Abstract
Purpose
Sevoflurane is a common used inhaled anesthetic that was reported to regulate the progression of multiple cancers. Here, we aimed to investigate the function and regulatory mechanism underlying sevoflurane in glioma cells.
Methods
A172 and U251 cells were treated with different concentrations of sevoflurane. Colony formation, EdU satining and 3-(4,5-dimethyl-2-thiazolyl)-2,5-diphenyl-2-H-tetrazolium bromide (MTT), flow cytometry, and transwell assays were performed to evaluate cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration and invasion, respectively. Circ_VCAN, microRNA-146b-5p (miR-146b-5p) and nuclear factor I B (NFIB) expression levels were assessed by real-time quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) or western blot. Bioinformatics analysis and dual-luciferase reporter assay were applied to evaluate the correlation between miR-146b-5p and circ_VCAN or NFIB. A xenograft glioma mice model was established to verify the effect of sevoflurane on tumor growth in vivo.
Results
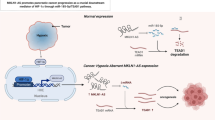
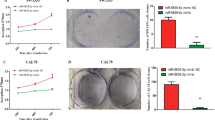
Sevoflurane (Sev) inhibited proliferation, migration, invasion, and elevated apoptosis of A172 and U251 cells. Sevoflurane treatment inhibited the expression of circ_VCAN and NFIB, but elevated the expression of miR-146b-5p in glioma cells. Overexpression of circ_VCAN alleviated the inhibition effects of sevoflurane on the malignant phenotypes of glioma in vitro and in vivo. Besides, miR-146b-5p is a target of circ_VCAN and negatively regulated NFIB expression. Overexpression of miR-146b-5p partly reversed the effects of circ_VCAN in Sev-treated glioma cells. Furthermore, miR-146b-5p deletion enhanced glioma progression in sevoflurane treated glioma cells by targeting NFIB. Moreover, circ_VCAN could upregulate NFIB expression by sponging miR-146b-5p in Sev-treated glioma cells.
Conclusion
Sevoflurane alleviated proliferation, migration and invasion, but enhanced apoptosis of glioma cells through regulating circ_VCAN/miR-146b-5p/NFIB axis.







Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The analyzed data sets generated during the present study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Becker-Santos DD, Lonergan KM, Gronostajski RM, Lam WL (2017) Nuclear Factor I/B: A Master Regulator of Cell Differentiation with Paradoxical Roles in Cancer. EBioMedicine 22:2–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2017.05.027
Chen KS, Lynton Z, Lim JWC, Robertson T, Gronostajski RM, Bunt J, Richards LJ (2021) NFIA and NFIB function as tumour suppressors in high-grade glioma in mice. Carcinogenesis 42:357–368. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/bgaa139
Chen LL, Yang L (2015) Regulation of circRNA biogenesis. RNA Biol 12:381–388. https://doi.org/10.1080/15476286.2015.1020271
Chen X, Yang F, Zhang T, Wang W, Xi W, Li Y, Zhang D, Huo Y, Zhang J, Yang A et al (2019) MiR-9 promotes tumorigenesis and angiogenesis and is activated by MYC and OCT4 in human glioma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 38:99. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-019-1078-2
Clark BS, Stein-O’Brien GL, Shiau F, Cannon GH, Davis-Marcisak E, Sherman T, Santiago CP, Hoang TV, Rajaii F, James-Esposito RE et al (2019) Single-Cell RNA-Seq Analysis of Retinal Development Identifies NFI Factors as Regulating Mitotic Exit and Late-Born Cell Specification. Neuron 102:1111-1126.e1115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2019.04.010
Cui XL, Wang XD, Lin SK, Miao CM, Wu M, Wei JG (2019) Circular RNA circ_0067934 functions as an oncogene in glioma by targeting CSF1. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 23: 8449–8455. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201910_19157
Fane M, Harris L, Smith AG, Piper M (2017) Nuclear factor one transcription factors as epigenetic regulators in cancer. Int J Cancer 140:2634–2641. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.30603
