Abstract
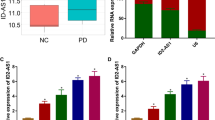
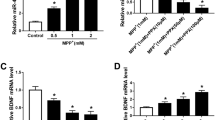
The study found that microRNAs play an important role in Parkinson’s disease (PD). However, the function of MicroRNA-216a (miR-216a) in PD is unclear. Therefore, this experiment aimed to investigate the pathogenesis of miR-216a in PD. Using the toxicity of MPP+ to polyhexamine neurons, apoptosis of SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells was induced at different time by MPP+ to construct a stable acute PD cell model. The effects of DNA breakage, mitochondrial membrane potential (A ^ m), caspase-3 activity and nucleosome enrichment on cell apoptosis were detected by flow cytometry, TUNEL. MPP+ increased the toxic effects of dopaminergic neurons in a PD model. The introduction of miR-216a inhibited MPP + -induced neuronal apoptosis. The main manifestations were the decreased levels of positive rate of Tunel cells, caspase 3 activity and nucleosome enrichment factor. Bax was a direct target of miR-216a. In addition, Bax overexpression reversed the effects of miR-216a on neural cells. Bax downstream factors were also involved in miR-216a regulation of MPP + -triggered neuronal apoptosis. miR-216a regulated the progression of PD by regulating Bax, and miR-216a may be a potential target for PD.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akh A, Filatova EV, Karabanov AV et al (2015) miRNA expression is highly sensitive to a drug therapy in Parkinson's disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 21(1):72–74
Armstrong RA (2017) Visual dysfunction in Parkinson's disease. Int Rev Neurobiol 134(6):921–946
Bai X, Tang Y, Yu M, Wu L, Wang J (2017) Downregulation of blood serum microRNA 29 family in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Sci Rep 7(1):5411
Cai X, Jia H, Liu Z et al (2010) Polyhydroxylated fullerene derivative C60(OH)24 prevents mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative damage in an MPP+-induced cellular model of Parkinson's disease. J Neurosci Res 86(16):3622–3634
Caneda-Ferrón B, Girolamo LAD, Costa T, Beck KE, Layfield R, Billett EE (2010) Assessment of the direct and indirect effects of MPP+ and dopamine on the human proteasome: implications for Parkinson’s disease aetiology. J Neurochem 105(1):225–238
Casas S, García S, Cabrera R, Nanfaro F, Escudero C, Yunes R (2011) Progesterone prevents depression-like behavior in a model of Parkinson's disease induced by 6-hydroxydopamine in male rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 99(4):614–618
Chang D, Nalls MA, Hallgrímsdóttir IB, Hunkapiller J, van der Brug M, Cai F, International Parkinson's Disease Genomics Consortium, 23andMe Research Team, Kerchner GA, Ayalon G, Bingol B, Sheng M, Hinds D, Behrens TW, Singleton AB, Bhangale TR, Graham RR (2017) A meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies identifies 17 new Parkinson's disease risk loci. Nat Genet 49(10):1511–1516
Chaudhuri KR, Healy DG, Schapira AH (2017) Non-motor symptoms of Parkinson's disease: diagnosis and management. Lancet Neurol 5(3):235–245
Da SF, Iop RD, Vietta GG et al (2016) microRNAs involved in Parkinson's disease: a systematic review. Mol Med Rep 14(5):4015–4022
Delavar MR, Baghi M, Yadegari E, Ghaedi K. Bioinformatic Prediction and Introducing of Some Targeting MicroRNAs of Sirt1 and Bcl2 Genes in Model of Parkinson's Disease. Majallah-i dānishgāh-i ̒ulūm-i pizishkī-i Arāk. 2017
Dong S, Huiqing Y, Cuicui D et al (2017) Corrigendum to “Predictive value of plasma MicroRNA-216a/b in the diagnosis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma”. Dis Markers 2017:1–2
Dunnewold RJ, Jacobi CE, van Hilten JJ (2018) Quantitative assessment of bradykinesia in patients with Parkinson's disease. J Clin Neurosurg 74(1):107
Falco MD, Luca LD, Acanfora F et al (2001) Alteration of the Bcl-2 : Bax Ratio in the placenta as pregnancy proceeds. Histochem J 33(7):421–425
Falup-Pecurariu C, Diaconu Ş (2017) Sleep dysfunction in Parkinson's disease. Int Rev Neurobiol 47(1):35
Guénin S, Mauriat M, Pelloux J, Wuytswinkel OV, Bellini C, Gutierrez L (2009) Normalization of qRT-PCR data: the necessity of adopting a systematic, experimental conditions-specific, validation of references. J Exp Bot 60(2):487–493
Harraz MM, Dawson TM, Dawson VL (2012) MicroRNAs in Parkinson's disease. J Chem Neuroanat 46(2):279–284
Hartmann A, Michel PP, Troadec JD et al (2001) Is Bax a mitochondrial mediator in apoptotic death of dopaminergic neurons in Parkinson's disease? . J Neurochem 76(6):1785–1793
He X, Yu Y, Awatramani R, Lu QR (2012) Unwrapping myelination by microRNAs. Neuroscientist 18(1):45
Jung YW, Zindl CL, Lai JF, Weaver CT, Chaplin DD (2010) MMP induced by Gr-1+ cells are crucial for recruitment of Th cells into the airways. Eur J Immunol 39(8):2281–2292
