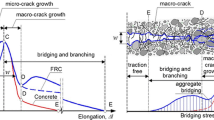
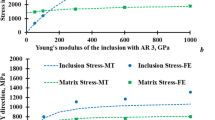
The overall elastic moduli of fiber-reinforced concrete composite materials are investigated by employing the theory of micromechanics. A method based on the Mori–Tanaka theory and triple inhomogeneities is found to provide a sufficiently accurate evaluation of the average elastic properties of fiber-reinforced concrete composite materials. The inhomogeneities of the materials are divided into three groups: a fine aggregate, a coarse aggregate, and fibers (steel or polymer). The elastic moduli of fiber-reinforced concrete composite materials are determined as functions of the physical properties and volume fraction of sand, gravel, fibers (steel or polymer), and cement paste as a matrix. The theoretical results obtained are compared with published experimental data. The parameters affecting the elastic moduli of fiber-reinforced concrete are discussed in detail.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Hori and S. Nemat-Nasser, “Double-inclusion model and overall moduli of multi-phase composites,” Mech. Mater., 14, 189-206 (1993).
W. Voig, Über die Beziehung zwischen den beiden Elastizitātskonstanten isotroper Körper. Wied Ann; 38, 573-587 (1889).
A. Reuss, Berechnung der Fliessgrenze von Mischkrisallen auf Grund der Plastizitatsbedingung fur Einkristalle. Z. Angew. Math. Mech., No. 9, 49-58 (1929).
Z. Hashin and S. Shtrikman, “A variational approach to the elastic behavior of multiphase materials,” J. Mech. Phys. Solids, 11, 127-240 (1963).
T. Mori and K. Tanaka, “Average stress in matrix and average elastic energy of materials with misfitting inclusions,” Acta Metallurgica, No. 21, 571-574 (1973).
J. D. Eshelby, “The determination of the elastic field of an ellipsoidal inclusion, and related problems,” Proc. Roy. Soc. Lond., 241. 376-392 (1957).
T. Mura, Micromechanics of Defects in Solids. Second Revised Edition. Martinus Nijhoff Publishers, 1987.
R. M. Christensen, “A critical evaluation for a class of micro-mechanics models,” J. Mech. Phys. Solids, 38, 379-404 (1990).
A. Lutfi, Steel Fibrous Cement Based Composites, Ph.D. Thesis, Sweden Royal Institute of Technology, 2004.
S. Ahmed and F. R. Jones, “A review of particulate reinforcement theories for polymer composites,” J. Mater. Sci., 25, 4933-4942 (1990).
M. Anson and K. Newman, “The effect of mix proportions and method of testing on Poisson’s ratio for mortars and concretes,” Magazine of Concrete Research, 18, No. 1, 115-130 (1966).
P. Simeonov and S. Ahmad, “Effect of transition zone on the elastic behaviour of cement-based compositesm,” Cement and Concrete Research, 25, No. 1, 165-176 (1995)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Russian translation published in Mekhanika Kompozitnykh Materialov, Vol. 50, No. 4, pp. 715-726, July-August, 2014.
Appendix
Appendix
The explicit expression needed to calculate the tensors used in the text are as follows:
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huan, Y.J., Yang, L., Jin, Y. et al. Micromechanics Solution for the Elastic Moduli of Fiber-Reinforced Concrete. Mech Compos Mater 50, 515–522 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11029-014-9438-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11029-014-9438-7