Abstract
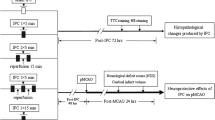
Ischemic preconditioning (IPC) in the brain increases ischemic tolerance to subsequent ischemic insults. In this study, we examined whether IPC protects neurons and attenuates microgliosis or not in the hippocampus following severe transient global cerebral ischemia (TCI) in gerbils. Gerbils were assigned to 8 groups; 5- and 15-min sham operated groups, 5-min and 15-min TCI operated groups, IPC plus 5- and 15-min sham operated groups, and IPC plus 5- and 15-min TCI operated groups. IPC was induced by subjecting animals to 2-min transient ischemia 1 day before 5-min TCI for a typical transient ischemia and 15-min TCI for severe transient ischemia. Neuronal damage was examined by cresyl violet staining and Fluoro-Jade B histofluorescence staining. In addition, microglial activation was examined using immunohistochemistry for Iba-1 (a marker for microglia). Delayed neuronal death and microgliosis was found in the CA1 alone in the 5-min TCI operated group at 5 days post-ischemia, and, in the 15-min TCI operated group, neuronal death and microgliosis was shown in all CA areas (CA1–3) and the dentate gyrus. IPC displayed neuroprotection and attenuated microglial activation in the 5-min TCI operated group. However, in the 15-min TCI operated group, IPC did not show neuroprotection and not attenuate microglial activation. Our present findings indicate that IPC hardly protect against severe transient cerebral ischemic injury.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barron KD (1995) The microglial cell. A historical review. J Neurol Sci 134(Suppl):57–68
Beresewicz M, Kowalczyk JE, Zablocka B (2008) Kalirin-7, a protein enriched in postsynaptic density, is involved in ischemic signal transduction. Neurochem Res 33:1789–1794
Bertolino G, De Araujo FL, Souza HC, Coimbra NC, De Araujo JE (2013) Neuropathology and behavioral impairments after bilateral global ischemia surgery and exposure to static magnetic field: evidence in the motor cortex, the hippocampal CA1 region and the neostriatum. Int J Radiat Biol 89:595–601
Cho S, Park EM, Zhou P, Frys K, Ross ME, Iadecola C (2005) Obligatory role of inducible nitric oxide synthase in ischemic preconditioning. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 25:493–501. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600058
Dave KR, Lange-Asschenfeldt C, Raval AP, Prado R, Busto R, Saul I, Perez-Pinzon MA (2005) Ischemic preconditioning ameliorates excitotoxicity by shifting glutamate/gamma-aminobutyric acid release and biosynthesis. J Neurosci Res 82:665–673
Dhodda VK, Sailor KA, Bowen KK, Vemuganti R (2004) Putative endogenous mediators of preconditioning-induced ischemic tolerance in rat brain identified by genomic and proteomic analysis. J Neurochem 89:73–89
Durukan A, Tatlisumak T (2010) Preconditioning-induced ischemic tolerance: a window into endogenous gearing for cerebroprotection. Exp Transl Stroke Med 2:2
Edwards RJ, Saurin AT, Rakhit RD, Marber MS (2000) Therapeutic potential of ischaemic preconditioning. Br J Clin Pharmacol 50:87–97
Feng Z, Davis DP, Sasik R, Patel HH, Drummond JC, Patel PM (2007) Pathway and gene ontology based analysis of gene expression in a rat model of cerebral ischemic tolerance. Brain Res 1177:103–123
Gidday JM (2006) Cerebral preconditioning and ischaemic tolerance. Nat Rev Neurosci 7:437–448
Hailer NP, Jarhult JD, Nitsch R (1996) Resting microglial cells in vitro: analysis of morphology and adhesion molecule expression in organotypic hippocampal slice cultures. Glia 18:319–331
Hashimoto M, Nitta A, Fukumitsu H, Nomoto H, Shen L, Furukawa S (2005) Involvement of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor in activation processes of rodent macrophages. J Neurosci Res 79:476–487
Hwang IK, Yoo KY, Kim DW, Choi SY, Kang TC, Kim YS, Won MH (2006) Ionized calcium-binding adapter molecule 1 immunoreactive cells change in the gerbil hippocampal CA1 region after ischemia/reperfusion. Neurochem Res 31:957–965
Hwang IK, Yoo KY, Kim do H, Lee BH, Kwon YG, Won MH (2007) Time course of changes in pyridoxal 5′-phosphate (vitamin B6 active form) and its neuroprotection in experimental ischemic damage. Exp Neurol 206:114–125
Hwang IK et al (2008) Differential changes in pyridoxine 5′-phosphate oxidase immunoreactivity and protein levels in the somatosensory cortex and striatum of the ischemic gerbil brain. Neurochem Res 33:1356–1364