Kim C, Ojoamaize E, Spencer B et al (2015) Hypoestoxide reduces neuroinflammation and α-synuclein accumulation in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. J Neuroinflammation 12(1):236
Kuhar MJ, Yoho LL (2015) CART peptide analysis by Western blotting. Synapse 33(3):163–171
Leggio L, Vivarelli S, L'Episcopo F et al (2017) microRNAs in Parkinson's disease: from pathogenesis to novel diagnostic and therapeutic approaches. Int J Mol Sci 18(12):2698
Lewis TB, Glasgow JN, Harms AS, Standaert DG, Curiel DT (2014) Fiber-modified adenovirus for central nervous system Parkinson's disease gene therapy. Viruses 6(8):3293–3310
Liu C, Xi G, Yan P, Zhang W, Tang Y (2004) Effect of scorpion venom on the expression of Bcl-2/Bax in dopaminergic neurons of PD mice. Neuroscientist 24:623–628
Marconi R, Lefebvrecaparros D, Bonnet AM, Vidailhet M, Dubois B, Agid Y (2010) Levodopa-induced dyskinesias in Parkinson's disease phenomenology and pathophysiology. Mov Disord 9(1):2–12
Mei JM, Niu CS (2014) Effects of CDNF on 6-OHDA-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells via modulation of Bcl-2/Bax and caspase-3 activation. Neurol Sci 35(8):1275–1280
Menghini R, Casagrande V, Marino A et al (2017) MiR-216a: a link between endothelial dysfunction and autophagy. Cell Death Dis 5(1):e1029
Mitchell PS, Parkin RK, Kroh EM, Fritz BR, Wyman SK, Pogosova-Agadjanyan EL, Peterson A, Noteboom J, O'Briant KC, Allen A, Lin DW, Urban N, Drescher CW, Knudsen BS, Stirewalt DL, Gentleman R, Vessella RL, Nelson PS, Martin DB, Tewari M (2008) Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105(30):10513–10518
O'Connor L, Strasser A, O'Reilly LA et al (2014) Bim: a novel member of the Bcl-2 family that promotes apoptosis. EMBO J 17(2):384–395
Onyango IG (2008) Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in Parkinson’s disease. Neurochem Res 33(3):589–597
Pang X, Hogan EM, Casserly A, Gao G, Gardner PD, Tapper AR (2014) Dicer expression is essential for adult midbrain dopaminergic neuron maintenance and survival. Mol Cell Neurosci 58(1):22–28
Reed JC (2006) Proapoptotic multidomain Bcl-2/Bax-family proteins: mechanisms, physiological roles, and therapeutic opportunities. Cell Death Differ 13(8):1378–1386
Rodriguezoroz MC, Jahanshahi M, Krack P et al (2009) Initial clinical manifestations of Parkinson's disease: features and pathophysiological mechanisms. Lancet Neurol 8(12):1128–1139
Singleton AB, Farrer M, Johnson J et al (2003) Alpha-Synuclein locus triplication causes Parkinson's disease. Science 302(5646):841–841
Staudt MD, Di SA, Xu H et al (2015) Advances in Neurotrophic factor and cell-based therapies for Parkinson's disease: a mini-review. Gerontology 62(3):371–380
Suh DC, Pahwa R, Mallya U (2012) Treatment patterns and associated costs with Parkinson's disease levodopa induced dyskinesia. J Neurol Sci 319(1–2):24–31
Titzedealmeida R, Titzedealmeida SS (2018) miR-7 replacement therapy in Parkinson's disease. Curr Gene Ther 18(3):143–153
Tolosa E, Bottaorfila T, Morató X et al (2018) MicroRNA alterations in iPSC-derived dopaminergic neurons from Parkinson disease patients. Neurobiol Aging 4(5):eaao5553
Wang Z, Li Y, Kong D, Ahmad A, Banerjee S, Sarkar FH (2010) Cross-talk between miRNA and notch signaling pathways in tumor development and progression. Cancer Lett 292(2):141–148
Wang DB, Uo T, Kinoshita C et al (2017) Bax interacting Factor-1 promotes survival and mitochondrial elongation in neurons. J Neurosci the Official Journal of the Society for Neuroscience 34(7):2674–2683
Willis AW, Schootman M, Kung N, Racette BA (2013) Epidemiology and neuropsychiatric manifestations of young onset Parkinson’s disease in the United States. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 19(2):202–206
Xiao M, Li J, Li W, Wang Y, Wu F, Xi Y, Zhang L, Ding C, Luo H, Li Y, Peng L, Zhao L, Peng S, Xiao Y, Dong S, Cao J, Yu W (2017) MicroRNAs activate gene transcription epigenetically as an enhancer trigger. RNA Biol 14(10):1326–1334
Xie Y, Chen Y (2016) microRNAs: emerging targets regulating oxidative stress in the models of Parkinson's disease. Front Neurosci 10
Yang B, Gao G, Wang Z, et al (2018) Long non-coding RNA HOTTIP promotes prostate cancer cells proliferation and migration by sponging miR-216a-5p. Biosci Rep 38(5):BSR20180566
Zhao N, Jin L, Fei G, Zheng Z, Zhong C (2014) Serum microRNA-133b is associated with low ceruloplasmin levels in Parkinson's disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 20(11):1177–1180
Zou XZ, Liu T, Gong ZC, Hu CP, Zhang Z (2017) MicroRNAs-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition in fibrotic diseases. Eur J Pharmacol 796:190–206
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, X., Zhang, M., Wei, M. et al. MicroRNA-216a inhibits neuronal apoptosis in a cellular Parkinson’s disease model by targeting Bax. Metab Brain Dis 35, 627–635 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-020-00546-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-020-00546-x