Abstract
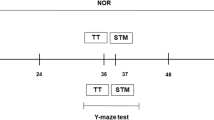
Ammonia is thought to be central in the development of hepatic encephalopathy. However, the specific relation of ammonia with brain energy depletions and learning has not been studied. Our work attempts to reproduce an increase in rat cerebral ammonia level, study the hyperamonemic animals’ performance of two learning tasks, an allocentric (ALLO) and a cue guided (CG) task, and elucidate the contribution of hyperammonemia to the differential energy requirements of the brain limbic system regions involved in these tasks. To assess these goals, four groups of animals were used: a control (CHA) CG group (n = 10), a CHA ALLO group (n = 9), a hyperammonemia (HA) CG group (n = 7), and HA ALLO group (n = 8). Oxidative metabolism of the target brain regions were assessed by histochemical labelling of cytochrome oxidase (C.O.). The behavioural results revealed that the hyperammonemic rats were not able to reach the behavioural criterion in either of the two tasks, in contrast to the CHA groups. The metabolic brain consumption revealed increased C.O. activity in the anterodorsal thalamus when comparing the HA ALLO group with the CHA ALLO group. Significant differences between animals trained in the CG task were observed in the prelimbic, infralimbic, parietal, entorhinal and perirhinal cortices, the anterolateral and anteromedial striatum, and the basolateral and central amygdala. Our findings may provide fresh insights to reveal how the differential damage to the brain limbic structures involved in these tasks differs according to the degree of task difficulty.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe H, Ishida Y, Nonaka H, Iwasaki T (2009) Functional difference between rat perirhinal cortex and hippocampus in object and place discrimination tasks. Behav Brain Res 197:388–397
Aggleton JP, Vann SD, Oswald CJ, Good M (2000) Identifying cortical inputs to the rat hippocampus that subserve allocentric spatial processes: A simple problem with a complex answer. Hippocampus 10:466–474
Aguilar MA, Miñarro J, Felipo V (2000) Chronic moderate hyperammonemia impairs active and passive avoidance behavior and conditional discrimination learning in rats. Exp Neurol 161:704–713
Aller MA, Arias JL, Cruz A, Arias J (2007) Inflammation: A way to understanding the evolution of portal hypertension. Theor Biol Med Model 4:44
Arias JL, Aller MA, Sánchez-Patan F, Arias J (2006) The inflammatory bases of hepatic encephalopathy. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 18:1297–1310
Arias N, Álvarez C, Conejo N, González-Pardo H, Arias JL (2010) Estrous cycle and sex as regulating factors of baseline brain oxidative metabolism and behavior. Revista Iberoamericana de Psicología y Salud 1:3–16
Arias N, Méndez M, Arias J, Arias JL (2012) Brain metabolism and spatial memory are affected by portal hypertension. Metab Brain Dis 27:183–191
Arias N, Méndez M, Fidalgo C, Aller MA, Arias J, Arias JL (2013) Mapping metabolic brain activity in three models of hepatic encephalopathy. Int J Hypertens 390872
Azorín I, Miñana MD, Felipo V, Grisolía S (1989) A simple animal model of hyperammonemia. Hepatology 10:311–314
Bernabeu R, Schmitz P, Faillace MP, Izquierdo I, Medina JH (1996) Hippocampal cGMP and cAMP are differentially involved in memory processing of inhibitory avoidance learning. Neuroreport 7:585–588
Bernabeu R, Schroder N, Quevedo J, Cammarota M, Izquierdo I, Medina JH (1997) Further evidence for the involvement of a Hippocampal cGMP/cGMP-dependent protein kinase cascade in memory consolidation. Neuroreport 8:2221–2224
Boulton CL, Southam E, Garthwaite J (1995) Nitric oxide-dependent long-term Potentiation is blocked by a specific inhibitor of soluble guanylyl cyclase. Neuroscience 69:699–703
Burns LH, Annett L, Kelley AE, Everitt BJ, Robbins TW (1996) Effects of lesions to amygdala, ventral subiculum, medial prefrontal cortex, and nucleus accumbens on the reaction to novelty: Implication for limbic-striatal interactions. Behav Neurosci 110:60–73
Butterworth RF (1991) Pathophysiology of hepatic encephalopathy: The ammonia hypothesis revisited. In: Bengtsson F, Jeppsson B, Aamdal T, Vistrup H (eds) Progress in hepatic encephalopathy and metabolic nitrogen exchange. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 9–24
Butterworth RF (2003) Hepatic encephalopathy. Alcohol Res Health 27:240–246
Calton JL, Turner CS, Cyrenne DL, Lee BR, Taube JS (2008) Landmark control and updating of self-movement cues are largely maintained in head direction cells after lesions of the posterior parietal cortex. Behav Neurosci 122:827–840
