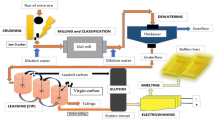
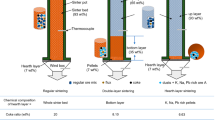
Features of gold cementation from cyanide solutions with electrolytic zinc powder are studied. The test powders are prepared by electro-extraction of alkaline solutions after leaching zinc-containing dust. Cementation is conducted in two regimes: under pressure (Merrill–Crowe process) and a fluidized bed regime. It is established that with respect to degree of gold extraction and specific consumption of test dendritic powder it is no worse or surpasses powders prepared by vapor condensation used traditionally in the gold extraction industry. The features established may be explained by physical features of powders prepared by electro-extraction from alkaline solutions.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Frenay, J. Hissel, and S. Ferlay, “Recovery of lead and zinc from electric steelmaking furnace dusts by the Cebedeau process,” in: Recycle and Secondary Recovery of Metals, TMS, Warrendale, PA (1985).
R. Chairaksa-Fujimoto, K. Maruyama, T. Miki, and T. Nagasaka, “The selective alkaline leaching of zinc oxide from electric arc furnace dust pre-treated with calcium oxide,” Hydrometallurgy, 159, 120–125 (2016).
Z. Q. Xie, Y. F. Guo, T. Jiang, et al., “The extraction of zinc from zinc ferrite by calcified-roasting and ammonia-leaching process,” in: 8th Int. Symp. on High-Temperature Metallurgical Processing, San Diego (2017).
J. A. Stegemann, A. Roy, and R. J. Caldwell, “Understanding environmental leachability of electric arc furnace dust,” J. Environ. Eng. (ASCE), 126, 112–120 (2000).
S. A. Yakornov, A. M. Pan’shin, P. A. Kozlov, and D. A. Ivakin, “Contemporary state of technology for leaching ferrous metallurgy dust and products of their pyrometallurgical treatment (acid, aluminum, and alkali technologies),” Tsvet. Met., No. 5, 37–43 (2017).
Y. I. Rubtsov, I. O. Shnel’, V. P. Myazin, et al., RF Patent 2198232, МPK C22B11/00. Method for Gold Precipitation and Device for Its Accomplishment, Claim 02.19.2001, Publ. 02.10.2003.
A. Stavart, C. Leroy, and A. Van Lierde, “Potential use of carbon felt in gold hydrometallurgy,” Miner. Eng., 12, No. 5, 545–558 (1999).
L. A. D. Barbosa, L. G. S. Sobral, and A. J. B. Dutra, “Gold electrowinning from diluted cyanide liquors: Performance evaluation of different reaction systems,” Miner. Eng., 14, No. 9, 963–974 (2001).
Yu. N. Rubtsov, P. M. Pavlov, and A. A. Mamul, RF Patent 2248413, МPK С25С7/02. Device for Gold Electrolysis from Production Cyanide Solutions, Claim 08.13.2002, Publ. 03.20.2005.
E. A. Kaplina, et al., “Effect of the nature of reducing agent on degree of metal extraction,” Proc. IX All-Russia Sci.-Tech. Conf. of Students, Aspirants, and Young Scientists with Internat. Participation Devoted to 385 Anniv. Of the Foundation of Krasnoyarsk, SibFRU, Krasnoyarsk (2013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Metallurg, Vol. 62, No. 5, pp. 50–55, May 2018.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yakornov, S.A., Naumov, K.D., Lobanov, V.G. et al. Use of Electrolytic Zinc Powder for Cementation of Gold from Cyanide Solutions. Metallurgist 62, 456–463 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11015-018-0681-3
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11015-018-0681-3