Abstract
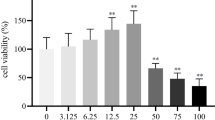
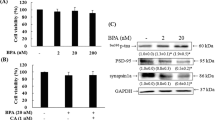
1,4-butanediol (1,4-BD) is a known γ-hydroxybutyric acid (GHB) precursor which affects the nervous system after ingestion, leading to uncontrolled behavioral consequences. In the present study, we investigated whether 1,4-BD induces oxidative stress and inflammation in PC12 cells and evaluated the toxic effects of 1,4-BD associates with learning and memory. CCK-8 results revealed a dose–effect relationship between the cell viability of PC12 cells and 1,4-BD when the duration of action was 2 h or 4 h. Assay kits results showed that 1,4-BD decreased the levels of Glutathione (GSH), Glutathione peroxidase (GSH-px), Superoxide dismutase (SOD), Acetylcholine (Ach) and increased the levels of Malondialdehyde (MDA), Nitric oxide (NO) and Acetylcholinesterase (AchE). Elisa kits results indicated that 1,4-BD decreased the levels of synaptophysin I (SYN-1), Postsynaptic density protein-95 (PSD-95), Growth associated protein-43 (GAP-43) and increased the levels of Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) and Interleukin- 6 (IL-6). RT-PCR results showed that the mRNA levels of PSD-95, SYN-1 and GAP-43 were significantly decreased. The expression of phosphorylation extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase 1/2 (p-ERK1/2), phosphorylation cAMP response element binding protein (p-CREB) and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) proteins were significantly decreased in PC12 cells by protein blotting. Overall, these results suggest that 1,4-BD may affect synaptic plasticity via the ERK1/2-CREB-BDNF pathway, leading to Ach release reduction and ultimately to learning and memory impairment. Furthermore, oxidative stress and inflammation induced by 1,4-BD may also result in learning and memory deficits. These findings will enrich the toxicity data of 1.4-BD associated with learning and memory impairment.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Alonso M, Medina JH, Pozzo-Miller L (2004) ERK1/2 activation is necessary for BDNF to increase dendritic spine density in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons. Learn Mem 11(2):172–178. https://doi.org/10.1101/lm.67804
Andresen H, Aydin BE, Mueller A, Iwersen-Bergmann S (2011) An overview of gamma-hydroxybutyric acid: pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics, toxic effects, addiction, analytical methods, and interpretation of results. Drug Test Anal 3(9):560–568. https://doi.org/10.1002/dta.254
Arancio O, Kiebler M, Lee CJ et al (1996) Nitric oxide acts directly in the presynaptic neuron to produce long-term potentiation in cultured hippocampal neurons. Cell 87(6):1025–1035. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81797-3
Barker SA, Snead OC, Poldrugo F, Liu CC, Fish FP, Settine RL (1985) Identification and quantitation of 1,4-butanediol in mammalian tissues: an alternative biosynthetic pathway for gamma-hydroxybutyric acid. Biochem Pharmacol 34(10):1849–1852. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-2952(85)90662-8
Bing Q, Lou J, Li B, Liu Z, University HN, Anatomy DO (2016) Study on changes of learning and memory functions and PSD-95 expression in hippocampus of AD-like rats. Chinese Journal of Neuroanatomy
Borgen LA, Okerholm RA, Lai A, Scharf MB (2004) The pharmacokinetics of sodium oxybate oral solution following acute and chronic administration to narcoleptic patients. J Clin Pharmacol 44(3):253–257. https://doi.org/10.1177/0091270003262795
Bosch OG, Seifritz E (2016) The behavioural profile of gamma-hydroxybutyrate, gamma-butyrolactone and 1,4-butanediol in humans. Brain Res Bull:47–60
Bowery NG, Bettler B, Froestl W et al (2002) International Union of Pharmacology. XXXIII. Mammalian gamma-aminobutyric acid(B) receptors: structure and function. Pharmacol Rev 54(2):247–64. https://doi.org/10.1124/pr.54.2.247
Brailsford AD, Cowan DA, Kicman AT (2012) Pharmacokinetic properties of gamma-hydroxybutyrate (GHB) in whole blood, serum, and urine. J Anal Toxicol 36(2):88–95. https://doi.org/10.1093/jat/bkr023
Bramham CR, Messaoudi E (2005) BDNF function in adult synaptic plasticity: the synaptic consolidation hypothesis. Prog Neurobiol 76(2):99–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2005.06.003
