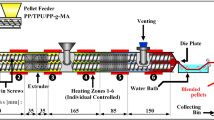
A high-performance bismaleimide (BMI) resin blends containing the polyaryletherketone (PAEK) were prepared. The nanomechanical behaviors, viscoelasticity, and tribological properties of the bismaleimide resins were investigated by nanoindentation/scratch methods. It was established that the hardness ( H ) decreased, while the elastic modulus ( E ) increased, i.e., a reduction of plasticity index ( H /E ) values through the quasi-static nano-indentation testing. Meanwhile, the indentation response was mainly affected by the plastic deformation in response to a stress. The unmodified bismaleimide resins demonstrated better load-bearing capacity and indentation recovery ability, lower penetration depth than the other three specimens. Effects of angular frequency and average contact force on the viscoelastic properties were also investigated by the dynamic nanoindentation mode. The results revealed that variations of the loss tangent curves nearly were similar to each other, first increased then decreased gradually at contact force of 150 and 300 μN. Topography and profiles of the indentation and scratch surfaces were also discussed. Based on the results of the nanoscratching tests, when the PAEK content was 10 phr, the coefficient of friction during plowing was the lowest, exhibited the better scratch/wear resistance.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. O. Park and T. S. Tang, “Synthesis and characterization of bismaleimides from epoxy resins,” J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem., 30, No. 5, 723-729 (1992).
C. M. Chan, Polymer Surface Modification and Characterization, Hanser Publications, New York, Chapter 1, 1-34 (1994).
X. L. Cheng, Q. Wu, S.E. Morgan, and J. S. Wiggins, “Morphologies and mechanical properties of polyethersulfone modified epoxy blends through multifunctional epoxy composition,” J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 134, No. 18, 44775 (2017).
H. X. Hu, Z. W. Liu, C. J. Wang, L. M. Meng, and Y. Z. Shen, “Nanomechanical Properties of a Bicomponent Epoxy Resin via Blending with Polyaryletherketone,”, J. Compos. Sci., 3, No. 4, 92-102 (2019).
M. Wong, G. T. Lim, A. Moyse, J. N. Reddy, and H. J. Sue, “A new test methodology for evaluating scratch resistance of polymers,” Wear, 256, 1214-1227 (2004).
B. D. Beake, A. J. Harrisand, and T. W. Liskiewicz, “Review of recent progress in nanoscratch testing,” Tribol. Mater. Surf. Interfaces, 7, No. 2, 87-96 (2013).
B. D. Beakeand and G. J. Leggett, “Nanoindentation and nanoscratch testing of uniaxially and biaxially drawn poly (ethylene terephthalate) film,” Polymer, 43, No. 2, 319-327 (2002).
A. Kareer, E. Tarleton, C. Hardie, S. V. Hainsworthand, and A. J. Wilkinson, “Scratching the surface: Elastic rotations beneath nanoscratch and nanoindentation tests,” Acta Mater. 200, 116-126 (2020).
K. Q. Liu, Z. J. Jin, L. B. Zeng, M. Ostadhassan, and X. M. Xu, “Understanding the creep behavior of shale via nano- DMA method,” Energy Reports, 7, 7478-7487 (2021).
A. Krupicka, M. Johansson, and A. Hult, “Viscoelasticity in polymer film on rigid substrates,” Macromol. Mater. Eng., 288, No. 2, 108-116 (2003).
Y. F. Zhang, S. L. Bai, D. Y. Yang, Z. Zhang, and K. W. Sharpon, “Study on the viscoelastic properties of the epoxy surface by means of nanodynamic mechanical analysis,” J. Polym. Sci.: Part B: Polym. Phys., 46, No. 3, 281-288 (2008).
M. George and A. Mohanty, “Viscoelastic and mechanical characterization of graphene decorated with graphene quantum dots reinforced epoxy composites,” Polym. Eng. Sci., 60, No. 12, 3011-3023 (2020).
C. C. White, M. R. Vanlandingham, P. L. Drzal, N. K. Chang, and S. H. Chang, “Viscoelastic characterization of polymers using instrumented indentation. II. Dynamic testing,” J. Polym. Sci. Part B: Polym. Phys., 43, No. 14, 1812-1824 (2005).
G. M. Odegard, T. S. Gates, and H. M. Herring, “Characterization of viscoelastic properties of polymeric materials through nanoindentation,” Exp. Mech., 45, No. 2, 130-136 (2005).
R. J. Iredale, C. Ward, and I. Hamerton, “Modern advances in bismaleimide resin technology: a 21st century perspective on the chemistry of addition polyimides,” Prog. Polym. Sci., 69, 1-21 (2017).
Z. Y. Yerlikaya, Z. Öktem, and E. Bayramli, “Chain-Extended bismaleimides. I. Preparation and characterization of maleimide-terminated resins,” J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 59, No. 1, 165-171 (1996).
Z. L. Zhang, X. H. Li, Y. Bao, W. Wei, X. J. Li, and X. Y. Liu, “Bismaleimide resins modified by an allyl ether of bio-based resveratrol with excellent halogen-free and phosphorus-free intrinsic flame retardancy and ultrahigh glass transition temperature,” Polym. Degrad. Stab., 193, 109717 (2021).
T. Takeichi, Y. Saito, T. Agag, H. Mutoand, and T. Kawauchi,“High-performance polymer alloys of polybenzoxazine and bismaleimide,” Polymer, 49, No. 5, 1173-1179(2008).
