Abstract
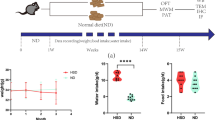
Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) improves obesity-induced cognitive dysfunction, but its mechanism is not fully clarified. The aim of the study was to reveal whether IGF-1 treated cognitive dysfunction by improving tau pathology and neuronal pyroptosis in high-fat diet mice. During in vitro experiment, C57BL/6J mice were fed with high-fat diet, and were treated with PEG-IGF-1, IGF-1 receptor blocker AXL1717, HO-1 blocker Znpp IX or their combinations. Cognitive function was evaluated using Morris water maze. Expression of Nrf2, HO-1, p-tau, NLRP3, caspase-1 and IL-1β in hippocampus was determined using western blotting. Pyroptosis rate in hippocampus was measured using flow cytometry. During in vivo experiment, HN-h cells were treated with palmitic acid, pyroptosis blocker nonecrosulfonamide or their combinations. The expression of the proteins and rate of pyroptosis were also measured using western blotting and flow cytometry. During in vitro experiment, high-fat diet mice showed cognitive dysfunction, significant hyperphosphorylation of tau protein and neuronal pyroptosis in hippocampus compared with the sham mice. After exogenous IGF-1 treatment, these abnormalities were reversed and Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway was activated. Inhibition of the signaling pathway using AXL1717 or Znpp IX re-deteriorated cognitive function, tau pathology and neuronal pyroptosis in hippocampus. During in vivo experiment, inhibition of pyroptosis using nonecrosulfonamide improved tau pathology in palmitic acid-treated HN-h cells. Exogenous IGF-1 improved tau pathology induced by high-fat diet through inhibition of neuronal pyroptosis and activation of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway.







Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
The data cannot be shared because this is an ongoing study.
Code availability
All analysis is performed by Statistical Product and Service Solutions 19.0.
References
Abu-Rumeileh S, Capellari S, Parchi P (2018) Rapidly progressive alzheimer’s disease: contributions to clinical-pathological definition and diagnosis. J Alzheimers Dis 63:887–897
Al Mamun A, Wu Y, Monalisa I et al (2020) Role of pyroptosis in spinal cord injury and its therapeutic implications. J Adv Res 28:97–109
Ali T, Kim T, Rehman SU et al (2018) Natural dietary supplementation of anthocyanins via PI3K/Akt/Nrf2/HO-1 pathways mitigate oxidative stress, neurodegeneration, and memory impairment in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Neurobiol 55:6076–6093
Barnhart CD, Yang D, Lein PJ (2015) Using the Morris water maze to assess spatial learning and memory in weanling mice. PLoS ONE 10:e0124521
Brito-Casillas Y, Melián C, Wägner AM (2016) Study of the pathogenesis and treatment of diabetes mellitus through animal models. Endocrinol Nutr 63:345–353
Brody DL, Holtzman DM (2006) Morris water maze search strategy analysis in PDAPP mice before and after experimental traumatic brain injury. Exp Neurol 197:330–340
Bromley-Brits K, Deng Y, Song W (2011) Morris water maze test for learning and memory deficits in Alzheimer's disease model mice. J Vis Exp 2920.
Chen W, He B, Tong W et al (2019) Astrocytic insulin-like growth factor-1 protects neurons against excitotoxicity. Front Cell Neurosci 13:298
Farias Quipildor GE, Mao K, Hu Z et al (2019) Central IGF-1 protects against features of cognitive and sensorimotor decline with aging in male mice. Geroscience 41:185–208
Guillemot-Legris O, Muccioli GG (2017) Obesity-induced neuroinflammation: beyond the hypothalamus. Trends Neurosci 40:237–253
Guo DH, Yamamoto M, Hernandez CM et al (2020) Visceral adipose NLRP3 impairs cognition in obesity via IL-1R1 on CX3CR1+ cells. J Clin Invest 130:1961–1976
Hansen AR, Rustin C, Opoku ST et al (2020) Trends in US adults with overweight and obesity reporting being notified by doctors about body weight status, 1999–2016. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 30:608–615
Hastings NB, Wang X, Song L et al (2017) Inhibition of O-GlcNAcase leads to elevation of O-GlcNAc tau and reduction of tauopathy and cerebrospinal fluid tau in rTg4510 mice. Mol Neurodegener 12:39
Heydemann A (2016) An overview of murine high fat diet as a model for type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Res 2016:2902351
Ising C, Venegas C, Zhang S et al (2019) NLRP3 inflammasome activation drives tau pathology. Nature 575:669–673
Kim Y, Li E, Park S (2012) Insulin-like growth factor-1 inhibits 6-hydroxydopamine-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis via regulation of heme oxygenase-1 and Nrf2 expression in PC12 cells. Int J Neurosci 122:641–649
Kletzl H, Guenther A, Höflich A et al (2017) First-in-man study with a novel PEGylated recombinant human insulin-like growth factor-I. Growth Horm IGF Res 33:9–16
Li Y, Xu P, Shan J et al (2020) Interaction between hyperphosphorylated tau and pyroptosis in forskolin and streptozotocin induced AD models. Biomed Pharmacother 121:109618
Liu L, Duff K (2008) A technique for serial collection of cerebrospinal fluid from the cisterna magna in mouse. J Vis Exp 960.
