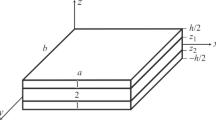
The vibration and buckling behavior of hybrid composite plates with a general state of nonuniform initial stress in thermal environments are investigated. Governing equations including the effects of transverse shear deformation are established using the energy variation method. The initial stress is taken to be a combination of uniaxial extension and pure bending stresses. The temperature distribution in the hybrid plate is assumed to be a combined uniform and linear temperature change in the transverse direction. An example problem on an initially and thermally stressed laminated plate is solved. The effects of various parameters on the thermal induced vibration and stability of hybrid composite plates are studied. The natural frequency and buckling load are found to be sensitive to the thickness ratio of Al to CRFP layers, the state of initial stresses, and temperature rise.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. M. Jones, “Thermal buckling of uniformly heated unidirectional and symmetric cross-ply laminated fiber-reinforced composite uniaxial in-plane restrained simply supported rectangular plates,” Composites: Part A, Appl. Sci. Manuf., 36, 1355–1367 (2005).
H. Matsunaga, “Thermal buckling of angle-ply laminated composite and sandwich plates according to a global higherorder deformation theory,” Compos. Struct., 72, 177–192 (2006).
H. R. H. Kabir, M. A. M. Hamad, and M. J. John, “Thermal buckling response of all-edge clamped rectangular plates with symmetric angle-ply lamination,” Compos. Struct., 79, 148–155 (2007).
V. Pradeep and N. Ganesan, “Thermal buckling and vibration behavior of multi-layer rectangular viscoelastic sandwich plates,” J. Sound Vibr., 310, 169–183 (2008).
A. Owhadi and B. S. Shariat, “Stability analysis of symmetric laminated composite plates with geometric imperfections under longitudinal temperature gradient,” J. Mech., 25, 161–165 (2009).
A. Lal and B. N. Singh, “Stochastic free vibration of laminated composite plates in thermal environments,” J Thermoplas. Compos. Mat., 23, 57–77 (2010).
S. H. Lo, W. Zhen, Y. K. Cheung, and C. Wanji, “Hygrothermal effects on multilayered composite plates using a refined higher order theory,” Compos. Struct., 92, 633–646 (2010).
Z. A. Rasid, A. Ayob, R. Zahari, F. Mustapha, D. L. Majid, and R. Varatharajoo, “Thermal buckling and post-buckling improvements of laminated composite plates using finite element method,” Key Eng. Mat., 471, 536–541 (2011).
X. Chang, Z. Liang, and Q. Liu, “Buckling and post-buckling analysis of symmetrically angle-ply laminated composite beams under thermal environments,” Adv. Mat. Res., 335, 182–186 (2011).
A. Yapici, “Thermal buckling behavior of hybrid-composite angle-ply laminated plates with an inclined crack,” Mech. Compos. Mat., 41,131-138 (2005).
A. Avci, O. S. Sahin, and M. Uyaner, “Thermal buckling of hybrid laminated composite plates with a hole,” Compos. Struct., 68, 247–254 (2005).
A. Avci, O. S. Sahin, and N. Ataberk, “Thermal buckling behavior of cross-ply hybrid composite laminates with inclined crack,” Compos. Sci. Technol., 66, 2965–2970 (2006).
H. H. Ibrahim, M. Tawfik, and H. M. Negm, “Thermoacoustic random response of shape memory alloy hybrid composite plates,” J. Aircraft, 45, 962–970 (2008).
H. H. Ibrahim, H. H. Yoo, and K. S. Lee, “Thermal buckling and flutter behavior of shape memory alloy hybrid composite shells,” J. Aircraft, l. 46, 895–902 (2009).
S. K. Panda and B N Singh, “Thermal post-buckling analysis of a laminated composite spherical shell panel embedded with shape memory alloy fibres using non-linear finite element method,” J. Mech. Eng. Sci., 224, 757–769 (2010).
Z. A. Rasid, A. Ayob, R. Zahari, D. L. Majid, and A. S. M. Rafie, “Thermal post-buckling of shape memory alloy composite plates under non-uniform temperature distribution,” Engineering and Technology, 56, 1465–1470 (2011).
A. H. Akbarzadeh, M. Abbasi, S. K. Hosseini zad, and M. R. Eslami, “Dynamic analysis of functionally graded plates using the hybrid Fourier-Laplace transform under thermomechanical loading,” Meccanica, 46, 1373–1392 (2011).
C. S. Chen, C. Y. Lin, and R. D. Chien, “Thermally induced buckling of functionally graded hybrid composite plates,” Int. J. Mech. Sci., 53, 51–58 (2011).
C. S. Chen, W. R. Chen, and R. D. Chien, “Stability of parametric vibrations of hybrid laminated plates,” Eur. J. Mech. A/Solids, 28, 329–337 (2009).
C. S. Chen, C. P. Fung, and J. G. Yang, “Assessment of plate theories for initially stressed hybrid laminated plates,” Compos. Struct., 88, 195–201 (2009).
E. J. Brunell and S. R. Robertson, “Initially stressed mindlin plates,” AIAA J., 12, 1036–1045 (1974).
H. Matsunaga “Thermal buckling of cross-ply laminated composite and sandwich plates according to a global higher order deformation theory,” Compos. Struct., 68, 439–454 (2005).
C. F. Liu and C. H. Huang “Free vibration of composite laminated plates subjected to temperature changes,” Comput. Struct., 60, 95–101 (1996)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Russian translation published in Mekhanika Kompozitnykh Materialov, Vol. 50, No. 5, pp. 811–828 , September-October, 2014.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsai, T.C., Chen, C.S., Fung, C.P. et al. Thermally Induced Vibration and Stability of Initially Stressed Hybrid Composite Plates. Mech Compos Mater 50, 579–592 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11029-014-9446-7
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11029-014-9446-7