Z Wang, W. Wu, M. H. Wagner, L. Zhang, and S. Bard, “Synthesis of DV-GO and its effect on the fire safety and thermal stability of bismaleimide,” Polym. Degrad. Stabil., 128, 209-216 (2016).
L. Qiu, P. Guo, X. Q. Yang, Y. X. Ouyang, Y. H. Feng, X. X. Zhang, J. N. Zhao, X. H. Zhang, and Q. W. Li,“Electro curing of oriented bismaleimide between aligned carbon nanotubes for high mechanical and thermal performances,” Carbon, 145, 650-657 (2019).
A. Wagner, I. Gouzman, N. Atar, E. Grossman, M. Pokrass, A. Fuchsbauer, L. Schranzhofer. and C. Paulik, “Cure kinetics of bismaleimides as basis for polyimide like inks for PolyJet (TM)-3D-printing,” J. Appli. Polym. Sci., 136, No. 12, 47244 (2019).
C. P. Reghunadhan and Nair, “Advances in addition-cure phenolic resins,” Prog. Polym. Sci., 29, 401-498 (2004).
S. Kamiyama, Y. Hirano, T. Okada, and T. Ogasawara, “Lightning strike damage behavior of carbon fiber reinforced epoxy, bismaleimide, and polyetheretherketone composites,” Compos. Sci. Technol., 161, 107-114 (2018).
C. Liu, Y. Qiao, N. Li, F. Y. Hu, Y. S. Chen, G. Z. Du, J. Y. Wang, and X. G. Jian, “Toughened of bismaleimide resin with improved thermal properties using amino-terminated Poly(phthalazinone ether nitrile sulfone)s,” Polymer, 206, 122887 (2020).
Q. Zou, F. Xiao, S. Q. Gu, J. Li, D. J. Zhang, Y. F. Liu, and X. B. Chen,“Toughening of bismaleimide resin based on the self-assembly of flexible aliphatic side chains,” Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 58, No. 36, 16526-16531 (2019).
Q. Yuan, F. Huang, and Y. Jiao, “Characterization of modified bismaleimide resin,” J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 62, No. 3, 459-464 (1996).
F. W. Huang, F. R. Huang, Y. Zhou, and L. Du, “Preparation and properties of bismaleimide resins modified with hydrogen silsesquioxane and dipropargyl ether and their composites,” Polym. J., 42, No. 3, 261-267 (2010).
W. C. Oliver and G. M. Pharr, “An improved technique for determining hardness and elastic-modulus using load and displacement sensing indentation experiments,” J. Mater. Res., 7, No. 6, 1564-1583 (1992).
M. M. Shokrieh, M. R. Hosseinkhani, M. R. Naimi-Jamal, and H. Tourani, “Nanoindentation and nanoscratch investigations on Graphene based nanocomposites,” Polym. Test., 32, No. 1, 45-51 (2013).
J. L. Koenig, Ch.4, Applications of IR Spectroscopy to Ppolymers, Spectroscopy of Polymers (Second Edition), 147-206 (1999).
Z. Chen, H. Yan, Q. Lyu, S. Niu, and C. Tang, “Ternary hybrid nanoparticles of reduced graphene oxide/graphene-like MoS2/zirconia as lubricant additives for bismaleimide composites with improved mechanical and tribological properties,” Compos., Part A, 101, 98-107 (2017).
F. Wang, L. T. Drzal, Y. Qinand, and Z. Huang, “Enhancement of fracture toughness, mechanical and thermal properties of rubber/epoxy composites by incorporation of graphene nanoplatelets,” Compos., Part A, 87, 10-22 (2016).
S. Rakesh, C. P. S. Dharan, M. Selladurai, V. Sudha, P. R. Sundararajan, and M. Sarojadevi, “Thermal and mechanical properties of POSS-Cyanate ester/epoxy nanocomposites,” High Peform. Polym., 25, No. 1, 87-96 (2013).
Z. H. Xu and J. Agren, “An analysis of piling-up or sinking-in behaviour of elastic–plastic materials under a sharp indentation,” Phil. Mag. Lett., 84, No. 23, 2367-2380 (2004).
W. M. Huang, J. F. Su, M. H. Hong, and B. Yang, “Pile-up and sink-in in micro-indentation of a NiTi shape-memory alloy,” Scr. Mater., 53, No. 9, 1055-1057 (2005).
A. Leyland and A. Matthews, “On the significance of the H/E ratio in wear control: a nanocomposite coating approach to optimised tribological behavior,” Wear, 246, No. 1-2, 1-11 (2000).
L. A. Donohue, J. Cawley, and D. B. Lewis, “Investigation of super lattice coatings deposited by a combined steered arc evaporation and unbalanced magnetron sputtering technique,” Surf. Coat. Technol. 76-77, No. 1, 149-158 (1995).
T. Zhang, S. L. Bai, Y. F. Zhang, and B. Thibaut, “Viscoelastic properties of wood materials characterized by nanoin- dentation experiments,” Wood Sci. Technol., 46, No. 5, 1003-1016 (2012).
S. P. Wen, R. L. Zong, F. Zeng, S. Guo, and F. Pan, “Nanoindentation and nanoscratch behaviors of Ag/Ni multilayers,” Appl. Surf. Sci., 255, No. 8, 4558-4562 (2009).
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the Key Program of the Education Department of Anhui Province (KJ2020A0282 and KJ2019A0127).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, H.X., Deng, Y.B., Fan, L. et al. Ano-Scale Mechanical, Viscoelastic, and Tribological Behaviors of Polyaryletherketone Modified Bismaleimide Blends. Mech Compos Mater 59, 825–836 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11029-023-10134-6
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11029-023-10134-6