Abstract
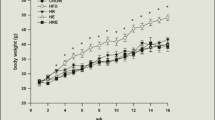
Atherosclerosis has been associated with the progression of cognitive impairment and the effect of metabolic changes in the brain on cognitive function may be pronounced. The aim is to reveal the metabolic changes during atherosclerosis and clarify the possible role of exercise in regulating hippocampal metabolism. Hence, A rat model of atherosclerosis was established by high-fat diet feeding in combination with vitamin D3 intraperitoneal injection, then 4 weeks of aerobic exercise was conducted. Metabolomics based on GC-MS was applied to detect small molecules metabolites and western blot was used to detect the concentration of enzymes involved in metabolic changes in rat hippocampus. Compared to the control group, metabolites including xylulose 5-phosphate, threonine, succinate, and nonanoic acid were markedly elevated, whereas methyl arachidonic acid and methyl stearate decreased in the AS group, accompanied by a raised concentration of aldose reductase and glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase as well as a declined concentration of acetyl-CoA carboxylase and fatty acid synthase. After 4 weeks’ aerobic exercise, the levels of succinic acid, branched chain amino acids, nonanoic acid, desmosterol, and aldose reductase decreased, whereas methyl arachidonic acid, methyl stearate, and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate elevated in the hippocampus of the TAS group in comparison with the AS group. These results suggest that atherosclerosis could cause a severe metabolic disturbance, and aerobic exercise plays an important role in regulating atherosclerosis-induced disorder of glucose metabolism in the hippocampus.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HDL:
-
high-density lipoprotein cholesterol
- PUFAs:
-
polyunsaturated fatty acids
- FATP-1:
-
fatty acid transporter-1
- GLUT-1:
-
glucose transporter-1
- SDHA:
-
succinate dehydrogenase subunit A
- G-6-PD:
-
glucose 6-phosphatedehydrogenase
- AR:
-
aldose reductase
- FASN:
-
fatty acid synthase
- p-ACC:
-
phospho-Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase
- ACC:
-
Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase
- G-6-P:
-
glucose 6-phosphate
- F-1,6-BP:
-
fructose 1,6-diphosphate
- Xyl-5-P:
-
xylulose 5-phosphate
- Rib-5-P:
-
ribose 5-phosphate
- 3-GP:
-
glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
- G-3-P:
-
glycerate 3-phosphate
- α-keto:
-
alpha-ketoglutarate
- FAME:
-
fatty acid methyl ester
- AA:
-
arachidonic acid
- NA:
-
nonanoic acid
- PPP:
-
Pentose Phosphate Pathway
- BCAA:
-
branched-chain amino acids;
References
Afzalpour ME, Chadorneshin HT, Foadoddini M, Eivari HA (2015) Comparing interval and continuous exercise training regimens on neurotrophic factors in rat brain. Physiol Behav 147:78–83
Ahmed HM, Blaha MJ, Nasir K, Rivera JJ, Blumenthal RS (2012) Effects of physical activity on cardiovascular disease. Am J Cardiol 109(2):288–295
Allen LB, G.-M. T., Porter NA, Mirnics K, Korade Z. (2019) Desmosterolosis and desmosterol homeostasis in the developing mouse brain. J Inherit Metab Dis
Astuya A, Caprile T, Castro M, Salazar K, García Mde L, Reinicke K, Rodríguez F, Vera JC, Millán C, Ulloa V, Low M, Martínez F, Nualart F (2005) Vitamin C uptake and recycling among normal and tumor cells from the central nervous system. J Neurosci Res 79(1–2):146–156
Cai M et al (2016) The signaling mechanisms of hippocampal endoplasmic reticulum stress affecting neuronal plasticity-related protein levels in high fat diet-induced obese rats and the regulation of aerobic exercise. Brain Behav Immun 57:347–359
