Abstract
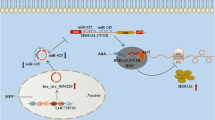
Circular RNAs (circRNAs) was suggested to play crucial regulatory roles in various human diseases, including Parkinson’s disease (PD). This research aimed to investigate the function and potential mechanism of circ_0070441 in PD. MPP+ (1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium)-treated SH-SY5Y cells was used as an in vitro cellular PD model. The expressions of circ_0070441, microRNA (miR)-626 and insulin receptor substrate 2 (IRS2) were measured by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) or western blot. Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) assay, Cytotoxicity Detection Kit (Lactate Dehydrogenase), flow cytometry and Caspase-3 Assay Kit were used to detect cell viability, LDH release, cell apoptosis and caspase-3 activity, respectively. The levels of inflammation-related factors were detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The correlation among circ_0070441, miR-626 and IRS2 were confirmed by dual-luciferase reporter assay, RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) assay and RNA pull-down assay. The levels of circ_0070441 and IRS2 were increased while miR-626 expression was decreased in MPP+-treated SH-SY5Y cells in dose- and time-dependent manners. Depletion of circ_0070441 alleviated MPP+-triggered neuronal damage by regulating cell apoptosis and inflammation. Circ_0070441 acted as a sponge for miR-626, and IRS2 was a target of miR-626. Besides, the neuroprotective effects of circ_0070441 knockdown or miR-626 overexpression were partly overturned by the suppression of miR-626 or IRS2 overexpression. Moreover, circ_0070441 upregulated IRS2 expression by interacting with miR-626. In summary, circ_0070441 aggravated MPP+-triggered neurotoxic effect in SH-SY5Y cells by regulating miR-626/IRS2 axis.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Armstrong MJ, Okun MS (2020) Diagnosis and treatment of Parkinson disease: a review. JAMA 323(6):548–560
Ascherio A, Schwarzschild MA (2016) The epidemiology of Parkinson’s disease: risk factors and prevention. Lancet Neurol 15(12):1257–1272
Coelho M, Ferreira JJ (2012) Late-stage Parkinson disease. Nat Rev Neurol 8(8):435–442
D’Ambra E, Capauto D, Morlando M (2019) Exploring the regulatory role of circular RNAs in neurodegenerative disorders. Int J Mol Sci 20(21):5477
Ding XM, Zhao LJ, Qiao HY, Wu SL, Wang XH (2019) Long non-coding RNA-p21 regulates MPP(+)-induced neuronal injury by targeting miR-625 and derepressing TRPM2 in SH-SY5Y cells. Chem Biol Interact 307:73–81
Dong W, Bi J, Liu H, Yan D, He Q, Zhou Q et al (2019) Circular RNA ACVR2A suppresses bladder cancer cells proliferation and metastasis through miR-626/EYA4 axis. Mol Cancer 18(1):95
Gámez-Valero A, Guisado-Corcoll A, Herrero-Lorenzo M, Solaguren-Beascoa M, Martí E (2020) Non-coding RNAs as sensors of oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. Antioxidants (Basel) 9(11):1095
Hallett PJ, Engelender S, Isacson O (2019) Lipid and immune abnormalities causing age-dependent neurodegeneration and Parkinson’s disease. J Neuroinflammation 16(1):153
Hanan M, Simchovitz A, Yayon N, Vaknine S, Cohen-Fultheim R, Karmon M et al (2020) A Parkinson’s disease CircRNAs Resource reveals a link between circSLC8A1 and oxidative stress. EMBO Mol Med 12(9):e11942
Hansen TB, Jensen TI, Clausen BH, Bramsen JB, Finsen B, Damgaard CK et al (2013) Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature 495(7441):384–388
Jia E, Zhou Y, Liu Z, Wang L, Ouyang T, Pan M et al (2020) Transcriptomic profiling of circular RNA in different brain regions of Parkinson’s disease in a mouse model. Int J Mol Sci 21(8):3006
Juzwik CA, S SD, Zhang Y, Paradis-Isler N, Sylvester A, Amar-Zifkin A et al (2019) microRNA dysregulation in neurodegenerative diseases: A systematic review. Prog Neurobiol 182:101664
Kalia LV, Lang AE (2015) Parkinson’s disease. Lancet 386(9996):896–912
Khoo SK, Petillo D, Kang UJ, Resau JH, Berryhill B, Linder J et al (2012) Plasma-based circulating MicroRNA biomarkers for Parkinson’s disease. J Parkinsons Dis 2(4):321–331
Kristensen LS, Andersen MS, Stagsted LVW, Ebbesen KK, Hansen TB, Kjems J (2019) The biogenesis, biology and characterization of circular RNAs. Nat Rev Genet 20(11):675–691
Liu Q, Cao G, Wan Y, Xu C, He Y, Li G (2021) Hsa_circ_0001073 targets miR-626/LIFR axis to inhibit lung cancer progression. Environ Toxicol 36(6):1052–1060
Peng T, Liu X, Wang J, Liu Y, Fu Z, Ma X et al (2019) Long noncoding RNA HAGLROS regulates apoptosis and autophagy in Parkinson’s disease via regulating miR-100/ATG10 axis and PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway activation. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 47(1):2764–2774
