Abstract
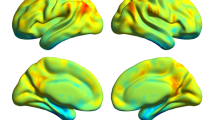
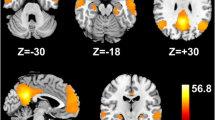
Neurocognitive dysfunction of varying degrees is common in patients with hepatitis B virus-related cirrhosis (HBV-RC) without overt hepatic encephalopathy (OHE). However, the neurobiological mechanisms underlying these dysfunctions are not well understood. We sought to identify changes in the neural activity of patients with HBV-RC without OHE in the resting state by using the amplitude of low-frequency fluctuation (ALFF) method and to determine whether these changes were related to impaired cognition. Resting-state functional MRI data from 30 patients with HBV-RC and 30 healthy controls matched for age, sex, and years of education were compared to determine any differences in the ALFF between the two groups. Cognition was measured with the psychometric hepatic encephalopathy score (PHES), and the relationship between these scores and ALFF variation was assessed. Compared with controls, patients showed widespread lower standardized ALFF (mALFF) values in visual association areas (bilateral lingual gyrus, middle occipital gyrus, and left inferior temporal gyrus), motor-related areas (bilateral precentral gyrus, paracentral lobule, and right postcentral gyrus), and the default mode network (bilateral cuneus/precuneus and inferior parietal lobule). Higher mALFF values were found in the bilateral orbital gyrus/rectal gyrus. In patients, mALFF values were significantly positive correlated with the PHES in the right middle occipital gyrus and bilateral precentral gyrus. Our findings of resting-state abnormalities in patients with HBV-RC without OHE suggest that neurocognitive dysfunction in patients with HBV-RC without OHE may be caused by abnormal neural activity in multiple brain regions.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HBV-RC:
-
HBV-related cirrhosis
- OHE:
-
Overt hepatic encephalopathy
- ALFF:
-
Amplitude of low-frequency fluctuation
- mALFF:
-
Standardized amplitude of low-frequency fluctuation
- PHES:
-
Psychometric hepatic encephalopathy score
- HE:
-
Hepatic encephalopathy
- fMRI:
-
Functional MRI
- BOLD:
-
Blood oxygenation level-dependent
References
Amodio P, Campagna F, Olianas S, Iannizzi P, Mapelli D, Penzo M, Angeli P, Gatta A (2008) Detection of minimal hepatic encephalopathy: normalization and optimization of the Psychometric Hepatic Encephalopathy Score. A neuropsychological and quantified EEG study. J Hepatol 49:346–353
Biswal B, Yetkin FZ, Haughton VM, Hyde JS (1995) Functional connectivity in the motor cortex of resting human brain using echo-planar MRI. Magn Reson Med 34:537–541
Burra P, Senzolo M, Pizzolato G, Ermani M, Chierichetti F, Bassanello M, Naccarato R, Dam M (2004) Does liver-disease aetiology have a role in cerebral blood-flow alterations in liver cirrhosis? Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 16:885–890
Chen HJ, Wang Y, Zhu XQ, Cui Y, Chen YC, Teng GJ (2012a) White matter abnormalities correlate with neurocognitive performance in patients with HBV-related cirrhosis. J Neurol Sci 321:65–72
Chen HJ, Zhu XQ, Jiao Y, Li PC, Wang Y, Teng GJ (2012b) Abnormal baseline brain activity in low-grade hepatic encephalopathy: a resting-state fMRI study. J Neurol Sci 318:140–145
Chen HJ, Zhu XQ, Yang M, Liu B, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Teng GJ (2012c) Changes in the regional homogeneity of resting-state brain activity in minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Neurosci Lett 507:5–9
Cordoba J (2011) New assessment of hepatic encephalopathy. J Hepatol 54:1030–1040
Dai Z, Yan C, Wang Z, Wang J, Xia M, Li K, He Y (2012) Discriminative analysis of early Alzheimer’s disease using multi-modal imaging and multi-level characterization with multi-classifier (M3). NeuroImage 59:2187–2195
Dhiman RK, Chawla YK (2009) Minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Indian J Gastroenterol 28:5–16
Duarte-Rojo A, Estradas J, Hernandez-Ramos R, Ponce-de-Leon S, Cordoba J, Torre A (2011) Validation of the psychometric hepatic encephalopathy score (PHES) for identifying patients with minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Dig Dis Sci 56:3014–3023
Forss N, Merlet I, Vanni S, Hamalainen M, Mauguiere F, Hari R (1996) Activation of human mesial cortex during somatosensory target detection task. Brain Res 734:229–235
Fox MD, Snyder AZ, Vincent JL, Corbetta M, Van Essen DC, Raichle ME (2005) The human brain is intrinsically organized into dynamic, anticorrelated functional networks. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:9673–9678
Hitomi T, Koubeissi MZ, Kaffashi F, Turnbull J, Luders HO (2012) Visual processing in the inferior temporal cortex: an intracranial event related potential study. Clin Neurophysiol
