Abstract
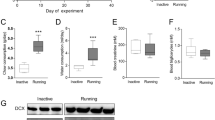
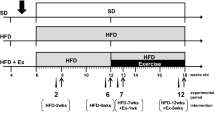
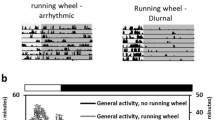
The search for strategies to develop resilience against metabolic and neuropsychiatric disorders has motivated the clinical and experimental assessment of early life interventions such as lifestyle-based and use of unconventional pharmacological compounds. In this study, we assessed the effects of voluntary physical activity and 7,8-Dihydroxy-4-methylcoumarin (DHMC), independently or in combination, over mice physiological and behavioral parameters, adult hippocampal and hypothalamic neurogenesis, and neurotrophic factors expression in the hypothalamus. C57Bl/6J mice were submitted to a 29-day treatment with DHMC and allowed free access to a running wheel. We found that DHMC treatment alone reduced fasting blood glucose levels. Moreover, physical activity showed an anxiolytic effect in the elevated plus maze task and DHMC produced additional anxiolytic behavior, evidenced by reduced activity during the light cycle in the physical activity group. Although we did not find any differences in hypothalamic or hippocampal adult neurogenesis, DHMC increased gene expression levels of VEGF, which was correlated to the reduced fasting glucose levels. In conclusion, our data emphasize the potential of physical activity in reducing development of neuropsychiatric conditions, such as anxiety, and highlights DHMC as an attractive compound to be investigated in future studies addressing neuropsychiatric disorders associated with metabolic conditions.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Adu-Nti F et al (2021) Osthole ameliorates estrogen deficiency-induced cognitive impairment in female mice. Front Pharmacol. https://doi.org/10.3389/FPHAR.2021.641909
Ahmed S, Nur-e-Alam M, Parveen I et al (2020) Stimulation of insulin secretion by 5-methylcoumarins and its sulfur analogues isolated from Clutia lanceolata Forssk. Phytochemistry 170:112213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2019.112213
Alkadhi KA (2018) Exercise as a positive modulator of brain function. Mol Neurobiol 55:3112–3130. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-017-0516-4
Alleva E, Francia N (2009) Psychiatric vulnerability: suggestions from animal models and role of neurotrophins. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 33:525–536. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2008.09.004
An JJ, Kinney CE, Tan J-W et al (2020) TrkB-expressing paraventricular hypothalamic neurons suppress appetite through multiple neurocircuits. Nat Commun 11:1729. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-15537-w
Andrikopoulos S et al (2008) Evaluating the glucose tolerance test in mice. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 295(6):1323–1332. https://doi.org/10.1152/AJPENDO.90617.2008
Angevaren M, Aufdemkampe G, Verhaar HJJ et al (2008) Physical activity and enhanced fitness to improve cognitive function in older people without known cognitive impairment. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD005381.pub3
Armstrong MJ, Okun MS (2020) Diagnosis and treatment of Parkinson disease: a review. JAMA 323:548–560. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2019.22360
Bădescu S, Tătaru C, Kobylinska L et al (2016) The association between diabetes mellitus and depression. J Med Life 9:120–125
Bhatti GK, Reddy AP, Reddy PH, Bhatti JS (2020) Lifestyle modifications and nutritional interventions in aging-associated cognitive decline and Alzheimer’s disease. Front Aging Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2019.00369
Caliskan H, Akat F, Tatar Y et al (2019) Effects of exercise training on anxiety in diabetic rats. Behav Brain Res 376:112084. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2019.112084
Carrera I, Martínez O, Cacabelos R (2020) Neuroprotection with natural antioxidants and nutraceuticals in the context of brain cell degeneration: the epigenetic connection. CTMC 19:2999–3011. https://doi.org/10.2174/1568026619666191202155738
Caspersen CJ, Powell KE, Christenson GM (1985) Physical activity, exercise, and physical fitness: definitions and distinctions for health-related research. Public Health Rep 100:126–131
Chen C, Shan W (2019) Pharmacological and non-pharmacological treatments for major depressive disorder in adults: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Psychiatry Res 281:112595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2019.112595
Choi SH, Bylykbashi E, Chatila ZK et al (2018) Combined adult neurogenesis and BDNF mimic exercise effects on cognition in an Alzheimer’s mouse model. Science 361:eaan8821. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aan8821
Cooper-Kuhn C et al (2002) Is it all DNA repair? Methodological considerations for detecting neurogenesis in the adult brain. Dev Brain Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0165-3806(01)00243-7