Conejo NM, González-Pardo H, González-Lima F, Arias JL (2010) Spatial learning of the water maze: Progression of brain circuits mapped with cytochrome oxidase histochemistry. Neurobiol Learn and Mem 93:362–371
Cooper AJ, Lai JC (1987) Cerebral ammonia metabolism in normal and hyperammonemic rats. Neurochem Pathol 6:67–95
Cooper AJ, Plum F (1987) Biochemistry and physiology of brain ammonia. Physiol Rev 67:440–519
Corbalán R, Chatauret N, Behrends S, Butterworth RF, Felipo V (2002) Region selective alterations of soluble guanylate cyclase content and modulation in brain of cirrhotic patients. Hepatology 36:1155–1162
de Bruin JP, Moita MP, de Brabander HM, Joosten RN (2001) Place and response learning of rats in a Morris water maze: Differential effects of fimbria fornix and medial prefrontal cortex lesions. Neurobiol Learn Mem 75:164–178
Delatour B, Gisquet-Verrier P (2000) Functional role of rat prelimbic-infralimbic cortices in spatial memory: Evidence for their involvement in attention and behavioural flexibility. Behav Brain Res 109:113–128
Dougherty KA, Islam T, Johnston D (2012) Intrinsic excitability of CA1 pyramidal neurones from the rat dorsal and ventral hippocampus. J Physiol 590:5707–5722
Erceg S, Monfort P, Hernández-Viadel M, Rodrigo R, Montoliu C, Felipo V (2005) Oral administration of sildenafil restores learning ability in rats with hyperammonemia and with portacaval shunts. Hepatology 41:299–306
Felipo V (2013) Hepatic encephalopathy: Effects of liver failure on brain function. Nat Rev Neurosci 14:851–858
Fuster JM (2001) The prefrontal cortex–an update: Time is of the essence. Neuron 30:319–333
Galani R, Obis S, Coutureau E, Jarrard L, Cassel JC (2002) A comparison of the effects of fimbria-fornix, Hippocampal, or entorhinal cortex lesions on spatial reference and working memory in rats: Short versus long postsurgical recovery period. Neurobiol Learn Mem 77:1–16
Glenn MJ, Nesbitt C, Mumby DG (2003) Perirhinal cortex lesions produce variable patterns of retrograde amnesia in rats. Behav Brain Res 141:183–193
González-Lima F, Cada A (1994) Cytochrome oxidase activity in the auditory system of the mouse: A qualitative and quantitative histochemical study. Neuroscience 63:559–578
Groenewegen HJ, Berendse HW, Wolters JG, Lohman AH (1990) The anatomical relationship of the prefrontal cortex with the striatopallidal system, the thalamus and the amygdala: Evidence for a parallel organization. Prog Brain Res 85:95–116
Hawkins RA, Mans AM (1989) Brain energy metabolism in hepatic encephalopathy. In: Boulton AA, Baker GB, Butterworth RF (eds) Hepatic encephalopathy. Pathophysiology and treatment. Humana Press, Clifton, pp 159–176
Hawkins RD (1996) NO honey, I don’t remember. Neuron 16:465–467
Hermenegildo C, Montoliu C, Llansola M, Muñoz MD, Gaztelu JM, Miñana MD, Felipo V (1998) Chronic hyperammonemia impairs glutamate-nitric oxide-cyclic GMP pathway in cerebellar neurons in culture and in the rat in vivo. Eur J Neurosci 10:3201–3209
Hoover WB, Vertes RP (2007) Anatomical analysis of afferent projections to the medial prefrontal cortex in the rat. Brain Struct Funct 212:149–179
Hunsaker MR, Fieldste PM, Rosenberg JS, Kesner RP (2008) Dissociating the roles of dorsal and ventral CA1 for the temporal processing of spatial locations, visual objects, and odors. Behav Neurosci 122:643–650
Ishikawa A, Nakamura S (2006) Ventral Hippocampal neurons project axons simultaneously to the medial prefrontal cortex and amygdala in the rat. J Neurophysiol 96:2134–2138
Jessy J, Mans AM, DeJoseph MR, Hawkins RA (1990) Hyperammonaemia causes many of the changes found after portacaval shunting. Biochem J 272:311–317
Jones BJ, Roberts DJ (1968) The quantitative measurement of motor incoordination in naïve mice using an accelerating rotarod. J Pharm Pharmacol 20:302–304
Jover R, Madaria E, Felipo V, Rodrigo R, Candela A, Compañ A (2005) Animal models in the study of episodic hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhosis. Metab Brain Dis 20:399–408
Kealy J, Commins S (2011) The rat perirhinal cortex: A review of anatomy, physiology, plasticity, and function. Prog Neurobiol 93:522–548
Kesner RP (1990) Memory for frequency in rats: Role of the hippocampus and medial prefrontal cortex. Behav Neural Biol 53:402–410
Kolb B, Whishaw IQ (2003) Fundamentals of human neuropsychology. Worth Publishers, New York
Llansola M, Hernandez-Viadel M, Erceg S, Montoliu C, Felipo V (2009) Increasing the function of the glutamate-nitric oxide-cyclic guanosine monophosphate pathway increases the ability to learn a Y-maze task. J Neurosci Res 87:2351–2355