Cao L, Zhang D, Chen J, Qin YY, Sheng R, Feng X, Chen Z, Ding Y, Li M, Qin ZH (2017) G6PD plays a neuroprotective role in brain ischemia through promoting pentose phosphate pathway. Free Radic Biol Med 112:433–444
Cicero AF, Minardi M, Mirembe S, Pedro E, Gaddi A (2004) Effects of a new low dose soy protein/beta-sitosterol association on plasma lipid levels and oxidation. Eur J Nutr 43(5):319–322
Cohen-Manheim I et al (2016) Measures of carotid atherosclerosis and cognitive function in midlife: the Jerusalem LRC longitudinal study. Intelligence 57:73–80
Coppola A, Wenner BR, Ilkayeva O, Stevens RD, Maggioni M, Slotkin TA, Levin ED, Newgard CB (2013) Branched-chain amino acids alter neurobehavioral function in rats. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 304(4):E405–E413
Corcoran SE, O'Neill LA (2016) HIF1alpha and metabolic reprogramming in inflammation. J Clin Invest 126(10):3699–3707
Cotter DG et al (2013) Ketone body metabolism and cardiovascular disease. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 304:H1060–H1076
Eker OF, Ameli R, Makris N, Jurkovic T, Montigon O, Barbier EL, Cho TH, Nighoghossian N, Berthezène Y (2019) MRI assessment of oxygen metabolism and hemodynamic status in symptomatic intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis: A pilot study. J Neuroimaging 29(4):467–475
Esposito G, Giovacchini G, Liow JS, Bhattacharjee AK, Greenstein D, Schapiro M, Hallett M, Herscovitch P, Eckelman WC, Carson RE, Rapoport SI (2008) Imaging neuroinflammation in Alzheimer's disease with radiolabeled arachidonic acid and PET. J Nucl Med 49(9):1414–1421
Freitas DA, Rocha-Vieira E, Soares BA, Nonato LF, Fonseca SR, Martins JB, Mendonça VA, Lacerda AC, Massensini AR, Poortamns JR, Meeusen R, Leite HR (2018) High intensity interval training modulates hippocampal oxidative stress, BDNF and inflammatory mediators in rats. Physiol Behav 184:6–11
Jaakkola P, Mole DR, Tian YM, Wilson MI, Gielbert J, Gaskell SJ, von Kriegsheim A, Hebestreit HF, Mukherji M, Schofield CJ, Maxwell PH, Pugh CW, Ratcliffe PJ (2001) Targeting of HIF-alpha to the von Hippel-Lindau ubiquitylation complex by O2-regulated prolyl hydroxylation. Science 292(5516):468–472
Jais A, Solas M, Backes H, Chaurasia B, Kleinridders A, Theurich S, Mauer J, Steculorum SM, Hampel B, Goldau J, Alber J, Förster CY, Eming SA, Schwaninger M, Ferrara N, Karsenty G, Brüning JC (2016) Myeloid-cell-derived VEGF maintains brain glucose uptake and limits cognitive impairment in obesity. Cell 165(4):882–895
Jansen GA, Wanders RJ (2006) Alpha-oxidation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1763(12):1403–1412
Jansen M, Wang W, Greco D, Bellenchi GC, di Porzio U, Brown AJ, Ikonen E (2012) What dictates the accumulation of desmosterol in the developing brain? FASEB J 27(3):865–870
Kim HW, Rapoport SI, Rao JS (2011) Altered arachidonic acid cascade enzymes in postmortem brain from bipolar disorder patients. Mol Psychiatry 16(4):419–428
Li J, Liu B, Cai M, Lin X, Lou S (2019) Glucose metabolic alterations in hippocampus of diabetes mellitus rats and the regulation of aerobic exercise. Behav Brain Res 364:447–456
Lopez-Oloriz J et al (2013) Asymptomatic cervicocerebral atherosclerosis, intracranial vascular resistance and cognition: the AsIA-neuropsychology study. Atherosclerosis 230(2):330–335
Madsen R, Lundstedt T, Trygg J (2010) Chemometrics in metabolomics--a review in human disease diagnosis. Anal Chim Acta 659(1–2):23–33
Mashima T, Seimiya H, Tsuruo T (2009) De novo fatty-acid synthesis and related pathways as molecular targets for cancer therapy. Br J Cancer 100(9):1369–1372
Matsui T et al (2019) Tyrosine as a mechanistic-based biomarker for brain glycogen decrease and Supercompensation with endurance exercise in rats: A metabolomics study of plasma. Front Neurosci 13:200
