Abstract
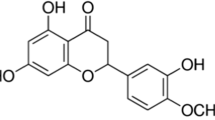
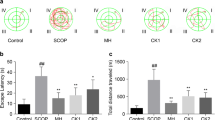
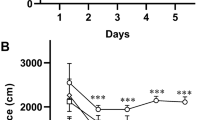
Neuroinflammation is a critical feature in the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Hesperetin can exert anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and other neuroprotective effects. In this study, the scopolamine (SCOP)-induced cognitive dysfunction in mice model was used to evaluate the neuroprotective effects of hesperetin. Behavioral tests (Morris water maze, open field, and novel object recognition tests) were conducted to evaluate the effect of hesperetin on cognitive dysfunction behaviors. Nissl staining and Immunofluorescence were used to evaluate hippocampal neuronal damage and microglial activation in mice. The levels of proinflammatory factors, oxidant stress, and the cholinergic neurotransmitter were detected by real-time quantitative fluorescence PCR (RT-qPCR) or biochemical reagent kits. Western blotting was used to detect the relative protein expression of the sirtuin 6 (SIRT6) / NOD-like receptor thermal protein domain associated protein 3 (NLRP3) pathway. Results showed that hesperetin could ameliorate SCOP-induced cognitive impairment and neuronal damage, and regulate the levels of cholinergic neurotransmitters in the hippocampal of AD mice. Hesperetin could also enhance antioxidant defense by regulating the levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS), malondialdehyde (MDA), superoxide dismutase (SOD), and catalase (CAT). Hesperetin exerted anti-neuroinflammation effects through inhibiting of microglia activation and down-regulating the mRNA transcript levels of inflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6), interleukin-1β (IL-1β), cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS). Meanwhile, hesperetin could attenuate the expression of NLRP3, apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD (ASC), thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP), and caspase-1 p20 and upregulate the expression of SIRT6 in SCOP-induced mice. Overall, our study suggested that hesperetin might ameliorate SCOP-induced cognitive dysfunction by improving cholinergic system dysfunction and suppressing oxidative stress and attenuating neuroinflammation via SIRT6/NLRP3 pathway in mice.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data sets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Abbate A, Toldo S, Marchetti C, Kron J, Van Tassell BW, Dinarello CA (2020) Interleukin-1 and the Inflammasome as therapeutic targets in Cardiovascular Disease. Circ Res 126(9):1260–1280. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.315937
Alzheimer’s Disease International (2021) World Alzheimer’s Report 2021. https://www.alzint.org/resource/world-alzheimer-report-2021/
Alzhermer’sAssociation (2022) 2022 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement 18(4):700–789. https://doi.org/10.1002/alz.12638
Anand P, Singh B (2013) A review on cholinesterase inhibitors for Alzheimer’s disease. Arch Pharm Res 36(4):375–399. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-013-0036-3
Baek HS, Hong VS, Kim SH, Lee J, Kim S (2021) KMU-1170, a novel multi-protein kinase inhibitor, suppresses Inflammatory Signal Transduction in THP-1 cells and Human Osteoarthritic Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes by suppressing activation of NF-kappaB and NLRP3 Inflammasome Signaling Pathway. Int J Mol Sci 22(3). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031194
Boon BDC, Hoozemans JJM, Lopuhaa B, Eigenhuis KN, Scheltens P, Kamphorst W, Rozemuller AJM, Bouwman FH (2018) Neuroinflammation is increased in the parietal cortex of atypical Alzheimer’s disease. J Neuroinflammation 15(1):170. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-018-1180-y
Campbell NL, Perkins AJ, Gao S, Skaar TC, Li L, Hendrie HC, Fowler N, Callahan CM, Boustani MA (2017) Adherence and tolerability of Alzheimer’s Disease Medications: a pragmatic Randomized Trial. J Am Geriatr Soc 65(7):1497–1504. https://doi.org/10.1111/jgs.14827
Chen Z, Zhong C (2014) Oxidative stress in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci Bull 30(2):271–281. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-013-1423-y
Choi EJ, Ahn WS (2008) Neuroprotective effects of chronic hesperetin administration in mice. Arch Pharm Res 31(11):1457–1462. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-001-2130-1