Hye Kim I et al (2016) Time interval after ischaemic preconditioning affects neuroprotection and gliosis in the gerbil hippocampal CA1 region induced by transient cerebral ischaemia. Neurol Res 38:210–219
Kim IH et al (2013) Neuroprotection of a novel synthetic caffeic acid-syringic acid hybrid compound against experimentally induced transient cerebral ischemic damage. Planta Med 79:313–321
Kim IH et al (2014) Comparison of neuroprotective effects of extract and fractions from Agarum clathratum against experimentally induced transient cerebral ischemic damage. Pharm Biol 52:335–343
Kirino T, Sano K (1984) Selective vulnerability in the gerbil hippocampus following transient ischemia. Acta Neuropathol 62:201–208
Kirino T, Tsujita Y, Tamura A (1991) Induced tolerance to ischemia in gerbil hippocampal neurons. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 11:299–307
Kirino T, Nakagomi T, Kanemitsu H, Tamura A (1996) Ischemic tolerance. Adv Neurol 71:505–511
Kreutzberg GW (1996) Microglia: a sensor for pathological events in the CNS. Trends Neurosci 19:312–318
Laurenzi MA, Arcuri C, Rossi R, Marconi P, Bocchini V (2001) Effects of microenvironment on morphology and function of the microglial cell line BV-2. Neurochem Res 26:1209–1216
Lee JC et al (2013) Effects of transient cerebral ischemia on the expression of DNA methyltransferase 1 in the gerbil hippocampal CA1 region. Neurochem Res 38:74–81
Lee JC et al (2014a) Transient ischemia-induced change of CCR7 immunoreactivity in neurons and its new expression in astrocytes in the gerbil hippocampus. J Neurol Sci 336:203–210
Lee JC et al (2014b) Effect of transient cerebral ischemia on the expression of receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) in the gerbil hippocampus proper. Neurochem Res 39:1553–1563
Lee JC et al (2014c) Ischemic preconditioning-induced neuroprotection against transient cerebral ischemic damage via attenuating ubiquitin aggregation. J Neurol Sci 336:74–82
Lee JC et al (2015) Ischemic preconditioning protects hippocampal pyramidal neurons from transient ischemic injury via the attenuation of oxidative damage through upregulating heme oxygenase-1. Free Radic Biol Med 79:78–90
Lee JC et al (2016) Neuroprotection of ischemic preconditioning is mediated by Thioredoxin 2 in the hippocampal CA1 region following a subsequent transient cerebral ischemia. Brain Pathol 27(3):276–291
Lehotsky J, Burda J, Danielisova V, Gottlieb M, Kaplan P, Saniova B (2009) Ischemic tolerance: the mechanisms of neuroprotective strategy. Anat Rec 292:2002–2012. https://doi.org/10.1002/ar.20970
Lehrmann E, Kiefer R, Finsen B, Diemer NH, Zimmer J, Hartung HP (1995) Cytokines in cerebral ischemia: expression of transforming growth factor beta-1 (TGF-beta 1) mRNA in the postischemic adult rat hippocampus. Exp Neurol 131:114–123
Lin CS, Polsky K, Nadler JV, Crain BJ (1990) Selective neocortical and thalamic cell death in the gerbil after transient ischemia. Neuroscience 35:289–299
Lipton P (1999) Ischemic cell death in brain neurons. Physiol Rev 79:1431–1568
Liu Y, Kato H, Nakata N, Kogure K (1992) Protection of rat hippocampus against ischemic neuronal damage by pretreatment with sublethal ischemia. Brain Res 586:121–124
Lorrio S, Sobrado M, Arias E, Roda JM, Garcia AG, Lopez MG (2007) Galantamine postischemia provides neuroprotection and memory recovery against transient global cerebral ischemia in gerbils. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 322:591–599
Lu YZ, Lin CH, Cheng FC, Hsueh CM (2005) Molecular mechanisms responsible for microglia-derived protection of Sprague-Dawley rat brain cells during in vitro ischemia. Neurosci Lett 373:159–164
Malek M, Duszczyk M, Zyszkowski M, Ziembowicz A, Salinska E (2013) Hyperbaric oxygen and hyperbaric air treatment result in comparable neuronal death reduction and improved behavioral outcome after transient forebrain ischemia in the gerbil. Exp Brain Res 224:1–14
Miao Y, Zhang W, Lin Y, Lu X, Qiu Y (2010) Neuroprotective effects of ischemic preconditioning on global brain ischemia through up-regulation of acid-sensing ion channel 2a. Int J Mol Sci 11:140–153
Moncayo J, de Freitas GR, Bogousslavsky J, Altieri M, van Melle G (2000) Do transient ischemic attacks have a neuroprotective effect? Neurology 54:2089–2094
