Abstract
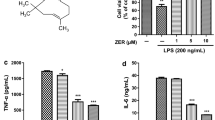
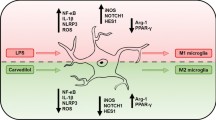
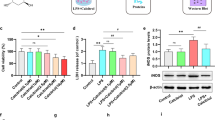
Microglial activation is a key event in neuroinflammation, which, in turn, is a central process in neurological disorders. In this study, we investigated the protective effects of D-beta-hydroxybutyrate (BHB) against microglial activation in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-treated mice and BV-2 cells. The effects of BHB in mice were assessed using behavioral testing, morphological analysis and immunofluorescence labeling for the microglial marker ionizing calcium-binding adaptor molecule 1 (IBA-1) and the inflammatory cytokine interleukin-6 (IL-6) in the hippocampus. Moreover, we examined the levels of the inflammatory IL-6 and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), as well as those of the neuroprotective brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) in the brain. In addition, we examined the effects of BHB on IL-6, TNF-α, BDNF, TGF-β, reactive oxygen species (ROS) level and cell viability in LPS-stimulated BV-2 cells. BHB treatments attenuated behavioral abnormalities, reduced the number of IBA-1-positive cells and the intensity of IL-6 fluorescence in the hippocampus, with amelioration of microglia morphological changes in the LPS-treated mice. Furthermore, BHB inhibited IL-6 and TNF-α generation, but promoted BDNF and TGF-β production in the brain of LPS-treated mice. In vitro, BHB inhibited IL-6 and TNF-α generation, increased BDNF and TGF-β production, reduced ROS level, ameliorated morphological changes and elevated cell viability of LPS-stimulated BV-2 cells. Together, our findings suggest that BHB exerts protective effects against microglial activation in vitro and in vivo, thereby reducing neuroinflammation.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The article contains all essential data. All the data and material from this study are available upon reasonable request through the corresponding author.
Change history
04 January 2023
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-022-01156-5
References
Benito A, Hajji N, O’Neill K, Keun HC, Syed N (2020) β-Hydroxybutyrate oxidation promotes the accumulation of immunometabolites in activated microglia cells. Metabolites 10(9):346
Chriett S, Dąbek A, Wojtala M, Vidal H, Balcerczyk A, Pirola L (2019) Prominent action of butyrate over β-hydroxybutyrate as histone deacetylase inhibitor, transcriptional modulator and anti-inflammatory molecule. Sci Rep 9(1):742
Fernando KKM, Wijayasinghe YS (2021) Sirtuins as potential therapeutic targets for mitigating neuroinflammation associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Front Cell Neurosci 15:746631
Field R, Field T, Pourkazemi F, Rooney K (2022) Low-carbohydrate and ketogenic diets: a scoping review of neurological and inflammatory outcomes in human studies and their relevance to chronic pain. Nutr Res Rev 19:1–71
Fu SP, Wang JF, Xue WJ, Liu HM, Liu BR, Zeng YL, Li SN, Huang BX, Lv QK, Wang W, Liu JX (2015) Anti-inflammatory effects of BHBA in both in vivo and in vitro Parkinson’s disease models are mediated by GPR109A-dependent mechanisms. J Neuroinflammation 12:9
Getachew B, Csoka AB, Bhatti A, Copeland RL, Tizabi Y (2020) Butyrate protects against salsolinol-induced toxicity in SH-SY5Y cells: implication for Parkinson’s disease. Neurotox Res 38(3):596–602
Getachew B, Csoka AB, Garden AR, Copeland RL, Tizabi Y (2021) Sodium butyrate protects against ethanol-induced toxicity in SH-SY5Y cell line. Neurotox Res 39(6):2186–2193
Han YM, Ramprasath T, Zou MH (2020) β-hydroxybutyrate and its metabolic effects on age-associated pathology. Exp Mol Med 52(4):548–555
Hu E, Du H, Shang S, Zhang Y, Lu X (2020) Beta-hydroxybutyrate enhances BDNF expression by increasing H3K4me3 and decreasing H2AK119ub in hippocampal neurons. Front Neurosci 14:591177
Huang J, Chai X, Wu Y, Hou Y, Li C, Xue Y, Pan J, Zhao Y, Su A, Zhu X, Zhao S (2022) β-Hydroxybutyric acid attenuates heat stress-induced neuroinflammation via inhibiting TLR4/p38 MAPK and NF-κB pathways in the hippocampus. FASEB J 36(4):e22264
Ji L, He Q, Liu Y, Deng Y, Xie M, Luo K, Cai X, Zuo Y, Wu W, Li Q, Zhou R, Li T (2022) Ketone body β-hydroxybutyrate prevents myocardial oxidative stress in septic cardiomyopathy. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2022:2513837