Gao C, Xu YJ, Qi L, Bao YF, Zhang L, Zheng L (2021) CircRNA VIM silence synergizes with sevoflurane to inhibit immune escape and multiple oncogenic activities of esophageal cancer by simultaneously regulating miR-124/PD-L1 axis. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-021-09613-0
He J, Zhao H, Liu X, Wang D, Wang Y, Ai Y, Yang J (2020) Sevoflurane suppresses cell viability and invasion and promotes cell apoptosis in colon cancer by modulating exosome-mediated circ-HMGCS1 via the miR-34a-5p/SGPP1 axis. Oncol Rep 44:2429–2442. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2020.7783
Jansson MD, Lund AH (2012) MicroRNA and cancer. Mol Oncol 6:590–610. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molonc.2012.09.006
Jiao B, Yang C, Huang NN, Yang N, Wei J, Xu H (2018) Relationship between Volatile Anesthetics and Tumor Progression: Unveiling the Mystery. Curr Med Sci 38:962–967. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-018-1970-6
Kvolik S, Dobrosevic B, Marczi S, Prlic L, Glavas-Obrovac L (2009) Different apoptosis ratios and gene expressions in two human cell lines after sevoflurane anaesthesia. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 53:1192–1199. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-6576.2009.02036.x
Li H, Xia T, Guan Y, Yu Y (2020) Sevoflurane Regulates Glioma Progression by Circ_0002755/miR-628-5p/MAGT1 Axis. Cancer Manag Res 12:5085–5098. https://doi.org/10.2147/cmar.s242135
Li J, Li Q, Lin L, Wang R, Chen L, Du W, Jiang C, Li R (2018) Targeting the Notch1 oncogene by miR-139-5p inhibits glioma metastasis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). BMC Neurol 18:133. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12883-018-1139-8
Li Y, Xu J, Zhang J, Zhang J, Zhang J, Lu X (2019a) MicroRNA-346 inhibits the growth of glioma by directly targeting NFIB. 19: 294. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-019-1017-5
Li Y, Xu J, Zhang J, Zhang J, Zhang J, Lu X (2019b) MicroRNA-346 inhibits the growth of glioma by directly targeting NFIB. Cancer Cell Int 19:294. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-019-1017-5
Li Z, Ruan Y, Zhang H, Shen Y, Li T, Xiao B (2019c) Tumor-suppressive circular RNAs: Mechanisms underlying their suppression of tumor occurrence and use as therapeutic targets. Cancer Sci 110:3630–3638. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.14211
Liang H, Gu M, Yang C, Wang H, Wen X, Zhou Q (2012) Sevoflurane inhibits invasion and migration of lung cancer cells by inactivating the p38 MAPK signaling pathway. J Anesth 26:381–392. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00540-011-1317-y
Liang H, Wang HB, Liu HZ, Wen XJ, Zhou QL, Yang CX (2013) The effects of combined treatment with sevoflurane and cisplatin on growth and invasion of human adenocarcinoma cell line A549. Biomed Pharmacother 67:503–509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2013.03.005
Linz U (2010) Commentary on Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial (Lancet Oncol. 2009;10:459–466). Cancer 116:1844–1846. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.24950
Liu J, Xu J, Li H, Sun C, Yu L, Li Y, Shi C, Zhou X, Bian X, Ping Y et al (2015) miR-146b-5p functions as a tumor suppressor by targeting TRAF6 and predicts the prognosis of human gliomas. Oncotarget 6: 29129–29142. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.4895
Liu L, Dong T, Sheng J (2021) Propofol Suppresses Gastric Cancer Progression by Regulating circPDSS1/miR-1324/SOX4 Axis. Cancer Manag Res 13:6031–6043. https://doi.org/10.2147/cmar.s312989
Liu RZ, Vo TM, Jain S, Choi WS, Garcia E, Monckton EA, Mackey JR, Godbout R (2019) NFIB promotes cell survival by directly suppressing p21 transcription in TP53-mutated triple-negative breast cancer. J Pathol 247:186–198. https://doi.org/10.1002/path.5182