Collaborators G (2022) Estimation of the global prevalence of dementia in 2019 and forecasted prevalence in 2050: an analysis for the global burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Public Health 7(2):e105–e125. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2468-2667(21)00249-8
Coll RC, Robertson AA, Chae JJ, Higgins SC, Munoz-Planillo R, Inserra MC, Vetter I, Dungan LS, Monks BG, Stutz A, Croker DE, Butler MS, Haneklaus M, Sutton CE, Nunez G, Latz E, Kastner DL, Mills KH, Masters SL, Schroder K, Cooper MA, O’Neill LA (2015) A small-molecule inhibitor of the NLRP3 inflammasome for the treatment of inflammatory diseases. Nat Med 21(3):248–255. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.3806
de Teles A, Diniz RB, Costa Pinto TC, de Oliveira Junior TC, Gama RG, de Lavor ESM, Fernandes EM, de Oliveira AWC, de Almeida Ribeiro AP, da Silva FPR, Cavalcante AAM, Junior TCFQ, L.J. and da, Silva Almeida (2018) J.R.G. Flavonoids as Therapeutic Agents in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Diseases: A Systematic Review of Preclinical Evidences. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2018, https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/7043213
Feng YS, Tan ZX, Wu LY, Dong F, Zhang F (2020) The involvement of NLRP3 inflammasome in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Ageing Res Rev 64:101192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2020.101192
Ferreira-Vieira TH, Guimaraes IM, Silva FR, Ribeiro FM (2016) Alzheimer’s disease: targeting the Cholinergic System. Curr Neuropharmacol 14(1):101–115. https://doi.org/10.2174/1570159x13666150716165726
Hampel H, Mesulam MM, Cuello AC, Farlow MR, Giacobini E, Grossberg GT, Khachaturian AS, Vergallo A, Cavedo E, Snyder PJ, Khachaturian ZS (2018) The cholinergic system in the pathophysiology and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 141(7):1917–1933. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awy132
Hoozemans JJ, Rozemuller AJ, van Haastert ES, Eikelenboom P, van Gool WA (2011) Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease wanes with age. J Neuroinflammation 8:171. https://doi.org/10.1186/1742-2094-8-171
Hwang SL, Lin JA, Shih PH, Yeh CT, Yen GC (2012) Pro-cellular survival and neuroprotection of citrus flavonoid: the actions of hesperetin in PC12 cells. Food Funct 3(10):1082–1090. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2fo30100h
Ikram M, Muhammad T, Rehman SU, Khan A, Jo MG, Ali T, Kim MO (2019) Hesperetin confers neuroprotection by regulating Nrf2/TLR4/NF-kappaB signaling in an Abeta Mouse Model. Mol Neurobiol 56(9):6293–6309. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-019-1512-7
Ishola IO, Jacinta AA, Adeyemi OO (2019) Cortico-hippocampal memory enhancing activity of hesperetin on scopolamine-induced amnesia in mice: role of antioxidant defense system, cholinergic neurotransmission and expression of BDNF. Metab Brain Dis 34(4):979–989. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-019-00409-0
Jiang C, Sun ZM, Hu JN, Jin Y, Guo Q, Xu JJ, Chen ZX, Jiang RH, Wu YS (2019) Cyanidin ameliorates the progression of osteoarthritis via the Sirt6/NF-kappaB axis in vitro and in vivo. Food Funct 10(9):5873–5885. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9fo00742c
Jiang H, He H, Chen Y, Huang W, Cheng J, Ye J, Wang A, Tao J, Wang C, Liu Q, Jin T, Jiang W, Deng X, Zhou R (2017) Identification of a selective and direct NLRP3 inhibitor to treat inflammatory disorders. J Exp Med 214(11):3219–3238. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20171419
Jia Y, Cui R, Wang C, Feng Y, Li Z, Tong Y, Qu K, Liu C, Zhang J (2020) Metformin protects against intestinal ischemia-reperfusion injury and cell pyroptosis via TXNIP-NLRP3-GSDMD pathway. Redox Biol 32:101534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2020.101534
Ju Y, Tam KY (2022) Pathological mechanisms and therapeutic strategies for Alzheimer’s disease. Neural Regen Res 17(3):543–549. https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.320970
Kaluski S, Portillo M, Besnard A, Stein D, Einav M, Zhong L, Ueberham U, Arendt T, Mostoslavsky R, Sahay A, Toiber D (2017) Neuroprotective functions for the histone deacetylase SIRT6. Cell Rep 18(13):3052–3062. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2017.03.008
