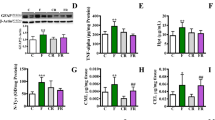
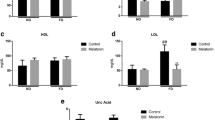
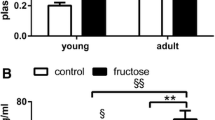
Abstract
A high-fructose diet causes metabolic abnormalities in rats, and the cluster of complications points to microvascular and neuronal disorders of the brain. The aim of this study was to evaluate i) the involvement of microvascular disorders and neuronal plasticity in the deleterious effects of a high-fructose diet on the rat brain and ii) a comparative assessment of the effectiveness of Phytocollection therapy (with antidiabetic, antioxidant, and acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activities) compared to Galantamine as first-line therapy for dementia and Diabeton as first-line therapy for hyperglycemia. The calcium adenosine triphosphate non-injection histoangiological method was used to assess capillary network diameter and density. A high-fructose diet resulted in a significant decrease in the diameter and density of the capillary bed, and pharmacological manipulations had a modulatory effect on microcirculatory adaptive mechanisms. In vivo single-unit extracellular recording was used to investigate short-term plasticity in the medial prefrontal cortex. Differences in the parameters of spike background activity and expression of excitatory and inhibitory responses of cortical neurons have been discovered, allowing for flexibility and neuronal function stabilization in pathology and pharmacological prevention. Integration of the coupling mechanism between microvascular function and neuronal spike activity could delay the progressive decline in cognitive function in rats fed a high fructose diet.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Raw data can be provided upon request to the corresponding author.
References
Allam AR, Sridhar GR, Thota H, Babu CS, Prasad AS, Divakar Ch (2006) Alzheimer’s disease and Type 2 diabetes mellitus: the cholinesterase connection? Lipids Health Dis 5:28. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-511X-5-28
Avagimyan A, Sukiasyan L, Kakturskiy L, Mkrtchyan L, Chavushyan V, Chelidze K, Ionov A, Pavluchenko I (2021) Diabefit as a Modifier of Fructose-induced Impairment of Cardio-vascular System. Curr Probl Cardiol 24:100943
Avetisyan LG, Sukiasyan LM, Babakhanyan MA, Hovhannisyan LE, Simonyan KV, Nahapetyan KhH, Isoyan AS, Avetisyan RA, Chavushyan VA (2019) Effects of phytotherapy on the cardiovascular changes induced by fructose overload. Electron J Nat Sci 33(2):14–20
Babakhanyan M, Hovhannisian L, Gulyan A, Nahapetyan K, Karagamyan P, Beglaryan G (2012) The introduction of a new technical culture of sweet-herb (Stevia Rebaudiana Bertoni) in RA and NKR: a promising and profitable offer for public and private investments. J Agrosci 5–6:296–302
Babel H, Bischofs IB (2016) Molecular and cellular factors control signal transduction via switchable allosteric modulator proteins (SAMPs). BMC Syst Biol 10:35
Badescu L, Badulescu O, Badescu M, Ciocoiu M. Mechanism by Sambucus nigra Extract Improves Bone Mineral Density in Experimental Diabetes. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2012:848269, 6 pages
Ballinger EC, Ananth M, Talmage DA, Role LW (2016) Basal forebrain cholinergic circuits and signaling in cognition and cognitive decline. Neuron 91:1199–1218
Barac A, Campia U, Panza JA (2007) Methods for evaluating endothelial function in humans. Hypertension 49(4):748–760
Ben-Eliezer D, Yechiam E (2016) Hypericum perforatum as a cognitive enhancer in rodents: A meta-analysis. Sci Rep 6:35700