Luo D, Guo Y, Cheng Y et al (2017) Natural product celastrol suppressed macrophage M1 polarization against inflammation in diet-induced obese mice via regulating Nrf2/HO-1, MAP kinase and NF-kappaB pathways. Aging (albany NY) 9:2069–2082
Ma Z, Lu Y, Yang F et al (2020) Rosmarinic acid exerts a neuroprotective effect on spinal cord injury by suppressing oxidative stress and inflammation via modulating the Nrf2/HO-1 and TLR4/NF-kappaB pathways. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 397:115014
McKenzie BA, Dixit VM, Power C (2020) Fiery cell death: pyroptosis in the central nervous system. Trends Neurosci 43:55–73
Miller AA, Spencer SJ (2014) Obesity and neuroinflammation: a pathway to cognitive impairment. Brain Behav Immun 42:10–21
Niu X, Zhao Y, Yang N et al (2020) Proteasome activation by insulin-like growth factor-1/nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 signaling promotes exercise-induced neurogenesis. Stem Cells 38:246–260
Puigoriol-Illamola D, Leiva R, Vázquez-Carrera M et al (2020) 11beta-HSD1 inhibition rescues SAMP8 cognitive impairment induced by metabolic stress. Mol Neurobiol 57:551–565
Ryter SW (2021) Heme oxgenase-1, a cardinal modulator of regulated cell death and inflammation. Cells 10:515
Sama DM, Carlson SW, Joseph B et al (2018) Assessment of systemic administration of PEGylated IGF-1 in a mouse model of traumatic brain injury. Restor Neurol Neurosci 36:559–569
Tsuchiya K, Nakajima S, Hosojima S et al (2019) Caspase-1 initiates apoptosis in the absence of gasdermin D. Nat Commun 10:2091
Wang F, Zhao M, Han Z et al (2017) Association of body mass index with amnestic and non-amnestic mild cognitive impairment risk in elderly. BMC Psychiatry 17:334
Wang H, Zhang H, Cao F et al (2018) Protection of insulin-like growth factor 1 on experimental peripheral neuropathy in diabetic mice. Mol Med Rep 18:4577–4586
Wang F, Wang L, Wang Y et al (2020) Exogenous IGF-1 improves cognitive function in rats with high-fat diet consumption. J Mol Endocrinol 64:115–123
Wang F, Wang L, Sui G et al (2021) Inhibition of miR-129 improves neuronal pyroptosis and cognitive impairment through IGF-1/GSK3beta signaling pathway: an in vitro and in vivo study. J Mol Neurosci
Xu J, Lei S, Ye G (2019a) Dexmedetomidine attenuates oxidative/nitrative stress in lung tissues of septic mice partly via activating heme oxygenase-1. Exp Ther Med 18:3071–3077
Xu L, Lin X, Guan M (2019b) Verapamil attenuated prediabetic neuropathy in high-fat diet-fed mice through Inhibiting TXNIP-mediated apoptosis and inflammation. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2019:1896041
Yang Y, Liang S, Li Y et al (2019) Effects of early administration of insulin-like growth factor-1 on cognitive function in septic encephalopathy. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 15:323–337
Yang W, Li G, Cao K et al (2020) Exogenous insulin-like growth factor 1 attenuates acute ischemic stroke-induced spatial memory impairment via modulating inflammatory response and tau phosphorylation. Neuropeptides 83:102082
Yang C, Sui G, Li D et al (2021) Exogenous IGF-1 alleviates depression-like behavior and hippocampal mitochondrial dysfunction in high-fat diet mice. Physiol Behav 229:113236
Yao H, Tao X, Xu L et al (2018) Dioscin alleviates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease through adjusting lipid metabolism via SIRT1/AMPK signaling pathway. Pharmacol Res 131:51–60
Yi P, Lu FE, Xu LJ et al (2008) Berberine reverses free-fatty-acid-induced insulin resistance in 3T3-L1 adipocytes through targeting IKKbeta. World J Gastroenterol 14:876–883
Zeng R, Luo D, Li H et al (2019) MicroRNA-135b alleviates MPP +-mediated Parkinson’s disease in in vitro model through suppressing FoxO1-induced NLRP3 inflammasome and pyroptosis. J Clin Neurosci 65:125–133
Zhang L, Wang Z, Wang X et al (2020a) Prevalence of overweight and obesity in China: Results from a cross-sectional study of 441 thousand adults, 2012–2015. Obes Res Clin Pract 14:119–126
Zhang S, Zhao M, Wang F et al (2020b) Relationship between normal weight obesity and mild cognitive impairment is reflected in cognitive-related genes in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Psychogeriatrics 20:35–43
Zhou T, Liu L, Wang Q et al (2020) Naringenin alleviates cognition deficits in high-fat diet-fed SAMP8 mice. J Food Biochem 44:e13375
Acknowledgements
We want to thank Prof. Jia Qifen from TIANJIN UNIVERSITY (China) for the funding and laboratory support for this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Sui Guanghong, Wang Lu, Chen Zheng and Wang Feng conduct study design, literature research and manuscript preparation. Yang Caixia, Guo Mengtian and Xiong Xiangyang carry out experiment and performed data analysis.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
The study is approved by the ethics committees of Tianjin Anding Hospital and Tianjin Medical University General Hospital.
Consent to participate
This is an in vivo and in vitro study, and no human subjects are included.
Consent for publication
All authors agree to submit this article to your journal.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sui, G., Yang, C., Wang, L. et al. Exogenous IGF-1 improves tau pathology and neuronal pyroptosis in high-fat diet mice with cognitive dysfunction. Metab Brain Dis 36, 2079–2088 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-021-00787-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-021-00787-4