Khan S, Barve KH, Kumar MS (2020) Recent advancements in Pathogenesis, Diagnostics and Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Curr Neuropharmacol 18(11):1106–1125. https://doi.org/10.2174/1570159X18666200528142429
Kheradmand E, Hajizadeh Moghaddam A, Zare M (2018) Neuroprotective effect of hesperetin and nano-hesperetin on recognition memory impairment and the elevated oxygen stress in rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. Biomed Pharmacother 97:1096–1101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.11.047
Lai MC, Liu WY, Liou SS, Liu IM (2022) The Citrus Flavonoid Hesperetin Encounters diabetes-mediated Alzheimer-Type Neuropathologic Changes through Relieving Advanced glycation end-products inducing endoplasmic reticulum stress. Nutrients 14(4). https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14040745
Li L, Zhang H, Chen B, Xia B, Zhu R, Liu Y, Dai X, Ye Z, Zhao D, Mo F, Gao S, Orekhov AN, Prentki M, Wang L, Guo S, Zhang D (2022) BaZiBuShen alleviates cognitive deficits and regulates Sirt6/NRF2/HO-1 and Sirt6/P53-PGC-1alpha-TERT signaling pathways in aging mice. J Ethnopharmacol 282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2021.114653
Liu PP, Xie Y, Meng XY, Kang JS (2019) History and progress of hypotheses and clinical trials for Alzheimer’s disease. Signal Transduct Target Ther 4:29. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-019-0063-8
Liu P, Zhou X, Zhang H, Wang R, Wu X, Jian W, Li W, Yuan D, Wang Q, Zhao W (2022) Danggui-Shaoyao-San attenuates cognitive impairment via the Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis with regulation of lipid metabolism in Scopolamine-Induced Amnesia. Front Immunol 13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.796542
Lu J, Holmgren A (2014) The thioredoxin antioxidant system. Free Radic Biol Med 66:75–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.07.036
Mangialasche F, Solomon A, Winblad B, Mecocci P, Kivipelto M (2010) Alzheimer’s disease: clinical trials and drug development. Lancet Neurol 9(7):702–716. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(10)70119-8
More SV, Kumar H, Cho DY, Yun YS, Choi DK (2016) Toxin-Induced Experimental Models of Learning and Memory Impairment. Int J Mol Sci 17(9). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17091447
Paik S, Kim JK, Silwal P, Sasakawa C, Jo EK (2021) An update on the regulatory mechanisms of NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Cell Mol Immunol 18(5):1141–1160. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41423-021-00670-3
Parhiz H, Roohbakhsh A, Soltani F, Rezaee R, Iranshahi M (2015) Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of the citrus flavonoids hesperidin and hesperetin: an updated review of their molecular mechanisms and experimental models. Phytother Res 29(3):323–331. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.5256
Pizzino G, Irrera N, Cucinotta M, Pallio G, Mannino F, Arcoraci V, Squadrito F, Altavilla D, Bitto A (2017) Oxidative Stress: Harms and Benefits for Human Health. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2017, https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/8416763
Salehi B, Cruz-Martins N, Butnariu M, Sarac I, Bagiu IC, Ezzat SM, Wang J, Koay A, Sheridan H, Adetunji CO, Semwal P, Schoebitz M, Martorell M, Sharifi-Rad J (2022) Hesperetin’s health potential: moving from preclinical to clinical evidence and bioavailability issues, to upcoming strategies to overcome current limitations. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 62(16):4449–4464. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2021.1875979
Schetters STT, Gomez-Nicola D, Garcia-Vallejo JJ, Van Kooyk Y (2017) Neuroinflammation: Microglia and T cells get ready to Tango. Front Immunol 8:1905. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2017.01905
Shao J, Yang X, Liu T, Zhang T, Xie QR, Xia W (2016) Autophagy induction by SIRT6 is involved in oxidative stress-induced neuronal damage. Protein Cell 7(4):281–290. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13238-016-0257-6
Sies H (2015) Oxidative stress: a concept in redox biology and medicine. Redox Biol 4:180–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2015.01.002