Long JM, Kesner RP (1996) The effects of dorsal versus ventral Hippocampal, total Hippocampal, and parietal cortex lesions on memory for allocentric distance in rats. Behav Neurosci 110:922–932
McDonald RJ, White NM (1994) Parallel information processing in the water maze: Evidence for independent memory systems involving dorsal striatum and hippocampus. Behav Neural Biol 61:260–270
Méndez M, Méndez-López M, López L, Aller MA, Arias J, Arias JL (2011) Portosystemic hepatic encephalopathy model shows reversal learning impairment and dysfunction of neural activity in the prefrontal cortex and regions involved in motivated behavior. J Clin Neurosci 18:690–694
Mizumori SJ, Puryear CB, Martig AK (2009) Basal ganglia contributions to adaptive navigation. Behav Brain Res 199:32–42
Moghaddam B, Homayoun H (2008) Divergent plasticity of prefrontal cortex networks. Neuropsychopharmacology 33:42–55
Murthy CR, Rama Rao KV, Bai G, Norenberg MD (2001) Ammonia-induced production of free radicals in primary cultures of rat astrocytes. J Neurosci Res 66:282–288
Norenberg MD, Huo Z, Neary JT, Roig-Cantesano A (1997) The glial glutamate transporter in hyperammonemia and hepatic encephalopathy: Relation to energy metabolism and glutamatergic neurotransmission. Glia 21:124–133
Paxinos G, Watson CH (2005) The rat brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates—the new coronal set 5th ed. Elsevier Academic Press.
Raabe WA (1989) Neuropathology of ammonia intoxication. In (RF Butterworth and G Pomier Layrargues, eds.) Hepatic encephalopathy: Pathophysiology and Treatment, Humana Press, Clifton, NJ.
Rao KV, Norenberg MD (2001) Cerebral energy metabolism in hepatic encephalopathy and hyperammonemia. Metab Brain Dis 16:67–78
Rodrigo R, Erceg S, Rodriguez-Diaz J, Saez-Valero J, Piedrafita B, Suarez I, Felipo V (2007) Glutamate-induced activation of nitric oxide synthase is impaired in cerebral cortex in vivo in rats with chronic liver failure. J Neurochem 102:51–64
Rodrigo R, Felipo V (2006) Brain regional alterations in the modulation of the glutamate-nitric oxide-cGMP pathway in liver cirrhosis. Role of hyperammonemia and cell types involved. Neurochem Int 48:472–477
Rogers JL, Kesner RP (2006) Lesions of the dorsal hippocampus or parietal cortex differentially affect spatial information processing. Behav Neurosci 120:852–860
Rutten K, Vente JD, Sik A, Ittersum MM, Prickaerts J, Blokland A (2005) The selective PDE5 inhibitor, sildenafil, improves object memory in Swiss mice and increases cGMP levels in Hippocampal slices. Behav Brain Res 164:11–16
Save E, Poucet B (2000) Involvement of the hippocampus and associative parietal cortex in the use of proximal and distal landmarks for navigation. Behav Brain Res 109:195–206
Shawcross DL, Wright G, Olde Damink SW, Jalan R (2007) Role of ammonia and inflammation in minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Metab Brain Dis 22:125–138
Smith S, Dringenberg HC, Bennett BM, Thatcher GR, Reynolds JN (2000) A novel nitrate ester reverses the cognitive impairment caused by scopolamine in the Morris water maze. Neuroreport 11:3883–3886
Stewart VC, Sharpe MA, Clark JB, Heales SJ (2000) Astrocyte-derived nitric oxide causes both reversible and irreversible damage to the neuronal mitochondrial respiratory chain. J Neurochem 75:694–700
Sutherland RJ, Hoesing JM (1993) Posterior cingulate cortex and spatial memory: A microlimnology analysis. In: Vogt BA, Gabriel M (eds) Neurobiology of cingulate cortex and limbic thalamus. Birkhauser, Boston
Wang V, Saab S (2003) Ammonia levels and the severity of hepatic encephalopathy. Am J Med 114:237–238
Weissenborn K, Heidenreich S, Giewekemeyer K, Rückert N, Hecker H (2003) Memory function in early hepatic encephalopathy. J Hepatol 39:320–325
Wiig KA, Bilkey DK (1994) The effects of perirhinal cortical lesions on spatial reference memory in the rat. Behav Brain Res 63:101–109
Wolff M, Gibb SJ, Cassel JC, Dalrymple-Alford JC (2008) Anterior but not intralaminar thalamic nuclei support allocentric spatial memory. Neurobiol Learn Mem 90:71–80
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Grants MICINN PSI2010-19348 and MEC AP2009-1714 to NA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arias, N., Fidalgo, C., Felipo, V. et al. The effects of hyperammonemia in learning and brain metabolic activity. Metab Brain Dis 29, 113–120 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-013-9477-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-013-9477-0