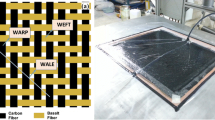
The aim of the present work was to investigate the effect of thermal cycling on the tensile behavior of three types of polymer-matrix composites — a phenolic resin reinforced with woven basalt fibers, woven carbon fibers, and hybrid basalt and carbon fibers — in an ambient environment. For this purpose, tensile tests were performed on specimens previously subjected to a certain number of thermal cycles. The ultimate tensile strength of the specimen reinforced with woven basalt fibers had by 5% after thermal cycling, but the strength of the specimen with woven carbon fibers had reduced to a value by 11% higher than that before thermal cycling.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. L. Brown, “The Effect of Long-Term Thermal Cycling on the Micro-cracking Behavior and Dimensional Stability of Composite Materials,” PhD thesis, Blacksburg, Virginia, USA, 1–6 (2000).
R. Y. Kim, A. S. Crasto, and G. A. Schoeppner, “Dimensional stability of composites in a space thermal environment,”, Compos. Sci. Technol, 60, 2601–2608 (1996).
M. C. Lafarie-Frenot, S. Rouquie, N. Q. Ho, and V. Bellenger, “Comparison of damage development in C/epoxy laminates during isothermal ageing or thermal cycling,” Composites: Part A, 37, 662–671 (2006).
G. C. Papanicolaou, A. G. Xepapadaki, and G. D. Tagaris, “Effect of thermal shock cycling on the creep behavior of glass-epoxy composites,” Compos. Struct., 88, 436–442 ( 2009).
A. H. Nayfeh, “Thermomechanically induced interfacial stresses in fibrous composites,” Fiber Sci. Technol., 10, 195–209 (1977).
B. C. Ray, “Study of the influence of thermal shock on interfacial damage in thermosetting matrix aramid fiber composites,” J. Mater. Sci. Lett, 22, 201–202 (2003).
B. Z. Jang, “Advanced polymer composites- principles and applications,” Proc. ASM Int., Ohio, USA (1994).
W. Shoukai and D. D. L. Chung, “Thermal fatigue in carbon fibre polymer-matrix composites, monitored in real time by electrical resistance measurements,” Polym. Polym. Compos., 9, 135–140 (2001).
K. B. Shin, C. G. Kim, C. S. Hong, and H. H. Lee, “Prediction of failure thermal cycles in graphite/epoxy composite materials under simulated low earth orbit environments,” Composites: Part B, 31, 223–235 (2000).
A. Paillous and C. Pailler, “Degradation of multiply polymer-matrix composites induced by space environment,” Composites, 25, 287–295 (1994).
T. K. Tsotis, K. Keller, K. Lee, J. Bardis, and J. Bish, “Aging of polymeric composite specimens for 5000 hours at elevated pressure and temperature,” Compos. Sci. Technol., 61,75-86 (2001).
K. J. Bowles and A. Meyers, “Specimen geometry effects on graphite/pmr 15 composites during thermo-oxidative ageing,” Proc. 31st Int. SAMPE Symp., Los Angeles, USA (1986), 1285–1299.
J. D. Nam and J. C. Seferis, “Anisotropic thermooxidative stability of carbon fibre reinforced polymeric composites,” SAMPE Q., 24, 10–18 (1992).
I. M. Salin and J. C. Seferis, “Anisotropic effects in thermogravimetry of polymeric composites”, J. Polym. Sci., Part B, 31, 1019–1027 (1993).
K. J. Bowles, M. S. Madhukar, D. S. Papadopoulos, L. Inghram, and L. McCorkle, “The effects of fiber surface modification and thermal aging on composite toughness and its measurement,” J. Compos. Mater., 31, 552–579 (1997).
M. C. Lafarie-Frenot and S. Rouquie, “Influence of oxidative environments on damage in c/epoxy laminates subjected to thermal cycling,” Compos. Sci. Technol., 64, 1725–1735 (2004).
V. P. Sergeev, Y. U. Chuvashov, O. V. Galushchak, I. G. Pervak, and N. S. Fatikova, “Basalt fibers- a reinforcing filler for composites,” Powder Metall. Met. Ceram., 33, 555–557 (1994).
M. Bednar and M. Hajek, “Hitzeschutztextilien aus neuartigen Basalt-Filamentgarnen,” Technische Textilien, 43, 252–254 (2000).
A. Pegoretti, E. Fabbri, C. Migliaresi, and F. Pilatiet, “Intraply and interply hybrid composites based on E-glass and poly (vinyl alcohol) woven fabrics: tensile and impact properties,” Polym. Int., 53, 1290–1297 (2004).
A. Bakar, A. Hariharan, and H. P. S. Abdul Khalil, “Lignocellulose-based hybrid bilayer laminate composite: Part I- studies on tensile and impact behavior of oil palm fiber-glass fiber-reinforced epoxy resin,” J. Compos. Mater., 39, 663–684 (2005).
K. Chung, J. C. Seferis, and J. D. Nam, “Investigation of thermal degradation behavior of polymeric composites: prediction of thermal cycling effect from isothermal data,” Composites: Part A, 31, 945–957 (2000).
R. Griffiths and A. Ball, “An assessment of the properties and degradation behaviour of glass-fibre-reinforced polyester polymer concrete,” Compos. Sci. Technol., 60, 2747–2753 (2000).
F. Segovia, C. Ferrer, M. D. Salvador, and V. Amigo, “Influence of processing variables on mechanical characteristics of sunlight aged polyester-glass fibre composites,” Polym. Degrad. Stab., 71, 179–184 (2001).
M. D. Golder and B. Mulholland, “Improved UV stabilization expands uses for polyester elastomers,” Plast. Eng., 46, 43–44 (1990).
A. W. Signor, M. R. Vanlandingham, and J. W. Chin, “Effects of ultraviolet radiation exposure on vinyl ester resins: characterization of chemical, physical and mechanical damage,” Polym. Degrad. Stab., 79, 359–368 (2002).
W. Sakai, T. Sadakane, W. Nishimoto, M. Nagata, and N. Tsutsumi, “Photosensitised degradation and cross-linking of linear aliphatic polyesters studied by GPC and ESR,” Polymer, 43, 6231–6238 (2002).
G. Li, N. Pourmohamadian, A. Cygan, J. Peck, J. E. Helms, and S. S. Pang, “Fast repair of laminated beams using UV curing composites,” Compos. Struct., 60, 73–81 (2003).
E. Grossman and I. Gouzman, “Space environment effects on polymers in low earth orbit,” Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. B., 208, 48–57 (2003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Russian translation published in Mekhanika Kompozitnykh Materialov, Vol. 52, No. 6, pp. 1141–1154 , November-December, 2016.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khalili, S.M.R., Najafi, M. & Eslami-Farsani, R. Effect of Thermal Cycling on the Tensile Behavior of Polymer Composites Reinforced by Basalt and Carbon Fibers. Mech Compos Mater 52, 807–816 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11029-017-9632-5
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11029-017-9632-5