Brunt TM, van Amsterdam JG, van den Brink W (2014) GHB, GBL and 1,4-BD addiction. Curr Pharm Des 20(25):4076–4085. https://doi.org/10.2174/13816128113199990624
Carai MA, Colombo G, Quang LS, Maher TJ, Gessa GL (2006) Resuscitative treatments on 1,4-butanediol mortality in mice. Ann Emerg Med 47(2):184–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annemergmed.2005.10.011
Carter LP, Koek W, France CP (2009) Behavioral analyses of GHB: receptor mechanisms. Pharmacol Ther 121(1):100–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2008.10.003
Carter LP, Koek W, France CP (2010) Lack of effects of GHB precursors GBL and 1,4-BD following i.c.v. administration in rats. Eur J Neurosci 24(9):2595–2600
Chen LY, Renn TY, Liao WC et al (2017) Melatonin successfully rescues hippocampal bioenergetics and improves cognitive function following drug intoxication by promoting Nrf2-ARE signaling activity. J Pineal Res 63(2) https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12417
Choi JG, Yang WM, Kang TH, Oh MS (2011) Effects of optimized-SopungSunkiwon on memory impairment and enhancement. Neurosci Lett 491(2):93–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2010.12.058
Chu JJ, Zhou JY, Zhao DF, Wang MZ, Qiang F (2003) Gamma-hydroxybutyrate Combine with Radiotherapy to Treat Malignant Brain Gliomas. Chinese Journal of Neuro-Oncology
Cooper GMJSA (2000) Protein Synthesis, Processing, and Regulation.
Corkery JM, Loi B, Claridge H et al (2015) Gamma hydroxybutyrate (GHB), gamma butyrolactone (GBL) and 1,4-butanediol (1,4-BD; BDO): A literature review with a focus on UK fatalities related to non-medical use. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 53:52–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2015.03.012
Couve A, Moss SJ, Pangalos MN (2000) GABAB receptors: a new paradigm in G protein signaling. Mol Cell Neurosci 16(4):296–312. https://doi.org/10.1006/mcne.2000.0908
Eitner A, Muller S, Konig C et al (2021) Inhibition of Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase Prevents IL-1beta-Induced Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Human Chondrocytes. Int J Mol Sci 22(5) https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22052477
Franzon R, Lamers ML, Stefanello FM, Wannmacher CM, Wajner M, Wyse AT (2003) Evidence that oxidative stress is involved in the inhibitory effect of proline on Na(+), K(+)-ATPase activity in synaptic plasma membrane of rat hippocampus. Int J Dev Neurosci 21(6):303–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0736-5748(03)00076-5
Fuxe K, Agnati L, Everitt BJ, Hkfelt T, Mora M (1977) Action of beta(4-chlorphenyl)GABA, gamma-hydroxybutyrolactone, and apomorphine on central dopamine neurons. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol 16:489–494
Galloway GP, Frederick-Osborne SL, Seymour R, Contini SE, Smith DE (2000) Abuse and therapeutic potential of gamma-hydroxybutyric acid. Alcohol 20(3):263–269
Giacomino NJ, Mc CE (1947) On the toxic reactions of unsaturated lactones and their saturated analogs. Fed Proc 6(1):331
Giarman NJ, Schmidt KF (2012) Some neurochemical aspects of the depressant action of gamma-butyrolactone on the central nervous system. Br J Pharmacol 20(3):563–568
Gold PE (2003) Acetylcholine modulation of neural systems involved in learning and memory. Neurobiol Learn Mem 80(3):194–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nlm.2003.07.003
Goodwin AK, Gibson KM, Weerts EM (2013) Physical dependence on gamma-hydroxybutrate (GHB) prodrug 1,4-butanediol (1,4-BD): Time course and severity of withdrawal in baboons. Drug Alcohol Depend 132(3):427–433
Greene LA, Tischler AS (1976) Establishment of a noradrenergic clonal line of rat adrenal pheochromocytoma cells which respond to nerve growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 73(7):2424–2428. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.73.7.2424
Gupta SK, Mishra R, Kusum S et al (2009) GAP-43 is essential for the neurotrophic effects of BDNF and positive AMPA receptor modulator S18986. Cell Death Differ 16(4):624–637. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2008.188