Simpson DSA, Oliver PL (2020) ROS Generation in Microglia: understanding oxidative stress and inflammation in neurodegenerative disease. Antioxid (Basel) 9(8). https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9080743
Song MY, Yi F, Xiao H, Yin J, Huang Q, Xia J, Yin XM, Wen YB, Zhang L, Liu YH, Xiao B, Gu WP (2022) Energy restriction induced SIRT6 inhibits microglia activation and promotes angiogenesis in cerebral ischemia via transcriptional inhibition of TXNIP. Cell Death Dis 13(5). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-022-04866-x
Tang BL (2017) Is SIRT6 activity neuroprotective and how does it differ from SIRT1 in this regard? Front Cell Neurosci 11:165. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2017.00165
Tang KS (2019) The cellular and molecular processes associated with scopolamine-induced memory deficit: a model of Alzheimer’s biomarkers. Life Sci 233:116695. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2019.116695
Wang SW, Sheng H, Bai YF, Weng YY, Fan XY, Zheng F, Fu JQ, Zhang F (2021) Inhibition of histone acetyltransferase by naringenin and hesperetin suppresses txnip expression and protects pancreatic beta cells in diabetic mice. Phytomedicine 88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153454
Wan T, Wang Z, Luo Y, Zhang Y, He W, Mei Y, Xue J, Li M, Pan H, Li W, Wang Q, Huang Y (2019) FA-97, a New Synthetic Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester Derivative, Protects against Oxidative Stress-Mediated Neuronal Cell Apoptosis and Scopolamine-Induced Cognitive Impairment by Activating Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2019, https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/8239642
Wong W (2020) Economic burden of Alzheimer disease and managed care considerations. Am J Manag Care 26(8 Suppl):S177–S183. https://doi.org/10.37765/ajmc.2020.88482
Wu M, Zhu X, Zhang Y, Wang M, Liu T, Han J, Li J, Li Z (2021) Biological evaluation of 7-O-amide hesperetin derivatives as multitarget-directed ligands for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Chem Biol Interact 334:109350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2020.109350
Yang H, Wang Y, Xu S, Ren J, Tang L, Gong J, Lin Y, Fang H, Su D (2022) Hesperetin, a Promising Treatment option for diabetes and related complications: a Literature Review. J Agric Food Chem 70(28):8582–8592. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.2c03257
Zhang N, Gordon ML (2018) Clinical efficacy and safety of donepezil in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease in chinese patients. Clin Interv Aging 13:1963–1970. https://doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S159920
Zhou R, Tardivel A, Thorens B, Choi I, Tschopp J (2010) Thioredoxin-interacting protein links oxidative stress to inflammasome activation. Nat Immunol 11(2):136–140. https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.1831
Zhu WL, Zheng JY, Cai WW, Dai Z, Li BY, Xu TT, Liu HF, Liu XQ, Wei SF, Luo Y, Wang H, Pan HF, Wang Q, Zhang SJ (2020) Ligustilide improves aging-induced memory deficit by regulating mitochondrial related inflammation in SAMP8 mice. Aging 12(4):3175–3189. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.102793
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
The work was supported by the Key Laboratory Project for General Universities in Guangdong Province (No. 2019KSYS005), and Guangdong Province Science and Technology Plan International Cooperation Project (No.2020A0505100052).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SWJ, XCW, DDC, and ZRZ performed the experiment and prepared the manuscript; KLH, YTW, and ZZL helped with data acquisition and analysis; QW and SJS carried out the conception, and designed of the study, and performed manuscript review; All authors have read and approved the content of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing of interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval
The animal study was reviewed and approved by the Ethics committee member of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine (approval no. 20220617002).
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jing, S., Wang, X., Zhang, Z. et al. Hesperetin attenuates cognitive dysfunction via SIRT6/NLRP3 pathway in scopolamine-induced mice. Metab Brain Dis 38, 2443–2456 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-023-01250-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-023-01250-2