Biane J, Conner JM, Tuszynski MH (2014) Nerve growth factor is primarily produced by GABAergic neurons of the adult rat cortex. Front Cell Neurosci 8:220
Brown LS, Foster CG, Courtney JM, King NE, Howells DW, Sutherland BA (2019) Pericytes and Neurovascular Function in the Healthy and Diseased Brain. Front Cell Neurosci 13:282. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2019.00282
Brownlee M (2001) Biochemistry and molecular cell biology of diabetic complications. Nature 414(6865):813–820
Carmichael OT, Neiberg RH, Dutton GR, Hayden KM, Horton E, Pi-Sunyer FX, Johnson KC, Rapp SR, Spira AP, Espeland MA (2020) Long-term Change in Physiological Markers and Cognitive Performance in Type 2 Diabetes: The Look AHEAD Study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1;105(12):dgaa591 https://doi.org/10.1210/clinem/dgaa591
Carvajal FJ, Inestrosa NC (2011) Interactions of AChE with Aβ aggregates in Alzheimer’s brain: therapeutic relevance of IDN 5706. Front Mol Neurosci 4:19. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2011.00019
Casanova F, Adingupu DD, Adams F, Gooding KM, Looker HC, Aizawa K et al (2017) The impact of cardiovascular co-morbidities and duration of diabetes on the association between microvascular function and glycaemic control. Cardiovasc Diabetol 16:114. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12933-017-0594-7
Chabot C, Massicotte G, Milot M, Trudeau F, Gagne J (1997) Impaired modulation of AMPA receptors by calcium-dependent processes in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Brain Res 768:249–256
Chavushyan VA, Simonyan KV, Simonyan RM, Isoyan AS, Simonyan GM, Babakhanyan MA, Hovhannisyian LE, Nahapetyan KhH, Avetisyan LG, Simonyan MA (2017) Effects of stevia on synaptic plasticity and NADPH oxidase level of CNS in conditions of metabolic disorders caused by fructose. BMC Complement Altern Med 17(540):1–13
Chavushyan V, Soghomonyan A, Karapetyan G, Simonyan K, Yenkoyan K (2020) Disruption of cholinergic circuits as an area for targeted drug treatment of Alzheimer’s disease: In vivo assessment of short-term plasticity in rat brain. Pharmaceuticals (basel) 13:1–12
Chilelli NC, Burlina S, Lapolla A (2013) AGEs, rather than hyperglycemia, are responsible for microvascular complications in diabetes: A “glycoxidation-centric” point of view. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 23:913–919
Chilingaryan A,Chilingaryan AM, MartinGG (2006) The three-dimensional detection of microvasculatory bed in the brain of white rat Rattusnorvegicus by a Ca2+-ATPase method. Brain Res 1070:131-138
Coen DA (2018) Stehouwer Microvascular Dysfunction and Hyperglycemia: A Vicious Cycle With Widespread Consequences. Diabetes 67:1729–1741
Conner JM, Chiba AA, Tuszynski MH (2005) The basal forebrain cholinergic system is essential for cortical plasticity and functional recovery following brain injury. Neuron 46:173–179
Consolim-Colombo FM, Sangaleti CT, Costa FO, Morais TL, Lopes HF et al (2017) Galantamine alleviates inflammation and insulin resistance in patients with metabolic syndrome in a randomized trial. JCI Insight 2(14):e93340
Davtyan GS (1980) Hydroponics, The Reference Book on the Chemicalization of Agriculture, Moscow, Russia
Farooqui AA, Farooqui T, Panza F, Frisardi V (2012) Metabolic syndrome as a risk factor for neurological disorders. Cell Mol Life Sci 69:741–762
Farooqui AA (2013) Metabolic Syndrome: An Important Risk Factor for Stroke, Alzheimer Disease, and Depression. Springer Science+Business Media, New York
Food and Drug Association. Guidance for industry (2008) Diabetes mellitus - evaluating cardiovascular risk in new antidiabetic therapies to treat type 2 diabetes.
