Abstract
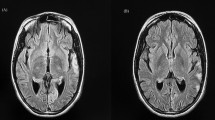
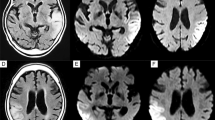
Epilepsy is one of the most common presentations of patients with mitochondrial myopathy, encephalopathy, lactic acidosis, and stroke-like episodes (MELAS). MELAS is typically caused by an A-to-G substitution at nucleotide position 3243 of mitochondrial DNA. Valproic acid, a common anticonvulsant, can actually increase the frequency of seizures in individuals with MELAS. Here, we report a single case-study of a 38-year-old man who presented with focal seizures and had MELAS Syndrome due to the A3243G mitochondrial DNA mutation. Manifestation of epilepsia partialis continua was aggravated by use of valproic acid. Convulsions abated after discontinuation of valproic acid. Our experience suggests that valproic acid should be avoided for the treatment of epilepsy in individuals with mitochondrial disease.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altrup U, Gerlach G, Reith H, Said MN, Speckmann EJ (1992) Effects of valproate in model nervous system (buccal ganglia of Helix pomatia): I. Antiepileptic actions. Epilepsia 33:743–752
Altrup U, Reith H, Speckmann EJ (1992) Effects of valproate in a model nervous system (buccal ganglia of Helix pomatia): II. Epileptogenic actions. Epilepsia 33:753–759
Aure K, Jardel C, Lombes A (2005) Mitochondrial diseases: Molecular mechanisms, clinical presentations and diagnosis investigations. Ann Pathol 25:270–281
Chabrol B, Mancini J, Chretien D, Rustin P, Munnich A, Pinsard N (1994) Valproate-induced hepatic failure in a case of cytochrome c oxidase deficiency. Eur J Pediatr 153:133–135
Chinnery PF, Howell N, Lightowlers RN, Tumball DM (1997) Molecular pathology of MELAS and MERRF: The relationship between mutation load and clinical phenotypes. Brain 120:1713–1721
Dimauro S, Davidzon G (2005) Mitochondrial DNA and disease. Ann Med 37:222–232
Krahenbuhl S, Brandner S, Kleinle S, Liechti S, Straumann D (2000) Mitochondrial diseases represent a risk factor for valproate-induced fulminant liver failure. Liver 20:346–348
Kunz WS (2002) The role of mitochondria in epileptogenesis. Curr Opin Neurol 15:179–184
Lam CW, Lau CH, Williams JC, Chan YW, Wong LJ (1997) Mitochondrial myopathy, encephalopathy, lactic acidosis and stroke-like episodes (MELAS) triggered by valproate therapy. Eur J Pediatr 156:562–564
Liou CW, Huang CC, Chee EC, Jong YJ, Tsai JL, Pang CY, Lee HC, Wei YH (1994) MELAS Syndrome: Correlation between clinical features and molecular genetic analysis. Acta Neurol Scand 90:354–359
Morris AA (1999) Mitochondrial respiratory chain disorders and the liver. Liver 19:357–368
Pavlakis SG, Phillips PC, DiMauro S, De Vivo DC, Rowland LP (1984) Mitochondrial myopathy, encephalopathy, lactic acidosis, and stroke-like episodes: A distinctive clinical syndrome. Ann Neurol 16:481–488
Ponchaut S, Van Hoof F, Veitch K (1992) Cytochrome aa3 depletion is the cause of the deficient mitochondrial respiration induced by chronic valproate administration. Biochem Pharmacol 43:644–647
Ponchaut S, Van Hoof F, Veitch K (1995) Valproate and cytochrome c oxidase deficiency. Eur J Pediatr 154:79
Scaglia F, Northrop JP (2006) The mitochondrial myopathy encephalopathy, lactic acidosis with stroke-like episodes (MELAS) syndrome: A review of treatment options. CNS Drugs 20:443–464
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11011-007-9056-3
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, CM., Thajeb, P. Valproic Acid Aggravates Epilepsy due to MELAS in a Patient with an A3243G Mutation of Mitochondrial DNA. Metab Brain Dis 22, 105–109 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-006-9039-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-006-9039-9