Kolb H, Kempf K, Röhling M, Lenzen-Schulte M, Schloot NC, Martin S (2021) Ketone bodies: from enemy to friend and guardian angel. BMC Med 19(1):313
Kong G, Liu J, Li R, Lin J, Huang Z, Yang Z, Wu X, Huang Z, Zhu Q, Wu X (2021) Ketone metabolite β-hydroxybutyrate ameliorates inflammation after spinal cord injury by inhibiting the NLRP3 inflammasome. Neurochem Res 46(2):213–229
Kumar A, Kumari S, Singh D (2022) Insight into the cellular interactions and molecular mechanisms of ketogenic diet for comprehensive management of epilepsy. Curr Neuropharmacol 20(11):2034–2049
Li B, Yu Y, Liu K, Zhang Y, Geng Q, Zhang F, Li Y, Qi J (2021a) β-Hydroxybutyrate inhibits histone deacetylase 3 to promote claudin-5 generation and attenuate cardiac microvascular hyperpermeability in diabetes. Diabetologia 64(1):226–239
Li Z, Zhang S, Zhang Y, Chen J, Wu F, Liu G, Chen GQ (2021b) Applications and mechanism of 3-hydroxybutyrate (3HB) for prevention of colonic inflammation and carcinogenesis as a food supplement. Mol Nutr Food Res 65(24):e2100533
Lilamand M, Mouton-Liger F, Di Valentin E, Sànchez Ortiz M, Paquet C (2022) Efficacy and safety of ketone supplementation or ketogenic diets for Alzheimer’s disease: a mini review. Front Nutr 8:807970
Margolis LM, O’Fallon KS (2020) Utility of ketone supplementation to enhance physical performance: a systematic review. Adv Nutr 11(2):412–419
McFarland KN, Chakrabarty P (2022) Microglia in Alzheimer’s disease: a key player in the transition between homeostasis and pathogenesis. Neurotherapeutics 19(1):186–208
Medrano-Jiménez E, Meza-Sosa KF, Urbán-Aragón JA, Secundino I, Pedraza-Alva G, Pérez-Martínez L (2022) Microglial activation in Alzheimer’s disease: The role of flavonoids and microRNAs. J Leukoc Biol 112(1):47–77
Nasser S, Vialichka V, Biesiekierska M, Balcerczyk A, Pirola L (2020) Effects of ketogenic diet and ketone bodies on the cardiovascular system: Concentration matters. World J Diabetes 11(12):584–595
Norgren J, Daniilidou M, Kåreholt I, Sindi S, Akenine U, Nordin K, Rosenborg S, Ngandu T, Kivipelto M, Sandebring-Matton A (2021) Serum proBDNF is associated with changes in the ketone body β-hydroxybutyrate and shows superior repeatability over mature BDNF: secondary outcomes from a cross-over trial in healthy older adults. Front Aging Neurosci 13:716594
Norwitz NG, Jaramillo JG, Clarke K, Soto A (2020) Ketotherapeutics for neurodegenerative diseases. Int Rev Neurobiol 155:141–168
Pérez-Liébana I, Casarejos MJ, Alcaide A, Herrada-Soler E, Llorente-Folch I, Contreras L, Satrústegui J, Pardo B (2020) βOHB protective pathways in Aralar-KO neurons and brain: an alternative to ketogenic diet. J Neurosci 40(48):9293–9305
Poff AM, Rho JM, D’Agostino DP (2019) Ketone administration for seizure disorders: history and rationale for ketone esters and metabolic alternatives. Front Neurosci 13:1041
Qi H, Gu L, Xu D, Liu K, Zhou M, Wang Y, Wang X, Li Y, Qi J (2021) β-Hydroxybutyrate inhibits cardiac microvascular collagen 4 accumulation by attenuating oxidative stress in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats and high glucose treated cells. Eur J Pharmacol 899:174012
Qiao G, Lv T, Zhang M, Chen P, Sun Q, Zhang J, Li Q (2020) β-hydroxybutyrate (β-HB) exerts anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated macrophages in Liza haematocheila. Fish Shellfish Immunol 107(Pt B):444–451
Sánchez-Sarasúa S, Fernández-Pérez I, Espinosa-Fernández V, Sánchez-Pérez AM, Ledesma JC (2020) Can we treat neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease? Int J Mol Sci 21(22):8751
Saha S, Buttari B, Profumo E, Tucci P, Saso L (2022) A perspective on Nrf2 signaling pathway for neuroinflammation: a potential therapeutic target in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. Front Cell Neurosci 15:787258
Saxena S, Kruys V, Vamecq J, Maze M (2021) The role of microglia in perioperative neuroinflammation and neurocognitive disorders. Front Aging Neurosci 13:671499
Shao F, Wang X, Wu H, Wu Q, Zhang J (2022) Microglia and neuroinflammation: crucial pathological mechanisms in traumatic brain injury-induced neurodegeneration. Front Aging Neurosci 14:825086
Shippy DC, Wilhelm C, Viharkumar PA, Raife TJ, Ulland TK (2020) β-Hydroxybutyrate inhibits inflammasome activation to attenuate Alzheimer’s disease pathology. J Neuroinflammation 17(1):280
Siniscalco D, Schultz S, Brigida AL, Antonucci N (2018) Inflammation and neuro-immune dysregulations in autism spectrum disorders. Pharmaceuticals (basel) 11(2):56
