Abstract
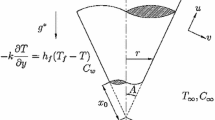
The paper studies the problem of free convection about a vertical frustum of a cone in a micropolar fluid. It is assumed that the flow is laminar, steady and the wall is subjected to a constant heat flux and the angle of the frustum of the cone is large enough so that the transverse curvature effects are negligible. Under these assumptions, the governing boundary layer equations subject to appropriate boundary conditions are transformed into a set of equations of parabolic type, that are solved using the local non-similarity method. The space of parameters contains the Prandtl number Pr, the micropolar parameter Δ and the microrotation parameter n. Numerical solutions are obtained by varying Pr from 6.7 to 100, Δ from 0 (Newtonian fluid) to 2 and considering two values of n with physical significance (0 and 0.5). Flow and heat transfer characteristics are determined and are shown in graphs. The results are discussed and compared at some extent with those reported by the present author in a previous study (Postelnicu in Int. J. Eng. Sci. 44:672–682, 2006) on the isothermal case.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eringen AC (1964) Simple microfluids. Int J Eng Sci 2:205–217
Eringen AC (1966) Theory of micropolar fluids. J Math Mech 16:1–18
Ariman T, Turk MA, Sylvester ND (1973) Microcontinuum fluid mechanics—a review. Int J Eng Sci 11:905–930
Ariman T, Turk MA, Sylvester ND (1974) Application microcontinuum fluid mechanics. Int J Eng Sci 12:273–293
Lukaszewicz G (1999) Micropolar fluids: theory and applications. Birkhauser, Basel
Eringen AC (2001) Microcontinuum field theories II. Fluent media. Springer, New-York
Peddieson J, McNitt RP (1970) Boundary layer theory for micropolar fluid. Recent Adv. Eng. Sci. 5:405–426
Wilson AJ (1970) Boundary layers in micropolar fluids. Proc Camb Philol Soc 67:460–476
Na T-Y, Chiou JP (1979) Laminar natural convection over a frustum of a cone. Appl Sci Res 35:409–421
Singh P, Radhakrishnan V, Narayan KA (1989) Natural convection flow over a vertical frustum of a cone for constant wall heat flux. Appl Sci Res 46:335–345
Pop I, Na T-Y (1999) Natural convection over a vertical wavy frustum of a cone. Int J Non-Linear Mech 34:925–934
Pop I, Na T-Y (1999) Laminar flow due to rotating frustum of a cone. Appl Mech Eng 4:113–120
Gorla RSR, Takhar HS (1987) Free convection boundary-layer flow of a micropolar fluid past slender bodies. Int J Eng Sci 25:949–962
Gorla RSR, Nakamura S (1995) Mixed convection of a micropolar fluid from a rotating cone. Int J Heat Fluid Flow 16:69–73
Abo-Eldahab E, El Aziz A (2004) Hall current and ohmic heating effects on mixed convection boundary layer flow of a micropolar fluid from a rotating cone with power-law variation in surface temperature. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf 31:751–762
Postelnicu A (2006) Free convection about a vertical frustum of a cone in a micropolar fluid. Int J Eng Sci 44:672–682
Cheng C-Y (2008) Natural convection of a micropolar fluid from a vertical truncated cone with power-law variation in temperature. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf 35:39–46
Cheng C-Y (2010) Double diffusion from a vertical truncated cone in a non-Newtonian fluid saturated porous medium with variable heat and mass fluxes. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf 37:261–265
Jena SK, Mathur MN (1991) Similarity solutions for laminar free convective flow of a thermomicropolar fluid past a nonisothermal vertical plate. Int J Eng Sci 19:1431–1439
Ahmadi G (1976) Self-similar solution of incompressible micropolar boundary layer flow over a semi-infinite plate. Int J Eng Sci 14:639–646
Peddieson J (1972) An application of the micropolar fluid model to the calculation of turbulent shear flow. Int J Eng Sci 10:23–32
Sparrow EM, Quack H, Boerner CJ (1970) Local non-similarity boundary layer solutions. AIAA J 8:1936–1942
Sparrow EM, Yu MS (1971) Local nonsimilarity thermal boundary-layer solutions. J Heat Transf 93:328–332
Hossain MA, Vafai K, Khanafer K (1999) Non-Darcy natural convection heat and mass transfer along a vertical permeable cylinder embedded in a porous medium. Int J Therm Sci 38:854–862
Maple 8.00 (2002) Waterloo Maple Inc
Gorla RSR, Takhar HS, Slaouti A (1998) Magnetohydrodynamic free convection boundary layer flow of a thermomicropolar fluid over a vertical plate. Int J Eng Sci 36:315–327
Acknowledgements
The anonymous reviewers are gratefully acknowledged for their constructive comments and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Postelnicu, A. Free convection from a truncated cone subject to constant wall heat flux in a micropolar fluid. Meccanica 47, 1349–1357 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11012-011-9518-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11012-011-9518-x