Formica JV, Regelson W (1995) Review of the biology of quercetin and related bioflavonoids. Food Chem Toxicol 33:1061–1080
Gaweł-Bęben K, Bujak T, Nizioł-Łukaszewska Z, Antosiewicz B, Jakubczyk A, Karaś M, Rybczyńska K (2015) Stevia Rebaudiana Bert. Leaf Extracts as a Multifunctional Source of Natural Antioxidants. Molecules 20:5468–5486
Geula C, Dunlop SR, Ayala I, Kawles AS, Flanagan ME, Gefen T, Mesulam MM (2021) Basal forebrain cholinergic system in the dementias: Vulnerability, resilience, and resistance. J Neurochem 158(6):1394–1411
Goyal S, Samsher S, Goyal R (2010) Stevia (Stevia rebaudiana) a bio-sweetener: A review. Int J Food Sci Nutr 61:1–10
Gupta E, Purwar S, Sandaram S, Gai GK (2013) Nutritional and therapeutic values of Stevia rebaudiana: A review. J Med Plants Res 7:3343–3353
Hamilton Nicola B, Attwell David, Hall Catherine N (2010) Pericyte-mediated regulation of capillary diameter: a component of neurovascular coupling in health and disease . Front Neuroenergetics 2. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnene.2010.00005
Hanafy DM, Burrows GE, Prenzler PD, Hill RA (2020) Potential Role of Phenolic Extracts of Mentha in Managing Oxidative Stress and Alzheimer's Disease. Antioxidants (Basel) 17;9(7):631
Heinrich M, Teoh HL (2004) Galanthamine from snowdrop - The development of a modern drug against Alzheimer’s disease from local caucasian knowledge. J Ethnopharmacol 92:147–162
Hung TM, Luan TC, Vinh BT, Cuong TD, Min BS (2011) Labdane-type Diterpenoids from Leonurus heterophyllus and Their Cholinesterase Inhibitory Activity. Phytother Res 25:611–614
Jeppesen PB, Gregersen S, Poulsen CR, Hermansen K (2000) Stevioside acts directly on pancreatic beta cells to secrete insulin: actions independent of cyclic adenosine monophosphate and adenosine triphosphate-sensitive K+-channel activity. Metab Clin Exp 49(2):208–14
Jud P, Sourij H, Philipp J, Harald S (2019) Therapeutic options to reduce advanced glycation end products in patients with diabetes mellitus: A review. Diabetes Res Clin Pr 148:54–63
Kakkar S, Bais S (2014) A review on protocatechuic acid and its pharmacological potential. ISRN Pharmacol 2014:952943. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/952943
Kanbay M, Sánchez-Lozada LG, Franco M, Madero M, Solak Y, Rodriguez-Iturbe B, Covic A, Johnson RJ (2011) Microvascular disease and its role in the brain and cardiovascular system: a potential role for uric acid as a cardiorenal toxin. Nephrol Dial Transplant 26:430–437. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfq635
Kasa P, Papp H, Kasa P Jr, Torok I (2000) Donepezil dosedependently inhibits acetylcholinesterase activity in various areas and in the presynaptic cholinergic and the postsynaptic cholinoceptive enzyme-positive structures in the human and rat brain. Neuroscience 101:89–100
Kilgard MP, Merzenich MM (1998) Cortical map reorganization enabled by nucleus basalis activity. Science 279:1714–1718
Kirkpatrick CJ, Bittinger F, Nozadze K, Wessler I (2003) Expression and function of the non-neural cholinergic system in endothelial cells. Life Sci 72:2111–2116
Kisler K, Nelson AR, Montagne A, Zlokovic BV (2017) Cerebral blood flow regulation and neurovascular dysfunction in Alzheimer disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 18:419–434
Kopylova VS, Boronovskiy SE, Nartsissov YR (2017) Fundamental principles of vascular network topology. Biochem Soc Trans 45:839–844. https://doi.org/10.1042/BST20160409
LaneRoger M, Potkin Steven G, Enz Albert (2006) Targeting acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase in dementia. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 9:101–124