Qin LX, Tan JQ, Zhang HN, Tang JG, Jiang B, Shen XM et al (2019) Preliminary study of hsa-miR-626 change in the cerebrospinal fluid of Parkinson’s disease patients. J Clin Neurosci 70:198–201
Qin LX, Tan JQ, Zhang HN, Tang JG, Jiang B, Shen XM et al (2021) Preliminary study of hsa-mir-626 change in the cerebrospinal fluid in Parkinson’s disease. Neurol India 69(1):115–118
Ravanidis S, Bougea A, Karampatsi D, Papagiannakis N, Maniati M, Stefanis L et al (2021) Differentially expressed circular RNAs in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 36(5):1170–1179
Rostamian Delavar M, Baghi M, Safaeinejad Z, Kiani-Esfahani A, Ghaedi K, Nasr-Esfahani MH (2018) Differential expression of miR-34a, miR-141, and miR-9 in MPP+-treated differentiated PC12 cells as a model of Parkinson’s disease. Gene 662:54–65
Salmena L, Poliseno L, Tay Y, Kats L, Pandolfi PP (2011) A ceRNA hypothesis: the Rosetta Stone of a hidden RNA language? Cell 146(3):353–358
Sang Q, Liu X, Wang L, Qi L, Sun W, Wang W et al (2018) CircSNCA downregulation by pramipexole treatment mediates cell apoptosis and autophagy in Parkinson’s disease by targeting miR-7. Aging 10(6):1281–1293
Schildknecht S, Di Monte DA, Pape R, Tieu K, Leist M (2017) Tipping points and endogenous determinants of nigrostriatal degeneration by MPTP. Trends Pharmacol Sci 38(6):541–555
Shi J, Bao X, Liu Z, Zhang Z, Chen W, Xu Q (2019) Serum miR-626 and miR-5100 are promising prognosis predictors for oral squamous cell carcinoma. Theranostics 9(4):920–931
Soreq L, Ben-Shaul Y, Israel Z, Bergman H, Soreq H (2012) Meta-analysis of genetic and environmental Parkinson’s disease models reveals a common role of mitochondrial protection pathways. Neurobiol Dis 45(3):1018–1030
Sun Q, Wang S, Chen J, Cai H, Huang W, Zhang Y et al (2019) MicroRNA-190 alleviates neuronal damage and inhibits neuroinflammation via Nlrp3 in MPTP-induced Parkinson’s disease mouse model. J Cell Physiol 234(12):23379–23387
Wakabayashi T, Yamaguchi K, Matsui K, Sano T, Kubota T, Hashimoto T et al (2019) Differential effects of diet- and genetically-induced brain insulin resistance on amyloid pathology in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Neurodegener 14(1):15
Wang M, Sun H, Yao Y, Tang X, Wu B (2019) MicroRNA-217/138-5p downregulation inhibits inflammatory response, oxidative stress and the induction of neuronal apoptosis in MPP(+)-induced SH-SY5Y cells. Am J Transl Res 11(10):6619–6631
White MF (2002) IRS proteins and the common path to diabetes. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 283(3):E413–E422
White MF (2014) IRS2 integrates insulin/IGF1 signalling with metabolism, neurodegeneration and longevity. Diabetes Obes Metab 16(Suppl 1):4–15
Xie Y, Zhang S, Lv Z, Long T, Luo Y, Li Z (2021) SOX21-AS1 modulates neuronal injury of MMP(+)-treated SH-SY5Y cells via targeting miR-7-5p and inhibiting IRS2. Neurosci Lett 746:135602
Yang L, Mao K, Yu H, Chen J (2020) Neuroinflammatory responses and Parkinson’ disease: pathogenic mechanisms and therapeutic targets. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 15(4):830–837
Zhou DN, Ye CS, Deng YF (2020) CircRNAs: potency of protein translation and feasibility of novel biomarkers and therapeutic targets for head and neck cancers. Am J Transl Res 12(5):1535–1552
Zhu P, Liang H, Huang X, Zeng Q, Liu Y, Lv J et al (2020) Circular RNA Hsa_circ_0004018 inhibits Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway by targeting microRNA-626/DKK3 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Onco Targets Ther 13:9351–9364
Funding
The project was funded by Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region Key Research and Development Project (No. 2017BY037) and Ningxia Natural Science Foundation Project (No. NZ17189).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XC and JG designed, supervised the study, conducted the experiments and drafted the manuscript. DX, TZ and HH collected and analyzed the data. HM and TM contributed the methodology and analyzed the data. MQ and JH operated the software and edited the manuscript. XC was a major contributor in writing the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Xuqing Cao and Jiangtao Guo are co-authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, X., Guo, J., Mochizuki, H. et al. Circular RNA circ_0070441 regulates MPP+-triggered neurotoxic effect in SH-SY5Y cells via miR-626/IRS2 axis. Metab Brain Dis 37, 513–524 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-021-00869-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-021-00869-3