Huda A, Gupta RK, Rajakumar N, Thomas MA (2008) Role of magnetic resonance in understanding the pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy. Magn Reson Insights 2:109–122
Lee HW, Hong SB, Seo DW, Tae WS, Hong SC (2000) Mapping of functional organization in human visual cortex: electrical cortical stimulation. Neurology 54:849–854
Li YY, Nie YQ, Sha WH, Zeng Z, Yang FY, Ping L, Jia L (2004) Prevalence of subclinical hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhotic patients in China. World J Gastroenterol 10:2397–2401
Lim SH, Dinner DS, Pillay PK, Luders H, Morris HH, Klem G, Wyllie E, Awad IA (1994) Functional anatomy of the human supplementary sensorimotor area: results of extraoperative electrical stimulation. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 91:179–193
Lockwood AH, Weissenborn K, Bokemeyer M, Tietge U, Burchert W (2002) Correlations between cerebral glucose metabolism and neuropsychological test performance in nonalcoholic cirrhotics. Metab Brain Dis 17:29–40
Lowe MJ, Mock BJ, Sorenson JA (1998) Functional connectivity in single and multislice echoplanar imaging using resting-state fluctuations. NeuroImage 7:119–132
Lv XF, Qiu YW, Tian JZ, Xie CM, Han LJ, Su HH, Liu ZY, Peng JP, Lin CL, Wu MS, Jiang GH, Zhang XL (2013) Abnormal regional homogeneity of resting-state brain activity in patients with HBV-related cirrhosis without overt hepatic encephalopathy. Liver Int 33:375–383
Mantini D, Perrucci MG, Del GC, Romani GL, Corbetta M (2007) Electrophysiological signatures of resting state networks in the human brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:13170–13175
McPhail MJ, Taylor-Robinson SD (2010) The role of magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy in hepatic encephalopathy. Metab Brain Dis 25:65–72
Moriwaki H, Shiraki M, Iwasa J, Terakura Y (2010) Hepatic encephalopathy as a complication of liver cirrhosis: an Asian perspective. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 25:858–863
Ni L, Qi R, Zhang LJ, Zhong J, Zheng G, Zhang Z, Zhong Y, Xu Q, Liao W, Jiao Q, Wu X, Fan X, Lu GM (2012) Altered regional homogeneity in the development of minimal hepatic encephalopathy: a resting-state functional MRI study. PLoS One 7:e42016
Qi R, Zhang L, Wu S, Zhong J, Zhang Z, Zhong Y, Ni L, Zhang Z, Li K, Jiao Q, Wu X, Fan X, Liu Y, Lu G (2012) Altered resting-state brain activity at functional MR imaging during the progression of hepatic encephalopathy. Radiology 264:187–195
Raichle ME, MacLeod AM, Snyder AZ, Powers WJ, Gusnard DA, Shulman GL (2001) A default mode of brain function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:676–682
Wandell BA, Dumoulin SO, Brewer AA (2007) Visual field maps in human cortex. Neuron 56:366–383
Weiskopf N, Hutton C, Josephs O, Turner R, Deichmann R (2007) Optimized EPI for fMRI studies of the orbitofrontal cortex: compensation of susceptibility-induced gradients in the readout direction. MAGMA 20:39–49
Weissenborn K (2008) PHES: one label, different goods?! J Hepatol 49:308–312
Weissenborn K, Ennen JC, Schomerus H, Ruckert N, Hecker H (2001) Neuropsychological characterization of hepatic encephalopathy. J Hepatol 34:768–773
Weissenborn K, Ahl B, Fischer-Wasels D, van den Hoff J, Hecker H, Burchert W, Kostler H (2007) Correlations between magnetic resonance spectroscopy alterations and cerebral ammonia and glucose metabolism in cirrhotic patients with and without hepatic encephalopathy. Gut 56:1736–1742
Zafiris O, Kircheis G, Rood HA, Boers F, Haussinger D, Zilles K (2004) Neural mechanism underlying impaired visual judgement in the dysmetabolic brain: an fMRI study. NeuroImage 22:541–552
Zang YF, He Y, Zhu CZ, Cao QJ, Sui MQ, Liang M, Tian LX, Jiang TZ, Wang YF (2007) Altered baseline brain activity in children with ADHD revealed by resting-state functional MRI. Brain Dev 29:83–91
Zhu Z, Lu Q, Meng X, Jiang Q, Peng L, Wang Q (2012) Spatial patterns of intrinsic neural activity in depressed patients with vascular risk factors as revealed by the amplitude of low-frequency fluctuation. Brain Res 1483:82–88
Acknowledgments
We thank the participants who magnanimously donate their time to participate in this study. Also, the authors are highly grateful to the anonymous reviewers for their significant and constructive comments and suggestions, which greatly improve the article.
Disclosures
The authors declare that no conflict of interest exists concerning this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Drs. Xiao-Fei Lv, Min Ye and Lu-Jun Han contributed to the work equally.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lv, XF., Ye, M., Han, LJ. et al. Abnormal baseline brain activity in patients with HBV-related cirrhosis without overt hepatic encephalopathy revealed by resting-state functional MRI. Metab Brain Dis 28, 485–492 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-013-9420-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-013-9420-4