Lassègue B, San Martín A, Griendling KK (2012) Biochemistry, Physiology and Pathophysiology of NADPH Oxidases in the Cardiovascular System. Circ Res 110(10):1364–1390. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.111.243972
Le K, Chiu F, Ng K (2007) Identification and quantification of antioxidants in Fructus lycii. Food Chem 105:353–363
Lessmann V, Gottmann K, Malcangio M (2003) Neurotrophin secretion: current facts and future prospects. Prog Neurobiol 69:341–374
Levy BI, Schiffrin EL, Mourad JJ, Agostini D, Vicaut E, Safar ME et al (2008) Impaired tissue perfusion: a pathology common to hypertension, obesity, and diabetes mellitus. Circulation 118:968–976
Li XL, Zhou AG (2007) Evaluation of the antioxidant effects of polysaccharides extracted from Lycium barbarum. Med Chem Res 15:471–482
Lind L (2008) Endothelium-dependent vasodilation, insulin resistance and the metabolic syndrome in an elderly cohort: the Prospective Investigation of the Vasculature in Uppsala Seniors (PIVUS) study. Atherosclerosis 196(2):795–802
Lojkowska W, Ryglewicz D, Jedrzejczak T, Minc S, Jakubowska T, Jarosz H, Bochynska A (2003) The effect of cholinesterase inhibitors on the regional blood flow in patients with Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia. J Neurol Sci 216:119–126
Lozano I, Van der Werf R, Bietiger W, Seyfritz E, Peronet C, Pinget M, Jeandidier N, Maillard E, Marchioni E, Sigrist S, Dal S (2016) High-fructose and high-fat diet-induced disorders in rats: impact on diabetes risk, hepatic and vascular complications. Nutr Metab 13(15):1–13
Mainardi M, Fusco S, Grassi C (2015) Modulation of Hippocampal Neural Plasticity by Glucose-Related Signaling. Neural Plast 657928, 10 pages
Makhoba XH, Viegas CJ, Mosa RA, Viegas FPD, Pooe OJ (2020) Potential Impact of the Multi-Target Drug Approach in the Treatment of Some Complex Diseases. Drug Des Dev Ther 11.14.3235–3249
Malenka RC, Bear MF (2004) LTP and LTD: an embarrassment of riches. Neuron 44:5–21
Malinow R, Malenka RC (2002) AMPA receptor trafficking and synaptic plasticity. Annu Rev Neurosci 25:103–126
Martinelli I, Tomassoni D, Moruzzi M, Traini E, Amenta F, Tayebati SK (2017) Obesity and metabolic syndrome affect the cholinergic transmission and cognitive functions. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 16(6):664–676. https://doi.org/10.2174/1871527316666170428123853
Marucci G, Michela Buccioni, Diego DalBen, Catia Lambertucci, Rosaria Volpini, Francesco Amenta (2021) Efficacy of acetylcholinesterase inhibitors in Alzheimer's disease. Neuropharmacology 190:108352
Mohammedi K, Woodward M, Marre M, Colagiuri S, Cooper M, Harrap S et al (2017) Comparative effects of microvascular and macrovascular disease on the risk of major outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. Cardiovasc Diabetol 16:95
Moretti R, Torre P, Antonello RM, Cazzato G, Bava A (2002) Rivastigmine in subcortical vascular dementia : an open 22-month study. J Neurol Sci 203–204:141–146
Muniyappa R, Montagnani M, Koh KK, Quon MJ (2007) Cardiovascular actions of insulin. Endocr Rev 28(5):463–491
Muniyappa R, Sowers JR (2013) Role of Insulin Resistance in Endothelial Dysfunction. Rev Endocr Metab Disord 14(1):5–12
Myint KZ, Wu K, Xia Y, Fan Y, Shen J, Zhang P, Gu J (2020) Polyphenols from Stevia rebaudiana (Bertoni) leaves and their functional properties. J Food Sci 85–2:240–248
Nishikawa T (2000) Normalizing mitochondrial superoxide production blocks three pathways of hyperglycaemic damage. Nature 404:787–790
Nolan CJ, Damm P, Prentki M (2011) Type 2 diabetes across generations: from pathophysiology to prevention and management. Lancet 378(9786):169–181
Nordstrom P, Religa D, Wimo A, Winblad B, Eriksdotter M (2013) The use of cholinesterase inhibitors and the risk of myocardial infarction and death: a nationwide cohort study in subjects with Alzheimer’s disease. Eur Heart J 34(33):2585–2591
