases. Mol Divers 12, 119–129 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-008-9084-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-008-9084-x