Mehta MA, Gumaste D, Montgomery AJ, McTavish S, Grasby PM (2005) The effects of acute tyrosine and phenylalanine depletion on spatial working memory and planning in healthy volunteers are predicted by changes in striatal dopamine levels. Psychopharmacology 180(4):654–663
Nadjar A et al (2017) Bioactive lipids as new class of microglial modulators: when nutrition meets neuroimunology. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 79(Pt A):19–26
Ogoh S et al (2014) The effect of changes in cerebral blood flow on cognitive function during exercise. Phys Rep 2(9)
Pinto A, Raimondo DD, Tuttolomondo A et al (2012) Effects of Physical Exercise on Inflammatory Markers of Atherosclerosis. Curr Pharm Des 28(18):4326–4349
Pushpendra Singh RS, Paila YD (2009) Differential effects of cholesterol and desmosterol on the ligand binding function of the hippocampal serotonin1A receptor: implications in desmosterolosis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1788:2169–2173
Rapoport SI (2008) Arachidonic acid and the brain. J Nutr 138:2515–2520
Reddy A, Ramana K (2010) Aldose Reductase Inhibition_ emerging drug target for the treatment of cardiovascular complications. Recent Patents Cardiovas Drug Discov 1(5):25–32
Rey G, Valekunja UK, Feeney KA, Wulund L, Milev NB, Stangherlin A, Ansel-Bollepalli L, Velagapudi V, O'Neill JS, Reddy AB (2016) The pentose phosphate pathway regulates the circadian clock. Cell Metab 24(3):462–473
Rossetti HC, Weiner M, Hynan LS, Cullum CM, Khera A, Lacritz LH (2015) Subclinical atherosclerosis and subsequent cognitive function. Atherosclerosis 241(1):36–41
Ruzzo EK, Capo-Chichi JM, Ben-Zeev B, Chitayat D, Mao H, Pappas AL, Hitomi Y, Lu YF, Yao X, Hamdan FF, Pelak K, Reznik-Wolf H, Bar-Joseph I, Oz-Levi D, Lev D, Lerman-Sagie T, Leshinsky-Silver E, Anikster Y, Ben-Asher E, Olender T, Colleaux L, Décarie JC, Blaser S, Banwell B, Joshi RB, He XP, Patry L, Silver RJ, Dobrzeniecka S, Islam MS, Hasnat A, Samuels ME, Aryal DK, Rodriguiz RM, Jiang YH, Wetsel WC, McNamara J, Rouleau GA, Silver DL, Lancet D, Pras E, Mitchell GA, Michaud JL, Goldstein DB (2013) Deficiency of asparagine synthetase causes congenital microcephaly and a progressive form of encephalopathy. Neuron 80(2):429–441
Saara Vainio, M. J., Mirkka Koivusalo,. (2006). Significance of sterol structural specificity desmosterol cannot replace cholesterol in lipid rafts. J Biol Chem, 28(1), pp348–355
Schonfeld P, Reiser G (2013) Why does brain metabolism not favor burning of fatty acids to provide energy? Reflections on disadvantages of the use of free fatty acids as fuel for brain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 33(10):1493–1499
Seghieri M., T. D., Natali A. . (2017). The impact of triglycerides on glucose tolerance: lipotoxicity revisited. Diabetes Metab(7)
Singer J, Trollor JN, Baune BT, Sachdev PS, Smith E (2014) Arterial stiffness, the brain and cognition: a systematic review. Ageing Res Rev 15:16–27
Sperringer JE, Addington A, Hutson SM (2017) Branched-Chain Amino Acids and Brain Metabolism. Neurochem Res 42(6):1697–1709
Claudia K. Suemoto, R. Nitrini, Lea T. Grinberg, et.al (2011). Atherosclerosis and Dementia:A Cross-Sectional Study With Pathological Analysis of the Carotid Arteries. Stroke(42), 3614–3615
Suemoto CK, Santos IS, Bittencourt MS, Pereira AC, Goulart AC, Rundek T, Passos VM, Lotufo P, Benseñor IM (2015) Subclinical carotid artery atherosclerosis and performance on cognitive tests in middle-aged adults: baseline results from the ELSA-Brasil. Atherosclerosis 243(2):510–515
Tan L, Yu JT, Tan L (2012) The kynurenine pathway in neurodegenerative diseases: mechanistic and therapeutic considerations. J Neurol Sci 323(1–2):1–8