Ogawa M, Magata Y, Ouchi Y, Fukuyama H, Yamauchi H, Kimura J, Yonekura Y, Konishi J (1994) Scopolamine abolishes cerebral blood flow response to somatosensory stimulation in anaesthetized cats : PET study. Brain Res 650:249–252
Okon EB, Szado T, Laher I, McManus B, van Breemen C (2003) Augmented contractile response of vascular smooth muscle in a diabetic mouse model. J Vasc Res 40(6):520–530. https://doi.org/10.1159/000075238
Orhan I, Kartal M, Tosun F, Sener B (2007) Screening of Various Phenolic Acids and Flavonoid Derivatives for their Anticholinesterase Potential. Z Naturforsch C J Biosci 62:829P832
Pan D, Zhang D, Wu J, Chen C, Xu Z, Yang H, Zhou P (2013) Antidiabetic, antihyperlipidemic and antioxidant activities of a novel proteoglycan from ganoderma lucidum fruiting bodies on db/db mice and the possible mechanism. PLoS One 8:e68332
Panchal SK, Brown L (2011) Rodent models for metabolic syndrome research. J Biomed Biotechnol 2011:351982. https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/351982
Papazafiropoulou AK (2020) Diabetes and dementia – the two faces of Janus / A. K. Papazafiropoulou, Ch. Koros, A. Melidonis, S. Antonopoulos // Arch Med Sci Atheroscler Dis e186-e197
Paxinos G, Watson C (2005) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates: compact, 6th edn. Academic Press, Cambridge
Potterat O (2010) Goji (Lycium barbarum and L. chinense): Phytochemistry, Pharmacology and Safety in the Perspective of Traditional Uses and Recent Popularity. Planta Med 76:7–19
Ranilla LG, Kwon YI, Apostolidis E, Shetty K (2010) Phenolic compounds, antioxidant activity and in vitro inhibitory potential against key enzymes relevant for hyperglycemia and hypertension of commonly used medicinal plants, herbs and spices in Latin America. Bioresour Technol 101(12):4676–4689
Ray J, Kumar S, Laor D, Shereen N, Nwamaghinna F, Thomson A, Perez Perez J, Soni L, McFarlane SI (2020) Effects of Stevia Rebaudiana on Glucose Homeostasis, Blood Pressure and Inflammation: A Critical Review of Past and Current Research Evidence. Int J Clin Res Trials 5:142
Richard E, van Gool WA, Hoozemans JJ et al (2010) Morphometric changes in the cortical microvascular network in Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 22:811–818
Rizzoni D, Porteri E, Guelfi D, Muiesan ML, Valentini U, Cimino A et al (2001) Structural alterations in subcutaneous small arteries of normotensive and hypertensive patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Circulation 103:1238–1244
Roberts CK, Barnard RJ, Sindhu RK, Jurczak M, Ehdaie A, Vaziri ND (2006) Oxidative stress and dysregulation of NAD(P)H oxidase and antioxidant enzymes in diet-induced metabolic syndrome. Metabolism 55:928–934
Roher AE, Kuo YM, Potter PE (2000) Cortical cholinergic denervation elicits vascular A beta deposition. Ann NY Acad Sci 903:374–386
Rust R, Kirabali T, Grönnert L, Dogancay B, Limasale YDP, Meinhardt A, Werner C, Laviña B, Kulic L, Nitsch RM, Tackenberg C, Schwab ME (2020) A Practical Guide to the Automated Analysis of Vascular Growth, Maturation and Injury in the Brain. Front Neurosci 14:244. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2020.00244
Sanodiya BS, Thakur GS, Baghel RK, Prasad GB, Bisen PS (2009) Ganoderma lucidum: A potent pharmacological macrofungus. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 10:717–742
Santilli FD, Ardes D, Davi G (2015) Oxidative stress in chronic vascular disease: from prediction to prevention. Vascul Pharmacol 74:23–37
Sassin I, Schultz C, Thal DR, Rub U, Arai K, Braak E, Braak H (2000) Evolution of Alzheimer’s disease-related cytoskeletal changes in the basal nucleus of Meynert. Acta Neuropathologica (berlin) 100:259–269
