Abstract
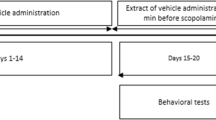
The blackberry (Rubus sp.) is a popular fruit that has a high concentration of phenolic compounds. Pharmacological investigations have demonstrated the important biological activities of the blackberry extract, such as neuroprotective actions. This study aimed to evaluate the effects of blackberry extract on memory and neurochemical parameters in rats subjected to scopolamine (SCO)-induced amnesia. Male rats were divided into five groups: I, control (saline); II, SCO; III, SCO + Rubus sp. (100 mg/kg); IV, SCO + Rubus sp. (200 mg/kg); and V, SCO + donepezil (5 mg/kg). Blackberry extract and donepezil were orally administered for 10 days. On day 11, group I received saline, and groups II, III, IV, and V received SCO (1 mg/kg) intraperitoneally after object recognition behavioral training. Twenty-four hours after the training session, animals were subjected to an object recognition test. Finally, the animals were euthanized, and the cerebral cortex, hippocampus, and cerebellum were collected to evaluate the oxidative stress and acetylcholinesterase (AChE) activity. Rubus sp. extract prevented memory impairment induced by SCO in a manner similar to that of donepezil. Additionally, Rubus sp. extract and donepezil prevented the increase in AChE activity induced by SCO in all the evaluated brain structures. SCO induced oxidative damage in the cerebral cortex, hippocampus, and cerebellum, which was prevented by Rubus sp. and donepezil. Our results suggest that the antioxidant and anticholinesterase activities of Rubus sp. are associated with memory improvement; hence, it can potentially be used for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases.
Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
References
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in Vitro Meth Enzymol 105:121–126
Aksenov MY, Markesbery WR (2001) Change in thiol content and expression of glutathione redox system gene in the hippocampus and cerebellum in Alzheimer´s disease. Neurosc Letters 302:141–145
Ali SF, Lebel CP, Bondy SC (1992) Reactive oxygen species formation as a biomarker of methylmercury and trimethyltin neurotoxicity. Neurotoxicol 13:637–648
Alle G, Barnad H, McColl R, Hester A, Fields J, Weiner M, Ringe W, Lipton A, Brooker M, McDonald E, Rubin C, Cullum M (2007) Reduced hippocampal functional connectivity in Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol 64:1482–1487. https://doi.org/10.1001/archneur.64.10.1482
Antunes L, Peres N (2013) Strawberry Production in Brazil and South America. Int J Fruit Sci 13:156–161
Atukeren P, Cengiz M, Yavuzer H, Gelizgen R, Altounoglu E, Oner S, Erdenen F, Yuceakin D, Derici H, Cakatay U, Uzun H (2017) The efficacy of donepezil administration on acetylcholinesterase activity and altered redox homeostasis in Alzheimer’s disease. Biomed Pharmacother 90:786–795. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.03.101
Bajo R, Pusil S, López M, Canuet L, Pereda E, Osipova D, Maestú F, Pekknen (2015) Scopolamine effects on functional brain connecetivity: a pharmacological model of Alzheimer Disease. Sci Rep 5:9748. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep0974
Bradford M (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein– dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Chaves V, Soares MS, Spohr L, Teixeira L, Vieira A, Constantino L, Dal Pizzol F, Lencina C, Spanevello RM, Freitas M, Simões CM, Reginatto F, Stefanello F (2020) Blackberry extract improves behavioral and neurochemical dysfunctions in a ketamine induced rats model of mania. Neurosci Lett 714:134566. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2019.134566
Chen Y (2018) Research Progress in the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Chin Med J 131:1618–1624
Chu LW (2012) Alzheimer´s disease: early diagnosis and treatment. Hong Kong Med J 18:228–237
Cosme F, Pinto T, Morais C, Bacelar E, Anjos R, Ferreira-Cardoso J, Oliveira I, Viela A, Gonçalvez B (2022) Red fruits composition and their health benefits – a review. Foods 11:644. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11050644
Daubeny H (1996) Brambles. Fruit Breeding 2:109–190
Ellman G, Courtney KD, Andres V, Featherstone RM (1961) A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7:88–95
Esterbauer H, Cheeseman K (1990) Determination of aldehydic lipid peroxidation products: malonaldehyde and 4-hydroxynonenal. Methods Enzymol 186:407–421
Fernandez AM, Torres-Aleman I (2012) The many faces of insulin-like peptide signalling in the brain. Nat Rev Neurosci 13:225–239
Floyd R, Hensley K (2022) Oxidative stress in brain aging: implications for therapeutics of neurodegenerative diseases. Neurobiol Aging 23:795–807. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0197-4580(02)00019-2