Ma N, Li X, Wei H, Zhang H, Zhang S (2020) Circular RNA circNFATC3 acts as a miR-9-5p sponge to promote cervical cancer development by upregulating SDC2. Cell Oncol (Dordr). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-020-00555-z
Maass PG, Glažar P, Memczak S, Dittmar G, Hollfinger I, Schreyer L, Sauer AV, Toka O, Aiuti A, Luft FC et al (2017) A map of human circular RNAs in clinically relevant tissues. J Mol Med (berl) 95:1179–1189. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-017-1582-9
Maher EA, Furnari FB, Bachoo RM, Rowitch DH, Louis DN, Cavenee WK, DePinho RA (2001) Malignant glioma: genetics and biology of a grave matter. Genes Dev 15:1311–1333. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.891601
Mao W, Huang X, Wang L, Zhang Z, Liu M, Li Y, Luo M, Yao X, Fan J, Geng J (2019) Circular RNA hsa_circ_0068871 regulates FGFR3 expression and activates STAT3 by targeting miR-181a-5p to promote bladder cancer progression. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 38:169. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-019-1136-9
Memczak S, Jens M, Elefsinioti A, Torti F, Krueger J, Rybak A, Maier L, Mackowiak SD, Gregersen LH, Munschauer M et al (2013) Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with regulatory potency. Nature 495:333–338. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11928
Meng S, Zhou H, Feng Z, Xu Z, Tang Y, Li P, Wu M (2017) CircRNA: functions and properties of a novel potential biomarker for cancer. Mol Cancer 16:94. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-017-0663-2
Muller-Edenborn B, Roth-Z’graggen B, Bartnicka K, Borgeat A, Hoos A, Borsig L, Beck-Schimmer B (2012) Volatile anesthetics reduce invasion of colorectal cancer cells through down-regulation of matrix metalloproteinase-9. Anesthesiology 117:293–301. https://doi.org/10.1097/ALN.0b013e3182605df1
O'Farrell RA, Foley AG, Buggy DJ, Gallagher HC (2018) Neurotoxicity of Inhalation Anesthetics in the Neonatal Rat Brain: Effects on Behavior and Neurodegeneration in the Piriform Cortex. 2018: 6376090. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/6376090
O’Leary G, Bacon CL, Odumeru O, Fagan C, Fitzpatrick T, Gallagher HC, Moriarty DC, Regan CM (2000) Antiproliferative actions of inhalational anesthetics: comparisons to the valproate teratogen. Int J Dev Neurosci 18:39–45
Ramassone A, Pagotto S, Veronese A, Visone R (2018) Epigenetics and MicroRNAs in Cancer. Int J Mol Sci 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020459
Rybak-Wolf A, Stottmeister C, Glažar P, Jens M, Pino N, Giusti S, Hanan M, Behm M, Bartok O, Ashwal-Fluss R et al (2015) Circular RNAs in the Mammalian Brain Are Highly Abundant, Conserved, and Dynamically Expressed. Mol Cell 58:870–885. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2015.03.027
Sun J, Li B, Shu C, Ma Q, Wang J (2020) Functions and clinical significance of circular RNAs in glioma. Mol Cancer 19:34. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-019-1121-0
Sun Q, Xu R, Xu H, Wang G, Shen X, Jiang H (2017) Extracranial metastases of high-grade glioma: the clinical characteristics and mechanism. World J Surg Oncol 15:181. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12957-017-1249-6
Tabnak P, Masrouri S, Geraylow KR, Zarei M, Esmailpoor ZH (2021) Targeting miRNAs with anesthetics in cancer: Current understanding and future perspectives. Biomed Pharmacother 144:112309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112309
Tang Q, Hann SS (2020) Biological Roles and Mechanisms of Circular RNA in Human Cancers. Onco Targets Ther 13:2067–2092. https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S233672
Wang L, Wang T, Gu JQ, Su HB (2018) Volatile anesthetic sevoflurane suppresses lung cancer cells and miRNA interference in lung cancer cells. Onco Targets Ther 11:5689–5693. https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S171672