Satapathy SK, Ochani M, Dancho M et al (2011) Galantamine alleviates inflammation and other obesity-associated complications in high-fat diet-fed mice. Mol Med 17(7–8):599–606
Schiano C, Grimaldi V, Franzese M, Fiorito C, Nigris F, Donatelli F, Soricelli A, Salvatore M, Napoli C (2020) Non-nutritional sweeteners effects on endothelial vascular function. Toxicol in Vitro 62:104694
Sena CM, Pereira AM, Seica R (2013) Endothelial dysfunction - a major mediator of diabetic vascular disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 1832(12):2216–2231
Seol GH, Ziburkus J, Huang SY et al (2007) Neuromodulators Control the Polarity of Spike-Timing-Dependent Synaptic Plasticity. Neuron 55(6):919–929
Seto SW, Yang GY, Kiat H, Bensoussan A, Kwan YW, Chang D (2015) Diabetes Mellitus, Cognitive Impairment, and Traditional Chinese Medicine. Int J Endocrinol 810439
Shaver SW, Sposito NM, Gross PM (1990) Quantitative fine structure of capillaries in subregions of the rat subfornical organ. J Comp Neurol 294:145–152
Shivanna N, Naika M, Khanum F, Kaul VK (2013) Antioxidant, anti-diabetic and renal protective properties of Stevia rebaudiana. J Diabetes Complicat 27:103–113
Sidor A, Gramza-Michałowska A (2015) Advanced research on the antioxidant and health benefit of elderberry (Sambucus nigra) in food. J Funct Foods V18 –Part B.941–958
Solanki ND, Bhavsar SK, Pandya DT (2018) Role of phytotherapy in diabetic neuropathy and neurodegeneration: from pathogenesis to treatment. J Phytopharmacol 7(2):152–161
Stanhope KL, Medici V, Bremer AA, Lee V, Lam HD, Nunez MV, Chen GX, Keim NL, Havel PJ (2015) A dose-response study of consuming high-fructose corn syrup–sweetened beverages on lipid/lipoprotein risk factors for cardiovascular disease in young adults. Am J Clin Nutr 101:1144–1154
Stephan BC, Wells JC, Brayne C et al (2010) Increased fructose intake as a risk factor for dementia. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 65:809–814
Stirban A, Gawlowski T, Roden M (2013) Vascular effects of advanced glycation endproducts: clinical effects and molecular mechanisms. Mol Metab 3:94–108
Strain WD, Paldánius PM (2018) Diabetes, cardiovascular disease and the microcirculation. Cardiovasc Diabetol 17:57
Styskal J, Van Remmen H, Richardson A, Salmon AB (2012) Oxidative stress and diabetes: what can we learn about insulin resistance from antioxidant mutant mouse models? Free Radic Biol Med 1;52(1):46–58
Sukiasyan LM, Danielyan MH, Hovhannisyan LE, Babakhanyan MA, Simonyan KV, Isoyan AS, Avetisyan LG, Lorikyan AG, Chavushyan VA (2021) Acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activity of Artsakh traditional antidiabetic remedy. International scientific conference "90 years - from plant to medicine: achievements and prospects. 346–352. https://doi.org/10.52101/9785870191003_2021_346
Taira T, Lamsa K, Kaila K (1997) Posttetanic excitation mediated by GABAA receptors in rat CA1 pyramidal neurons. J Neurophysiol 77:2213–2218
Tappy L, Le KA (2010) Metabolic effects of fructose and the worldwide increase in obesity. Physiol Rev 90(1):23–46
Tauffer L, Kumar A (2021) Short-term synaptic plasticity makes neurons sensitive to the distribution of presynaptic population firing rates. eNeuro 8 (2) ENEURO.0297-20.2021. https://doi.org/10.1523/ENEURO.0297-20.2021
Tayebati SK, Di Tullio MA, Amenta F (2008) Vesicular acetylcholine transporter (VAChT) in the brain of spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR): effect of treatment with an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. Clin Exp Hypertens 30:732–743
Toda N, Okamura T (2003) The pharmacology of nitric oxide in the peripheral nervous system of blood vessels. Pharmacol Rev 55:271–324