Folmer F, Basavaraju U, Jaspars M (2014) Anticancer effects of bioactive berry compounds. Phytochem Reviews 13:295–322
Golovinskaia O, Wang C (2021) Review of functional and pharmacological activities of berries. Molecules 26:3904. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26133904
Gutierres J, Carvalho F, Schetinger M, Agostinho P, Marisco P, Vieira J, Rosa M, Bohnert C, Rubin M, Morsch V, Spanevello R, Mazzanti C (2014) Neuroproctetive effect of anthocyanins on acetylcholinsterase activity and attenuation of scopolamine induced amnesia in rats. Int J Dev Neurosci 33:88–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2013.12.006
Haider S, Tabassum S, Perveen T (2016) Scopolamine -induced greater alterations in neurochemical profile and increased oxidative stress demonstrated a better model of dementia: a comparative study. Brain Res Bull 127:234–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2016.10.002
Hampel H, Mesulam M, Cuello A, Farlow M, Giacobini E, Grossberg GT, Khachaturian A, Vergallo A, cavedo E, Snyder P, Khachaturian Z, (2018) The colinergic system in the pathophysiology and treatment of Alzheimer´s disease. Brain 141:1917–1933. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awy132
Hicox H, Johson C, McGarry M, Marshall H, Ritchie C, Beek E, Roberts N, Starr J (2020) Mechanical property alterations across the cerebral cortex due to Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Commun 2:fcz049. https://doi.org/10.1093/braincomms/fcz049
Huang WC, Lin YS, Wang CY, Tsai CC, Tseng HC, Chen CL, Lu PJ, Chen PS, Qian L, Hong J, Lin C (2009) Glycogen synthase kinase-3 negatively regulates anti-inflammatory interleukin-10 for lipopolysaccharide-induced iNOS/NO biosynthesis and RANTES production in microglial cells. Immunology 128:275–286
Kasá P, Rakonczay Z, Gulya K (1997) The cholinergic system in Alzheimer´s disease. Progress Neurobiol 52:511–535. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0301-0082(97)00028-2
Kaume L, Howard L, Devareddy L (2012) The blackberry fruit: a review on its composition and chemistry, metabolism and bioavailability, and health benefits. J Agric Food Chem 60:5716–5727. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf203318p
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randal RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
McGleenon B, Dynan K, Passmore A (1999) Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors in Alzheimer´s disease. Br J Clin Pharmacol 48:471–480. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2125.1999.00026.x
Misra HP, Fridovich I (1972) The role of superoxide anion in the autoxidation of epinephrine and a simple assay for superoxide dismutase. J Biol Chem 247:3170–3175
Pacheco SM, Soares MSP, Gutierres JM, Gerzson MF, Carvalho FB, Azambuja JH, Schetinger MRC, Stefanello FM, Spanevello RM (2018) Anthocyanins as a potential pharmacological agent to manage memory deficit, oxidative stress and alterations in ion pump activity induced by experimental sporadic dementia of Alzheimer’s type. J Nutr Biochem 56:193–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnutbio.2018.02.014
Rao YL, Ganaraja B, Murlimanju BV, Joy T, Krishnamurthy A, Agrawal A (2022) Hippocampus and its involvement in Alzheimer’s disease: a review. 3 Biotech 12:55. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-022-03123-4
Saxena G, Singh S, Agrawal R, Nath C (2008) Effect of donepezil and tacrine on oxidative stress in intracerebral streptozotocin-induced model of dementia in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 581:283–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2007.12.009
Scheltens P, Strooper B, Kibipelto M, Chételat G, Teunissen C, Cummings J, Flier W (2021) Alzheimer´s Disease. Lancet 24:1577–1590. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32205-4
Schmahmann J (2016) Cerebellum in Alzheimer’s disease and frontotemporal dementia: not a silent bystander. Brain 139:1314–1318. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/aww064
Sharma K (2019) Cholinesterase Inhibitors as Alzheimer´s therapeutics (review). Mol Med Rep 20:1479–1487. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2019.10374
Shukitt-Hale B, Cheng V, Joseph J (2009) Effects of blackberries on motor and cognitive function in aged rats. Nutr Neurosci 12:135–140. https://doi.org/10.1179/147683009X423292
Soares MSP, Luduvico K, Chaves V, Sophr L, Meine B, Lencina CL, Reginatto F, Spanevello RM, Simões CMO, Stefanello FM (2021) The proctetive action of Rubus sp. fruit extract against oxidative damage in mice exposed to lipopolysaccharide. Neurochem Res 46:1129–1140. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-021-03248-7