Cotman CW, Berchtold NC, Christie L-A (2007) Exercise builds brain health: key roles of growth factor cascades and inflammation. Trends Neurosci 30:464–472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2007.06.011
Cunha MP, Oliveira Á, Pazini FL et al (2013) The antidepressant-like effect of physical activity on a voluntary running wheel. Med Sci Sports Exerc 45:851–859. https://doi.org/10.1249/MSS.0b013e31827b23e6
Curran E, Rosato M, Ferry F, Leavey G (2020) Prevalence and factors associated with anxiety and depression in older adults: gender differences in psychosocial indicators. J Affect Disord 267:114–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2020.02.018
Deng W, Aimone JB, Gage FH (2010) New neurons and new memories: how does adult hippocampal neurogenesis affect learning and memory? Nat Rev Neurosci 11:339–350. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn2822
Dugger BN, Dickson DW (2017) Pathology of neurodegenerative diseases. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 9:a028035. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a028035
Duman RS (2009) Neuronal damage and protection in the pathophysiology and treatment of psychiatric illness: stress and depression. Dialogues Clin Neurosci 11:239–255
Duman RS, Heninger GR, Nestler EJ (1997) A molecular and cellular theory of depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry 54:597–606. https://doi.org/10.1001/archpsyc.1997.01830190015002
Estrada JA, Contreras I (2019) Nutritional modulation of immune and central nervous system homeostasis: the role of diet in development of neuroinflammation and neurological disease. Nutrients 11:1076. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11051076
Fabel K, Fabel K, Tam B et al (2003) VEGF is necessary for exercise-induced adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Eur J Neurosci 18:2803–2812. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9568.2003.03041.x
Fargali S, Sadahiro M, Jiang C et al (2012) Role of neurotrophins in the development and function of neural circuits that regulate energy homeostasis. J Mol Neurosci 48:654–659. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-012-9790-9
Gao Z, Wen Q, Xia Y et al (2014) Osthole augments therapeutic efficiency of neural stem cells-based therapy in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Pharmacol Sci 124:54–65. https://doi.org/10.1254/jphs.13144fp
Gao Q, Jeon SJ, Jung HA et al (2015) Nodakenin enhances cognitive function and adult hippocampal neurogenesis in mice. Neurochem Res 40:1438–1447. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-015-1612-3
Hill AS, Sahay A, Hen R (2015) Increasing adult hippocampal neurogenesis is sufficient to reduce anxiety and depression-like behaviors. Neuropsychopharmacology 40:2368–2378. https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2015.85
Hötting K, Röder B (2013) Beneficial effects of physical exercise on neuroplasticity and cognition. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 37:2243–2257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2013.04.005
Ivić V, Blažetić S, Labak I et al (2016) Ovariectomy and chronic stress lead toward leptin resistance in the satiety centers and insulin resistance in the hippocampus of Sprague-Dawley rats. Croat Med J 57:194–206. https://doi.org/10.3325/cmj.2016.57.194
Jais A, Solas M, Backes H et al (2016) Myeloid-cell-derived VEGF maintains brain glucose uptake and limits cognitive impairment in obesity. Cell 165:882–895. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2016.03.033
Jameel E, Umar T, Kumar J, Hoda N (2016) Coumarin: a privileged scaffold for the design and development of antineurodegenerative agents. Chem Biol Drug Des 87:21–38. https://doi.org/10.1111/cbdd.12629
Jelenik T, Dille M, Müller-Lühlhoff S et al (2018) FGF21 regulates insulin sensitivity following long-term chronic stress. Mol Metab 16:126–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmet.2018.06.012
Jin X, Wang Y, Li X et al (2015) 7,8-Dihydroxy-4-methylcoumarin provides neuroprotection by increasing hippocalcin expression. Neurotox Res 27:268–274. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-014-9507-7
Kadakol A, Sharma N, Kulkarni YA, Gaikwad AB (2016) Esculetin: a phytochemical endeavor fortifying effect against non-communicable diseases. Biomed Pharmacother 84:1442–1448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2016.10.072
Kandola A, Vancampfort D, Herring M et al (2018) Moving to beat anxiety: epidemiology and therapeutic issues with physical activity for anxiety. Curr Psychiatry Rep 20:63. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11920-018-0923-x
Kang SY, Kim YC (2007) Decursinol and decursin protect primary cultured rat cortical cells from glutamate-induced neurotoxicity. J Pharm Pharmacol 59:863–870. https://doi.org/10.1211/jpp.59.6.0013
Kessing LV, Willer IS, Knorr U (2011) Volume of the adrenal and pituitary glands in depression. Psychoneuroendocrinology 36:19–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psyneuen.2010.05.007