Söderbom G, Zeng BY (2020) The NLRP3 inflammasome as a bridge between neuro-inflammation in metabolic and neurodegenerative diseases. Int Rev Neurobiol 154:345–391
Wang L, Chen P, Xiao W (2021) β-Hydroxybutyrate as an anti-aging metabolite. Nutrients 13(10):3420
White H, Heffernan AJ, Worrall S, Grunsfeld A, Thomas M (2021) A systematic review of intravenous β-hydroxybutyrate use in humans - a promising future therapy? Front Med (lausanne) 8:740374
Wu Y, Gong Y, Luan Y, Li Y, Liu J, Yue Z, Yuan B, Sun J, Xie C, Li L, Zhen J, Jin X, Zheng Y, Wang X, Xie L, Wang W (2020) BHBA treatment improves cognitive function by targeting pleiotropic mechanisms in transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. FASEB J 34(1):1412–1429
Wu XM, Ji MH, Yin XY, Gu HW, Zhu TT, Wang RZ, Yang JJ, Shen JC (2022a) Reduced inhibition underlies early life LPS exposure induced-cognitive impairment: Prevention by environmental enrichment. Int Immunopharmacol 108:108724
Wu Y, Teng Y, Zhang C, Pan Y, Zhang Q, Zhu X, Liu N, Su X, Lin J (2022b) The ketone body β-hydroxybutyrate alleviates CoCrMo alloy particles induced osteolysis by regulating NLRP3 inflammasome and osteoclast differentiation. J Nanobiotechnology 20(1):120
Xu X, Zhang Q, Tu J, Ren Z (2011) D-β-hydroxybutyrate inhibits microglial activation in a cell activation model in vitro. J Med Coll PLA 26(3):117–127
Yang L, Zhou R, Tong Y, Chen P, Shen Y, Miao S, Liu X (2020) Neuroprotection by dihydrotestosterone in LPS-induced neuroinflammation. Neurobiol Dis 140:104814
Yang X, Wang R, Zhou H, Wang L, Wang R, Li H, Tan B, Wu Q, Xu X, Cui L, Li Z, Li H (2021) β-Hydroxybutyrate alleviates learning and memory impairment through the SIRT1 pathway in D-Galactose-injured mice. Front Pharmacol 12:751028
Yao A, Li Z, Lyu J, Yu L, Wei S, Xue L, Wang H, Chen GQ (2021) On the nutritional and therapeutic effects of ketone body D-β-hydroxybutyrate. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 105(16–17):6229–6243
Youssef NA, Holland-Winkler AM, Phung P, Waller JL, Ponkshe S (2022) A randomized, double-blind, clinical pilot trial of adjunct ketone supplement compared to placebo for treating posttraumatic stress disorder. Ann Clin Psychiatry 34(4):240–244
Zhao P, Meng L, Dou M, Mao J, Zhang G, Zheng M, Yin X, Tao Z, Gong M, Song L, Lian K, de-la-Paz OIV, Guo Q, Shi H (2020) Long-lasting effects of postweaning sodium butyrate exposure on social behaviors in adult mice. Brain Res Bull 165:209-217
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82170846) and the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei (H2020206386 and H2020206328). The authors thank Professor Haishui Shi (Neuroscience Research Center, Institute of Medical and Health Science, Hebei Medical University, Hebei, China) for guidance of behavioral test. We thank Barry Patel, PhD, from Liwen Bianji (Edanz) (www.liwenbianji.cn/), for editing the English text of a draft of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yanning Li designed the study, reviewed and edited the manuscript. Yuping Zhang and Kun Liu performed experiments and analyzed the data. Yunpeng Li and Yujie Ma performed experiments and wrote the manuscript. Yu Wang and Zihan Fan performed experiments. Jinsheng Qi discussed the results and commented on the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Ethical approval was given by the Institutional Ethics Committee of Hebei Medical University.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest associated with this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.

Supplementary Figure 1
Effects of BHB on microglial IL-6 in the hippocampus of LPS-treated mice. (A) Immunofluorescence of IL-6 (green) and microglial marker IBA-1 (red) was shown to reflect microglial IL-6. Scale bar, 10 μm. (B) The relative intensity of IL-6 fluorescence was calculated (n = 3). Data were means ± SD. * p < 0.05 versus Con; # p < 0.05 versus LPS; analyzed by one-way ANOVA and least significant difference test. (PNG 292 kb)
Supplementary file1
(DOC 23.0 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Liu, K., Li, Y. et al. D-beta-hydroxybutyrate protects against microglial activation in lipopolysaccharide-treated mice and BV-2 cells. Metab Brain Dis 38, 1115–1126 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-022-01146-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-022-01146-7