Tannahill GM, Curtis AM, Adamik J, Palsson-McDermott E, McGettrick A, Goel G, Frezza C, Bernard NJ, Kelly B, Foley NH, Zheng L, Gardet A, Tong Z, Jany SS, Corr SC, Haneklaus M, Caffrey BE, Pierce K, Walmsley S, Beasley FC, Cummins E, Nizet V, Whyte M, Taylor CT, Lin H, Masters SL, Gottlieb E, Kelly VP, Clish C, Auron PE, Xavier RJ, O'Neill LA (2013) Succinate is an inflammatory signal that induces IL-1beta through HIF-1alpha. Nature 496(7444):238–242
Tian F, Gu L, Si A, Yao Q, Zhang X, Zhao J, Hu D (2016) The metabolomic study on atherosclerosis mice and its application in a traditional Chinese medicine Sishen granule. Biomed Chromatogr 30(6):969–975
Tretter L, Patocs A, Chinopoulos C (2016) Succinate, an intermediate in metabolism, signal transduction, ROS, hypoxia, and tumorigenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1857(8):1086–1101
Vikram Jakkamsetti, I. M.-V., Qian MA. (2019). Brain metabolism modulates neuronal excitability in a mouse model of pyruvate dehydrogenase deficiency. science translational medcine, 20 (11)
Wang YP, Zhou LS, Zhao YZ, Wang SW, Chen LL, Liu LX, Ling ZQ, Hu FJ, Sun YP, Zhang JY, Yang C, Yang Y, Xiong Y, Guan KL, Ye D (2014) Regulation of G6PD acetylation by SIRT2 and KAT9 modulates NADPH homeostasis and cell survival during oxidative stress. EMBO J 33(12):1304–1320
Wyse AT, Netto CA (2011) Behavioral and neurochemical effects of proline. Metab Brain Dis 26(3):159–172
Yang J, Cao RY, Gao R, Mi Q, Dai Q, Zhu F (2017) Physical exercise is a potential "medicine" for atherosclerosis. Adv Exp Med Biol 999:269–286
Yuan T, Yang T, Chen H, Fu D, Hu Y, Wang J, Yuan Q, Yu H, Xu W, Xie X (2019) New insights into oxidative stress and inflammation during diabetes mellitus-accelerated atherosclerosis. Redox Biol 20:247–260
Yudkoff M (2016) Interactions in the metabolism of glutamate and the branched-chain amino acids and Ketoacids in the CNS. Neurochem Res 42(1):1–9
Zheng L, Zhou B, Meng X, Zhu W, Zuo A, Wang X, Jiang R, Yu S (2014) A model of spontaneous mouse mammary tumor for human estrogen receptor- and progesterone receptor-negative breast cancer. Int J Oncol 45(6):2241–2249
Acknowledgements
We thank Qian Wang, Mingming Li, Xiao-huan Chen and lin lu for providing support to achieve this work. Thanks for the support from National Natural Science Foundation of China (81572241) and Shanghai Key Lab of Human Performance(Shanghai University of sport)(NO. 11DZ2261100).
Funding
This work was supported by the grant of National Natural Science Foundation of China (81572241) and Shanghai Key Lab of Human Performance(Shanghai University of sport)(NO. 11DZ2261100).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Beibei Liu and Jingjing Li. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Beibei Liu and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committees of the Shanghai University of Sport at which the studies were conducted.
Consent for publication
All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• Glucose and lipid metabolism disrupted in hippocampus of atherosclerotic rats.
• Expressions of key enzymes involved in glucose and lipid metabolism changed.
• Aerobic training may improve metabolism in the hippocampus of atherosclerotic rats.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 67 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, B., Li, J., Lin, X. et al. The metabolic changes in the hippocampus of an atherosclerotic rat model and the regulation of aerobic training. Metab Brain Dis 35, 1017–1034 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-020-00566-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-020-00566-7