Kokoeva MV (2005) Neurogenesis in the hypothalamus of adult mice: potential role in energy balance. Science 310:679–683. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1115360
Kokoeva MV, Yin H, Flier JS (2007) Evidence for constitutive neural cell proliferation in the adult murine hypothalamus. J Comp Neurol 505:209–220. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.21492
Kronenberg G, Bick-Sander A, Bunk E et al (2006) Physical exercise prevents age-related decline in precursor cell activity in the mouse dentate gyrus. Neurobiol Aging 27:1505–1513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2005.09.016
Langlet F, Levin BE, Luquet S et al (2013) Tanycytic VEGF-A boosts blood-hypothalamus barrier plasticity and access of metabolic signals to the arcuate nucleus in response to fasting. Cell Metab 17:607–617. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2013.03.004
Lee DA, Bedont JL, Pak T et al (2012) Tanycytes of the hypothalamic median eminence form a diet-responsive neurogenic niche. Nat Neurosci 15:700–702. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.3079
Li J, Tang Y, Cai D (2012) IKKβ/NF-κB disrupts adult hypothalamic neural stem cells to mediate a neurodegenerative mechanism of dietary obesity and pre-diabetes. Nat Cell Biol 14:999–1012. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb2562
Lyra e Silva NDM, Gonçalves RA, Boehnke SE et al (2019) Understanding the link between insulin resistance and Alzheimer’s disease: insights from animal models. Exp Neurol 316:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2019.03.016
Ming G, Song H (2011) Adult neurogenesis in the mammalian brain: significant answers and significant questions. Neuron 70:687–702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2011.05.001
Molina-Jiménez MF, Sánchez-Reus MI, Cascales M et al (2005) Effect of fraxetin on antioxidant defense and stress proteins in human neuroblastoma cell model of rotenone neurotoxicity. Comparative study with myricetin and N-acetylcysteine. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 209:214–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2005.04.009
Musiek ES, Holtzman DM (2016) Mechanisms linking circadian clocks, sleep, and neurodegeneration. Science 354:1004–1008. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aah4968
Myers MG, Olson DP (2012) Central nervous system control of metabolism. Nature 491:357–363. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11705
Niwa A, Nishibori M, Hamasaki S et al (2016) Voluntary exercise induces neurogenesis in the hypothalamus and ependymal lining of the third ventricle. Brain Struct Funct 221:1653–1666. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-015-0995-x
Nowacka MM, Paul-Samojedny M, Bielecka AM et al (2015) LPS reduces BDNF and VEGF expression in the structures of the HPA axis of chronic social stressed female rats. Neuropeptides 54:17–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.npep.2015.09.003
Potdar MK, Mohile SS, Salunkhe MM (2001) Coumarin syntheses via Pechmann condensation in Lewis acidic chloroaluminate ionic liquid. Tetrahedron Lett 42:9285–9287. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-4039(01)02041-X
Price JL, Drevets WC (2010) Neurocircuitry of mood disorders. Neuropsychopharmacology 35:192–216. https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2009.104
Qin T, Fang F, Song M et al (2017) Umbelliferone reverses depression-like behavior in chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced rats by attenuating neuronal apoptosis via regulating ROCK/Akt pathway. Behav Brain Res 317:147–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2016.09.039
Rajadurai M, Stanely Mainzen Prince P (2006) Preventive effect of naringin on lipid peroxides and antioxidants in isoproterenol-induced cardiotoxicity in Wistar rats: biochemical and histopathological evidences. Toxicology 228:259–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2006.09.005
Randjelovic PJ et al (2020) Anxiolytic-like action of selected 4-(alkylamino)-3-nitrocoumarin derivatives in BALB/c mice. Chem Biodivers. https://doi.org/10.1002/CBDV.202000206
Russell G, Lightman S (2019) The human stress response. Nat Rev Endocrinol 15:525–534. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41574-019-0228-0
Sahay A, Hen R (2008) Hippocampal neurogenesis and depression. Novartis Found Symp 289:152–160
Santarelli L, Saxe M, Gross C et al (2003) Requirement of hippocampal neurogenesis for the behavioral effects of antidepressants. Science 301:805–809. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1083328
Schneeberger M, Gomis R, Claret M (2014) Hypothalamic and brainstem neuronal circuits controlling homeostatic energy balance. J Endocrinol 220:T25–T46. https://doi.org/10.1530/JOE-13-0398
Schüler R, Seebeck N, Osterhoff MA et al (2018) VEGF and GLUT1 are highly heritable, inversely correlated and affected by dietary fat intake: consequences for cognitive function in humans. Mol Metab 11:129–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmet.2018.02.004