Wang M, Suo L, Yang S, Zhang W (2020) CircRNA 001372 Reduces Inflammation in Propofol-Induced Neuroinflammation and Neural Apoptosis through PIK3CA/Akt/NF-κB by miRNA-148b-3p. J Invest Surg: 1-11. https://doi.org/10.1080/08941939.2020.1771639
Wen J, Ding Y, Zheng S, Li X, Xiao Y (2020) Sevoflurane Suppresses Glioma Cell Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion Both In Vitro and In Vivo Partially Via Regulating KCNQ1OT1/miR-146b-5p/STC1 Axis. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. https://doi.org/10.1089/cbr.2020.3762
Westphal M, Lamszus K (2011) The neurobiology of gliomas: from cell biology to the development of therapeutic approaches. Nat Rev Neurosci 12:495–508. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn3060
Yang B, Zhou Z-H, Chen L, Cui X, Hou J-Y, Fan K-J, Han S-H, Li P, Yi S-Q, Liu Y (2018) Prognostic significance of NFIA and NFIB in esophageal squamous carcinoma and esophagogastric junction adenocarcinoma. Cancer Med 7:1756–1765. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.1434
Zhan X, Lei C, Yang L (2021) Sevoflurane inhibits cell proliferation and migration of glioma by targeting the miR‑27b/VEGF axis. Mol Med Rep 23. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2021.12047
Zhang L, Wang J, Fu Z, Ai Y, Li Y, Wang Y, Wang Y (2019a) Sevoflurane suppresses migration and invasion of glioma cells by regulating miR-146b-5p and MMP16. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 47:3306–3314. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2019.1648282
Zhang Y, Liu HL, An LJ, Li L, Wei M, Ge DJ, Su Z (2019b) miR-124-3p attenuates neuropathic pain induced by chronic sciatic nerve injury in rats via targeting EZH2. J Cell Biochem 120:5747–5755. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.27861
Zhao H, Xing F, Yuan J, Li Z, Zhang W (2020) Sevoflurane inhibits migration and invasion of glioma cells via regulating miR-34a-5p/MMP-2 axis. Life Sci 256:117897. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117897
Zheng J, Liu X, Xue Y, Gong W, Ma J, Xi Z, Que Z, Liu Y (2017) TTBK2 circular RNA promotes glioma malignancy by regulating miR-217/HNF1β/Derlin-1 pathway. J Hematol Oncol 10:52. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-017-0422-2
Zhu C, Mao X, Zhao H (2020) The circ_VCAN with radioresistance contributes to the carcinogenesis of glioma by regulating microRNA-1183. Medicine (baltimore) 99:e19171. https://doi.org/10.1097/md.0000000000019171
Zhu Y, Wu G, Yan W, Zhan H, Sun P (2017) miR-146b-5p regulates cell growth, invasion, and metabolism by targeting PDHB in colorectal cancer. Am J Cancer Res 7:1136–1150
Funding
This work was supported by Joint project of Medical Science and Technology Research Plan of Henan Province in 2019, project No.: LHGJ20191441.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization and Methodology: Guofang Cheng, Lili Quan and Haibo Qu; Formal analysis and Data curation: Ailing Yang, Jiangge Ye and Yuanbo Feng; Validation and Investigation: Haili Wang, Xiaofang Li, Xiaoli Shi and Hua Pan; Writing—original draft preparation and Writing—review and editing: Haili Wang, Guofang Cheng, Lili Quan, Haibo Qu and Hua Pan; Approval of final manuscript: all authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Consent for publication
Patients agree to participate in this work.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
1. Sevoflurane inhibited the malignant phenotypes of glioma in vitro and in vivo.
2. Circ_VCAN upregulated NFIB expression by sponging miR-146b-5p.
3. Sevoflurane repressed glioma progression by regulating circ_VCAN/miR-146b-5p/NFIB axis.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Cheng, G., Quan, L. et al. Sevoflurane inhibits the malignant phenotypes of glioma through regulating miR-146b-5p/NFIB axis. Metab Brain Dis 37, 1373–1386 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-022-00959-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-022-00959-w