Gwaram NS, Ali HM, Abdulla MA et al (2012) Synthesis, characterization, X-ray crystallography, acetyl cholinesterase inhibition and antioxidant activities of some novel ketone derivatives of gallic hydrazide-derived Schiff bases. Molecules 17(3):2408–2427. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules17032408
Hartikainen P, Soininen H, Partanen J, Helkala EL, Riekkinen P (2010) Aging and spectral analysis of EEG in normal subjects: a link to memory and CSF AChE. Acta Neurol Scand 86(2):148–155
Holahan MR, Honegger KS, Tabatadze N, Routtenberg A (2007) GAP-43 gene expression regulates information storage. Learn Mem 14(6):407–415. https://doi.org/10.1101/lm.581907
Hopper RA, Garthwaite J (2006) Tonic and phasic nitric oxide signals in hippocampal long-term potentiation. J Neurosci 26(45):11513–11521. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2259-06.2006
Huang SP, Wu MS, Shun CT et al (2005) Cyclooxygenase-2 increases hypoxia-inducible factor-1 and vascular endothelial growth factor to promote angiogenesis in gastric carcinoma. J Biomed Sci 12(1):229–241. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11373-004-8177-5
Jiao Y, Fan H, Wang K, Lu S (2019) Sevoflurane Impairs Short-Term Memory by Affecting PSD-95 and AMPA Receptor in the Hippocampus of a Mouse Model. Behav Neurol 2019:1068260. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/1068260
Jin G, Zhu L, Liu P et al (2019) Xanthoceraside prevented synaptic loss and reversed learning-memory deficits in APP/PS1 transgenic mice. J Physiol Sci 69(3):477–488. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12576-019-00664-x
Johansson J, Gronbladh A, Hallberg M (2014) Gamma-hydroxybutyrate (GHB) induces cognitive deficits and affects GABAB receptors and IGF-1 receptors in male rats. Behav Brain Res 269:164–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2014.04.034
Kaufman M, Corner MA, Ziv NE (2012) Long-term relationships between cholinergic tone, synchronous bursting and synaptic remodeling. PLoS ONE 7(7):e40980. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0040980
Kawashima T, Okuno H, Nonaka M et al (2009) Synaptic activity-responsive element in the Arc/Arg3.1 promoter essential for synapse-to-nucleus signaling in activated neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106(1):316–21. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0806518106
Kemmel V, Klein C, Dembele D et al (2010) A single acute pharmacological dose of gamma-hydroxybutyrate modifies multiple gene expression patterns in rat hippocampus and frontal cortex. Physiol Genomics 41(2):146–160. https://doi.org/10.1152/physiolgenomics.00208.2009
Klein C, Mathis C, Leva G et al (2015) γ-Hydroxybutyrate (Xyrem) ameliorates clinical symptoms and neuropathology in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 36(2):832–844
Kleinschmidt S, Bauer M, Wanner G, Bußmann D, Ziegenfuß T, Larsen MDM (1998) Einfluß von Gamma- Hydroxy-Buttersäure (GHB) auf die proinflammatorische Zytokin-Genexpression bei koronarchirurgischen Eingriffen. Der Anaesthesist
Kumagai-Tohda C, Tohda M, Nomura Y (2010) Increase in neurite formation and acetylcholine release by transfection of growth-associated protein-43 cDNA into NG108-15 cells. J Neurochem 61(2):526–532
Levenson JM, O’Riordan KJ, Brown KD, Trinh MA, Molfese DL, Sweatt JD (2004) Regulation of histone acetylation during memory formation in the hippocampus. J Biol Chem 279(39):40545–40559. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M402229200
Liu W, Xu C, Ran D et al (2018) CaMK mediates cadmium induced apoptosis in rat primary osteoblasts through MAPK activation and endoplasmic reticulum stress. Toxicology 406–407:70–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2018.06.002
Luo Y, Yu Y, Zhang M, He H, Fan N (2020) Chronic administration of ketamine induces cognitive deterioration by restraining synaptic signaling. Mol Psychiatry. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-020-0793-6
Mesa-Garcia M, Plaza-Diaz J, Gomez-Llorente C (2018) Molecular Basis of Oxidative Stress andInflammation. Obesity:41–62
Metzmann K (2010) Untersuchungen zur Neuropharmakologie des Langzeitsedativums Butamidol (Gamma-Hydroxybuttersäure-Ethanolamid).