Shapiro A, Cheng K-Y, Gao Y et al (2011) The act of voluntary wheel running reverses dietary hyperphagia and increases leptin signaling in ventral tegmental area of aged obese rats. GER 57:335–342. https://doi.org/10.1159/000321343
Skalicka-Woźniak K, Orhan IE, Cordell GA et al (2016) Implication of coumarins towards central nervous system disorders. Pharmacol Res 103:188–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2015.11.023
Spartano NL, Stevenson MD, Xanthakis V et al (2017) Associations of objective physical activity with insulin sensitivity and circulating adipokine profile: the Framingham Heart Study. Clin Obesity 7:59–69. https://doi.org/10.1111/cob.12177
Swift DL, McGee JE, Earnest CP et al (2018) The effects of exercise and physical activity on weight loss and maintenance. Prog Cardiovasc Dis 61:206–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pcad.2018.07.014
Togashi Y, Shirakawa J, Okuyama T et al (2016) Evaluation of the appropriateness of using glucometers for measuring the blood glucose levels in mice. Sci Rep 6:25465. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep25465
Togna AR, Firuzi O, Latina V et al (2014) 4-Methylcoumarin derivatives with anti-inflammatory effects in activated microglial cells. Biol Pharm Bull 37:60–66. https://doi.org/10.1248/bpb.b13-00568
Tyagi YK, Kumar A, Raj HG et al (2005) Synthesis of novel amino and acetyl amino-4-methylcoumarins and evaluation of their antioxidant activity. Eur J Med Chem 40:413–420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2004.09.002
van Praag H, Kempermann G, Gage FH (1999) Running increases cell proliferation and neurogenesis in the adult mouse dentate gyrus. Nat Neurosci 2:266–270. https://doi.org/10.1038/6368
van Praag H, Shubert T, Zhao C, Gage FH (2005) Exercise enhances learning and hippocampal neurogenesis in aged mice. J Neurosci 25:8680–8685. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1731-05.2005
Wilson ML (2017) Prediabetes: beyond the borderline. Nurs Clin North Am 52:665–677. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cnur.2017.07.011
Wu L, Wang X, Xu W et al (2009) The structure and pharmacological functions of coumarins and their derivatives. Curr Med Chem 16:4236–4260. https://doi.org/10.2174/092986709789578187
Xu B, Goulding EH, Zang K et al (2003) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor regulates energy balance downstream of melanocortin-4 receptor. Nat Neurosci 6:736–742. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1073
Yang M, Luo C-H, Zhu Y-Q et al (2020) 7, 8-Dihydroxy-4-methylcoumarin reverses depression model-induced depression-like behaviors and alteration of dendritic spines in the mood circuits. Psychoneuroendocrinology 119:104767. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psyneuen.2020.104767
Yao Y, Gao Z, Liang W et al (2015) Osthole promotes neuronal differentiation and inhibits apoptosis via Wnt/β-catenin signaling in an Alzheimer’s disease model. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 289:474–481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2015.10.013
Acknowledgements
We thank the access to equipment and assistance provided by the National Institute of Science and Technology on Photonics Applied to Cell Biology (INFABIC) at the State University of Campinas.
Funding
The study was supported by Grants from the Minas Gerais Research Support Foundation (FAPEMIG), Conselho Nacional de Pesquisa e Desenvolvimento Cientifico (CNPq), São Paulo Research Foundation (2013/07607-8), and financed in part by the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior—Brasil (CAPES); INFABIC is co-funded by São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP) (2014/50938-8) and Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) (465699/2014-6).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PKFL and DFE performed experiments and analyzed the data; MSAM and NOB assisted voluntary physical activity experiments. SST guided the DMHC synthesis process. LAV provision of materials and aid for molecular analysis. PKFL and DFE wrote the manuscript; RFM designed the study; all authors revised and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Ethical approval
All experimental procedures were carried out in accordance with the National Institutes of Health Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, with the approval of the Ethics Committee of the Federal University of Lavras/Brazil and Animal Experiments Control Council (CONCEA), according to protocol nº 078/17.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lopes, P.K.F., Engel, D.F., Bertolini, N.O. et al. Behavioral, neuroplasticity and metabolic effects of 7,8-dihydroxy-4-methylcoumarin associated with physical activity in mice. Metab Brain Dis 36, 2425–2436 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-021-00849-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-021-00849-7