Nakajima T, Ochi S, Oda C, Ishii M, Ogawa K (2011) Ischemic preconditioning attenuates of ischemia-induced degradation of spectrin and tau: implications for ischemic tolerance. Neurol Sci 32:229–239
Nakamura H, Katsumata T, Nishiyama Y, Otori T, Katsura K, Katayama Y (2006) Effect of ischemic preconditioning on cerebral blood flow after subsequent lethal ischemia in gerbils. Life Sci 78:1713–1719
Nakano M, Ueda H, Li JY, Matsumoto M, Yanagihara T (1998) Measurement of regional N-acetylaspartate after transient global ischemia in gerbils with and without ischemic tolerance: an index of neuronal survival. Ann Neurol 44:334–340
Nishi S et al (1993) Ischemic tolerance due to the induction of HSP70 in a rat ischemic recirculation model. Brain Res 615:281–288
Ohk TG et al (2012) Neuronal damage using Fluoro-jade B histofluorescence and gliosis in the striatum after various durations of transient cerebral ischemia in gerbils. Neurochem Res 37:826–834
Perez-Pinzon MA (2004) Neuroprotective effects of ischemic preconditioning in brain mitochondria following cerebral ischemia. J Bioenerg Biomembr 36:323–327
Schmued LC, Hopkins KJ (2000) Fluoro-jade B: a high affinity fluorescent marker for the localization of neuronal degeneration. Brain Res 874:123–130
Schwartz M, Butovsky O, Bruck W, Hanisch UK (2006) Microglial phenotype: is the commitment reversible? Trends Neurosci 29:68–74
Selakovic V, Korenic A, Radenovic L (2011) Spatial and temporal patterns of oxidative stress in the brain of gerbils submitted to different duration of global cerebral ischemia. Int J Dev Neurosci 29:645–654
Stagliano NE, Perez-Pinzon MA, Moskowitz MA, Huang PL (1999) Focal ischemic preconditioning induces rapid tolerance to middle cerebral artery occlusion in mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 19:757–761
Stenzel-Poore MP et al (2003) Effect of ischaemic preconditioning on genomic response to cerebral ischaemia: similarity to neuroprotective strategies in hibernation and hypoxia-tolerant states. Lancet 362:1028–1037
Stenzel-Poore MP, Stevens SL, King JS, Simon RP (2007) Preconditioning reprograms the response to ischemic injury and primes the emergence of unique endogenous neuroprotective phenotypes: a speculative synthesis. Stroke 38:680–685
Tanaka H, Calderone A, Jover T, Grooms SY, Yokota H, Zukin RS, Bennett MV (2002) Ischemic preconditioning acts upstream of GluR2 down-regulation to afford neuroprotection in the hippocampal CA1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:2362–2367
Tang Y, Pacary E, Freret T, Divoux D, Petit E, Schumann-Bard P, Bernaudin M (2006) Effect of hypoxic preconditioning on brain genomic response before and following ischemia in the adult mouse: identification of potential neuroprotective candidates for stroke. Neurobiol Dis 21:18–28
Toyoda T, Kassell NF, Lee KS (1997) Induction of ischemic tolerance and antioxidant activity by brief focal ischemia. Neuroreport 8:847–851
Wegener S et al (2004) Transient ischemic attacks before ischemic stroke: preconditioning the human brain? A multicenter magnetic resonance imaging study. Stroke 35:616–621
Weih M, Kallenberg K, Bergk A, Dirnagl U, Harms L, Wernecke KD, Einhaupl KM (1999) Attenuated stroke severity after prodromal TIA: a role for ischemic tolerance in the brain? Stroke 30:1851–1854
Yan BC et al (2013) Neuroprotective effect of a new synthetic aspirin-decursinol adduct in experimental animal models of ischemic stroke. PLoS One 8:e74886
Yu DK et al (2012) Neuronal damage in hippocampal subregions induced by various durations of transient cerebral ischemia in gerbils using Fluoro-jade B histofluorescence. Brain Res 1437:50–57
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Mr. Seung Uk Lee for his technical help in this study. This research was supported by the Bio & Medical Technology Development Program of the NRF funded by the Korean government, MSIP (NRF-2015M3A9B6066835), and by the Bio-Synergy Research Project (NRF-2015M3A9C4076322) of the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning through the National Research Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that there is no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, JC., Shin, BN., Cho, J.H. et al. Brain ischemic preconditioning protects against moderate, not severe, transient global cerebral ischemic injury. Metab Brain Dis 33, 1193–1201 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-018-0231-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-018-0231-5