Moncada S, Palmer RM, Higgs EA (1991) Nitric oxide: physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacol Rev 43(2):109–142
Nava F, Carta G, Bortolato M, Gessa GL (2001) gamma-Hydroxybutyric acid and baclofen decrease extracellular acetylcholine levels in the hippocampus via GABA(B) receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 430(2–3):261–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0014-2999(01)01163-3
Ottani A, Vergoni AV, Saltini S et al (2004) Effect of late treatment with gamma-hydroxybutyrate on the histological and behavioral consequences of transient brain ischemia in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol 485(1–3):183–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2003.11.072
Palmer RB (2004) Gamma-butyrolactone and 1,4-butanediol: abused analogues of gamma-hydroxybutyrate. Toxicol Rev 23(1):21–31. https://doi.org/10.2165/00139709-200423010-00003
Pedraza C, Garcia FB, Navarro JF (2009) Neurotoxic effects induced by gammahydroxybutyric acid (GHB) in male rats. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 12(9):1165–1177. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1461145709000157
Picciotto MR, Higley MJ, Mineur YS (2012) Acetylcholine as a neuromodulator: cholinergic signaling shapes nervous system function and behavior. Neuron 76(1):116–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2012.08.036
Qin X (2015) Improving effect of Tujia Medicine Tianzhusan on learning and memory impairment caused by cerebral ischemia. Chinese Traditional & Herbal Drugs 46(3):389–395
Rekart JL, Meiri K, Routtenberg A (2005) Hippocampal-dependent memory is impaired in heterozygous GAP-43 knockout mice. Hippocampus 15(1):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1002/hipo.20045
Russo I, Caracciolo L, Tweedie D et al (2012) TNF, memory, Alzheimer. J Neurochem 122(6):1181–1192
Sadasivan S, Maher TJ, Quang LS (2010) -Hydroxybutyrate (GHB), -Butyrolactone (GBL), and 1,4-Butanediol (1,4-BD) Reduce the Volume of Cerebral Infarction in Rodent Transient Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion. Annals of the New York Academy of ences 1074(Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Drugs of Abuse and Neurotoxicity: Cocaine):537–544
Schmitt U, Tanimoto N, Seeliger M, Schaeffel F, Leube RE (2009) Detection of behavioral alterations and learning deficits in mice lacking synaptophysin. Neuroscience 162(2):234–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.04.046
Sériès F, Sériès I, Cormier Y (1992) Effects of enhancing slow-wave sleep by gamma-hydroxybutyrate on obstructive sleep apnea. Am Rev Respir Dis 145(6):1378–1383
Sgaravatti AM, Sgarbi MB, Testa CG et al (2007) Gamma-hydroxybutyric acid induces oxidative stress in cerebral cortex of young rats. Neurochem Int 50(3):564–570. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2006.11.007
Sgaravatti AM, Magnusson AS, Oliveira AS et al (2009) Effects of 1,4-butanediol administration on oxidative stress in rat brain: study of the neurotoxicity of gamma-hydroxybutyric acid in vivo. Metab Brain Dis 24(2):271–282. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-009-9136-7
Shen J, Li Y, Qu C, Xu L, Sun H, Zhang J (2019) The enriched environment ameliorates chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced depressive-like behaviors and cognitive impairment by activating the SIRT1/miR-134 signaling pathway in hippocampus. J Affect Disord 248:81–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2019.01.031
Snead OC (2010) Evidence for a G protein-coupled gamma-hydroxybutyric acid receptor. J Neurochem 75(5):1986–1996
Steele MT, Watson WA (1995) Acute poisoning from gamma hydroxybutyrate (GHB). Mo Med 92(7):354
Tha KK, Okuma Y, Miyazaki H et al (2000) Changes in expressions of proinflammatory cytokines IL-1beta, TNF-alpha and IL-6 in the brain of senescence accelerated mouse (SAM) P8. Brain Res 885(1):25–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0006-8993(00)02883-3
Thai D, Dyer JE, Jacob P, Haller CA (2007) Clinical pharmacology of 1,4-butanediol and gamma-hydroxybutyrate after oral 1,4-butanediol administration to healthy volunteers. Clin Pharmacol Ther 81(2):178–184. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.clpt.6100037