Toop CR, Gentili Sh (2016) Fructose beverage consumption induces a metabolic syndrome phenotype in the rat: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrients 8(577):1–15
Tran V, De Silva TM, Sobey CG, Lim K, Drummond GR, Vinh A, Jelinic M (2020) The Vascular Consequences of Metabolic Syndrome: Rodent Models, Endothelial Dysfunction, and Current Therapies. Front Pharmacol 11:148
Tsubokawa H, Ross WN (1997) Muscarinic modulation of spike backpropagation in the apical dendrites of hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons. J Neurosci 17:5782–5791
Vaithianathan T, Bedi D, Kanju PM, Wang Z, Bahr BA, Dityatev A, Judd RL, Suppiramaniam VD (2003) Evidence of AMPA-glutamate receptor dysfunction in brain of streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Soc Neurosci 375:18
Valko M, Leibfritz D, Moncol J, Cronin MT, Mazur M, Telser J (2007) Free radicals and antioxidants in normal physiological functions and human disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 39(1):44–84
Vladimir-Knežević S, Blažeković B, Kindl M, Vladić J, Lower-Nedza AD, Brantner AH (2014) Acetylcholinesterase inhibitory, antioxidant and phytochemical properties of selected medicinal plants of the Lamiaceae family. Molecules 9;19(1):767–82 https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19010767
Woodruff-Pak DS, Lander C, Geerts H (2002) Nicotinic cholinergic modulation: galantamine as a prototype. CNS Drug Rev 8(4):405–26
Yan LJ (2018) Redox imbalance stress in diabetes mellitus: Role of the polyol pathway. Anim Model Exp Med 1:7–13
Yeh GY, Eisenberg DM, Kaptchuk TJ, Phillips RS (2003) Systematic review of herbs and dietary supplements for glycemic control in diabetes. Diabetes Care 26(4):1277–1294
Yilmaz CE, Latorre J, Yilmaz G (2013) Stevia – a natural sugar substitute- attenuates endothelial dysfunction induced by hypercholesterolemia. FASEB J 27(S1):lb36-lb36. https://doi.org/10.1096/fasebj.27.1_supplement.lb36
Yokeshwaran A, Venkatachalam VV, Sabarisenthil B, Kalaichelvan VK (2020) Anticholinesterase activity of plant extracts of Smilax zeylanica and Smilax china. Int J Pharm Sci Res 11(9):4370–4374
Zhang W, Zhang Q, Deng W, Li Y, Xing G, Shi X, Du Y (2014) Neuroprotective effect of pretreatment with ganoderma lucidum in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rat hippocampus. Neural Regen Res 9(15):1446–1452. https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.139461
Zhou ZQ, Xiao J, Fan HX, Yu Y, He RR, Feng XL, Kurihara H, So KF, Yao XS, Gao H (2017) Polyphenols from wolfberry and their bioactivities. Food Chem 214:644–654
Zhou ZY, Tang YP, Xiang J, Wua P, Jin HM, Wang Z, Mori M, Cai DF (2010) Neuroprotective effects of water-soluble Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides on cerebral ischemic injury in rats. J Ethnopharmacol 131:154–164
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
VAC, KVS, MHD, LGA, ASI, AGL, LMS, LEH, MAB conducted the experiments. All authors contributed to analyzing and discussing the results. KVS, LVD and VAC wrote the paper. All authors have read and approved of the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The experimental protocol corresponded to the conditions of the European Communities Council Directive (2010/63/ UE) and it was approved by the Ethics committee of the Yerevan State Medical University after Mkhitar Heratsi (IRB Approval N4, November 15, 2018).
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chavushyan, V.A., Simonyan, K.V., Danielyan, M.H. et al. Pathology and prevention of brain microvascular and neuronal dysfunction induced by a high-fructose diet in rats. Metab Brain Dis 38, 269–286 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-022-01098-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-022-01098-y