Spohr L, Soares MSP, Oliveira PS, da Silveira de Mattos B, Bona NP, Pedra NS, Teixeira FC, do Couto CAT, Chaves VC, Reginatto FH, Lisboa MT, Ribeiro AS, Lencina CL, Stefanello FM, Spanevello RM (2019) Combined actions of blueberry extract and lithium on neurochemical changes observed in an experimental model of mania: exploiting possible synergistic effects. Metab Brain Dis 34:605–619. https://doi.org/10.1016/10.1007/s11011-018-0353-9
Sukprasansap M, Chanvorachote P, Tencomnao (2020) Cyanidin-3-glucoside activates Nrf2-antioxidant response element and protects against glutamate-induced oxidative and endoplasmic reticulum stress in HT22 hippocampal neuronal cells. BMC Complement. Med Ther 20:46. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12906-020-2819-7
Tatar M, Bagheri Z, Varedi M, Naghibalhossaini F (2019) Blackberry extract inhibits teleomerase activity in human colorectal cancer cells. Nutr Cancer 71:461–471. https://doi.org/10.1080/01635581.2018.1506491
Tavares L, Figueira I, Macedo D, Mcdougall G, Leitão M, Vieira H, Stewart D, Alves P, Ferreira RB, Santos CN (2012) Neuroprotective effect of blackberry (Rubus sp.) polyphenols is potentiated after simulated gastrointestinal digestion. Food Chem 131:1443–1452
Teixeira FC, Gutierres JM, Soares MSP, Mattos B, Spohr L, Couto CAT, Bona N, Assmann C, Morsch VM, Cruz IBM, Stefanello FM, Spanevello RM (2020) Inosine protects against impairment of memory induced by experimental model of Alzheimer disease: a nucleoside with multitarget brain actions. Psychopharmacol 237:811–823. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-019-05419-5
Velde FV, Esposito D, Grace M, Pirovani M, Lila M (2019) Anti-inflammatory and woud healing properties of polyphenolic extract from strawberry and blackberry fruits. Food Res Int 121:453–462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2018.11.059
Wang S, Lin H (2000) Antioxidant activity in fruits and leaves of blackberry, raspberry, and strawberry varies with cultivar and developmental stage. J Agric Food Chem 48:140–146. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf9908345
Xie P, Zhang Y, Wang X, Wei X, Kang W (2017) Antithrombotic effect and mechanism of Rubus spp. Blackberry Food Funct 24:2000–2012. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6fo01717g
Yagi S, Galea L (2019) Sex differences in hippocampal cognition and neurogenesis. Neuropsychopharmacology 44:200–213. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41386-018-0208-4
Zhu X, Su B, Wang X, Smith M, Perry G (2007) Causes of oxidative stress in Alzheimer disease. Cell Mol Life Sci 64:2002–2210
Zhu D, Montagne A, Zhao Z (2021) Alzheimer’s pathogenic mechanisms and underlying sex difference. Cell Mol Life Sci 78:4907–4920. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-021-03830-w
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq), Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Rio Grande do Sul (FAPERGS), and Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES) for financial support. We would like to thank Editage (www.editage.com) for English language editing.
Funding
This research was supported by the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) and Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Rio Grande do Sul (FAPERGS). This study was financed, in part, by Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior- Brasil (CAPES)—Finance code 001. R.M.S is a recipient of the CNPq fellowship (310472/2021–0).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Material preparation was performed by Julia Eisenhardt de Mello, Juliane Cardoso, Wilson Cunico, and Marcia Vizzotto. Data collection and analysis was performed by Julia Eisenhardt de Mello, Karina Pereira Luduvico, Alessandra dos Santos, Fernanda Cardoso Teixeira, and Mayara Sandrielly Soares de Aguiar. Francieli Moro Stefanello and Roselia Maria Spanevello contributed to study conception, design, manuscript preparation and financial support. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Julia Eisenhardt de Mello and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethics approval
All animal experiments were carried out in accordance with the National Institutes of Health Guidelines for Care and Use of Laboratory Animals and approved by the Ethics Committee on the Use of Animals of the Federal University of Pelotas (protocol number: 027350/2021–12).
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
de Mello, J.E., Luduvico, K.P., dos Santos, A. et al. Therapeutic potential of blackberry extract in the preventing memory deficits and neurochemical alterations in the cerebral cortex, hippocampus and cerebellum of a rat model with amnesia. Metab Brain Dis 38, 1261–1272 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-023-01175-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-023-01175-w