Trifilieff P, Calandreau L, Herry C, Mons N, Micheau J (2007) Biphasic ERK1/2 activation in both the hippocampus and amygdala may reveal a system consolidation of contextual fear memory. Neurobiol Learn Mem 88(4):424–434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nlm.2007.05.004
Tu H, Rondard P, Xu C et al (2007) Dominant role of GABAB2 and Gbetagamma for GABAB receptor-mediated-ERK1/2/CREB pathway in cerebellar neurons. Cell Signal 19(9):1996–2002. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2007.05.004
van Amsterdam JG, Brunt TM, McMaster MT, Niesink R, van Noorden MS, van den Brink W (2012a) Cognitive impairment due to intensive use and overdoses of gammahydroxybutyric acid (GHB). Tijdschr Psychiatr 54(12):1001–1010
van Amsterdam JG, Brunt TM, McMaster MT, Niesink RJ (2012b) Possible long-term effects of gamma-hydroxybutyric acid (GHB) due to neurotoxicity and overdose. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 36(4):1217–1227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2012.02.002
Won J, Silva AJ (2008) Molecular and cellular mechanisms of memory allocation in neuronetworks. Neurobiol Learn Mem 89(3):285–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nlm.2007.08.017
Wong CG, Gibson KM, Snead OC 3rd (2004) From the street to the brain: neurobiology of the recreational drug gamma-hydroxybutyric acid. Trends Pharmacol Sci 25(1):29–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tips.2003.11.001
Yarube I, Ayo J, Magaji R, Umar I (2019) Insulin treatment increases brain nitric oxide and oxidative stress, but does not affect memory function in mice. Physiol Behav 211:112640. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2019.112640
Yellamma, Kuna, Nirmala, Kumari, Research BJJoP (2013) Chronic effects of anti-Alzheimer's drug, Galantamine hydrobromide on cholinergic system of mice brain.
Yeo IJ, Yun J, Son DJ, Han SB, Hong JT (2020) Antifungal drug miconazole ameliorated memory deficits in a mouse model of LPS-induced memory loss through targeting iNOS. Cell Death Dis 11(8):623. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-2619-5
Yosunkaya A, Ak A, Bariskaner H, Ustun ME, Tuncer S, Gurbilek M (2004) Effect of gamma-hydroxybutyric acid on lipid peroxidation and tissue lactate level in experimental head trauma. J Trauma 56(3):585–590. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.ta.0000058119.60074.25
Youn SC, Chen LY, Chiou RJ et al (2015) Comprehensive Application of Time-of-flight Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry (TOF-SIMS) for Ionic Imaging and Bio-energetic Analysis of Club Drug-induced Cognitive Deficiency. Sci Rep 5:18420. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep18420
Zhang WP, Lin-Liang SU, Qiu YL, Zheng JP, Zhang C (2008) Acetylcholine regulates the ability of learning and spatial memory in rats. Journal of Shanxi Medical University
Zhao Z, Zhang Z, Li J et al (2020) Sustained TNF-alpha stimulation leads to transcriptional memory that greatly enhances signal sensitivity and robustness. Elife 9https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.61965
Acknowledgements
The authors thank all of the individuals who assisted in this study. In particular, we thank the South China Agricultural University for providing a good laboratory environment.
Funding
This work were supported by the Guangdong Key R&D Program, Department of Science and Technology of Guangdong Province (No. 2019B020210002), Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (No. 2021A1515010825) and Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Food Quality and Safety (NO.2020B1212060059).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: CC, LB, HL. Literature search: CC, HH, XX, GO. Original draft preparation: CC, LB, YR. Reviewing and editing: CC, HL, CL.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
Congying Chen, Lingling Bu, Huan Liu, Yifeng Rang, Huiying Huang, Xueman Xiao, Genghua Ou and Chunhong Liu have no conflicts of interest that are directly relevant to the content of this study.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, C., Bu, L., Liu, H. et al. Learning and memory impairment induced by 1,4-butanediol is regulated by ERK1/2-CREB-BDNF signaling pathways in PC12 cells. Metab Brain Dis 37, 1451–1463 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-022-00963-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-022-00963-0