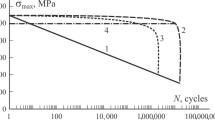
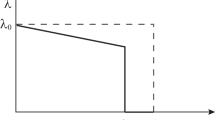
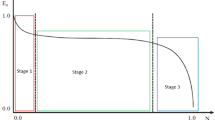
To perform engineering estimations of the fatigue life of quasi-randomly loaded layered composites, with geometric concentrators, representing the longitudinal elements of composite wing of a transport airplane, a special rule of fatigue damage accumulation is suggested. The main propositions of the method for calculating the fatigue life of these elements by using this rule are formulated. The examples of estimations presented show a good agreement between analytical results and experimental data. A number of important conclusions about the effect of different levels of cyclic loading and “GAG” cycles of different flight types of the quasi-random “TWIST” program on the total fatigue life are made.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. B. De Jonge, D. Schutz, H. Lowak, and J. Schijve, “A standardized load sequence for flight simulation tests on transport aircraft wing structures,” LBF Bericht FB-106 (NLR 73029U), 1973.
J. R. Schaff and B. D. Davidson, “A Life prediction methodology for composite structures. Pt I: Constant amplitude and two stress level fatigue loading, and Pt II: Spectrum fatigue loading,” J. Compos. Mater., 31, No. 2, 128−181 (1997).
R. Badaliance and H. D. Dill, Effects of Fighter Attack Spectrum on Composite Fatigue Life − AFWAL−TR−81−3001, Air Force Flight Dynamics Laboratory, 1981.
B.Harris, A Historical Review of the Fatigue Behavior of Fiber-Reinforced Plastics. in: Fatigue in Composites /Ed. by B. Harris, Woodhead Publishing Ltd and CRC Press LLC, 3-35, (2003).
R. J. Howe and M. J. Owen, “Accumulation of damage in glass-reinforced plastic under tensile and fatigue loading,” Proc. of the 8th Int. Reinforced Plastics Congr., London: British Plastic Federation, 137-148 (1972).
S. M. Marco and W. L. Starkey, “Effect of complex stress-time cycles on the fatigue properties of metals,” ASME Trans., 76 (1954).
I. P. Bond, “Fatigue life prediction for GRP subjected to variable amplitude fatigue,” Compos. Appl. Sci., Pt. A, 30, No. 8, 961-970 (1999).
W. Hwang and K. S. Han, “Cumulative damage models and multi-stress fatigue life prediction,” J. of Compos. Mater., 20, 125−153 (1986).
D. Schutz and J. J. Gerharz, “Fatigue strength of a fibre-reinforced material,” Composites, 8, 245-250 (1977).
I. P. Bond and I. R. Farrow, “Fatigue life prediction under complex loading for XAS/914 CFRP incorporating a mechanical fastener,” Int. J. Fatigue, 22, No. 8, 633-644 (2000).
H. T. Han and S. W. Choi, “The Effect of Loading Parameters on Fatigue of Composite Laminates: Part V,” Report DOT/FAA/AR−01/24 (2001).
E. P. Phillips, “Effects of truncation of a predominantly compression load spectrum on the life of a notched graphite/ epoxy laminate,” Fatigue of Fibrous Compos. Mater., ASTM STP 723/ ASTM, 197-212 (1981).
J. F. Mandell, Fatigue Behaviour of Fibre-Resin Composites. In: Developments in Reinforced Plastics 2., London. Appl. Sci. Publ., 67-108 (1982).
J. R. Schaff, Fatigue and Life Prediction. Vol. 21. Composites, ASM Handbook. 616-632 (2001).
J. M. C. Cadei, Fatigue of FRP Composites in Civil Engineering Applications. In: Fatigue in Composites. Ed. by B. Harris, Woodhead Publ. Ltd and CRC Press LLC, 658-685 (2003).
G. D. Sims, Fatigue Test Methods, Problems and Standards. In: Fatigue in Composites /Ed. by B. Harris, Woodhead Publ. Ltd and CRC Press LLC, 36-62 (2003).
R. S. Whitehead, “Northrop Corporation − qualification of primary aircraft structures,” 14th ICAF Symp. (1987).
M. H. Beheshty, B. Harris, and T. Adam, “An empirical fatigue-life model for high-performance fiber composites with and without impact damage,” Compos. A, Appl. Sci. and Manuf., A30, 971-987 (1999).
B. Harris, N. Gathercole, J. A. Lee, H. Reiter, and T. Adam, “Life prediction for constant-stress fatigue in carbon-fiber composites,” Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc. (Lond), A355, 1259−1294 (1997).
B. Harris, A Parametric Constant-Life Model for Prediction of the Fatigue Lives of Fiber-Reinforced Plastics. In: Fatigue in Composites /Ed. by B. Harris., Woodhead Publ. Ltd and CRC Press LLC, 546-567 (2003).
GOST 25.101-83. Methods for schematization of the random processes of loading of elements of machines and structures and of statistical representation of results, Moscow: Publishing house of standards, (1983).
T. Endo, et al., “Damage evaluation of metals for random or varying loading – Three Aspects of Rain Flow Method,” Proc., 1974 Symp. on Mech. Behavior of Mater., I, 371-380 (1974).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Mekhanika Kompozitnykh Materialov, Vol. 52, No. 4, pp. 645-664, July-August, 2016.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Strizhius, V. Fatigue Damage Accumulation Under Quasi-Random Loading of Composite Airframe Elements. Mech Compos Mater 52, 455–468 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11029-016-9597-9
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11029-016-9597-9