Abstract
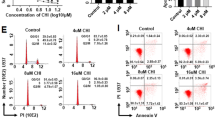
This research aimed to explore whether Chidamide works synergistically with Dasatinib in the therapy of Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and the potential molecular mechanism. The inhibition rate of the Dasatinib and Chidamide combination was significantly better than that of the single-drug application for HL-60 cells. The combination of Dasatinib and Chidamide significantly enhanced the Abnormal histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitory activity of Chidamide in Kasumi-1 and HL-60 cells. In the combined group, the proportion of S phase was significantly decreased, and the proportions of G2/M phase were significantly increased. The inhibitory rate of CD34+ CD38− HL-60 cells or Kasumi-1 cells was elevated when the cells were disposed with both Chidamide and Dasatinib. Dasatinib and Chidamide had synergistic antitumor effect. The combination with Dasatinib enhanced the HDAC inhibitory activity of Chidamide, promoted cell apoptosis and cell-cycle arrest of AML cells, and enhanced the inhibition of leukemia stem cell proliferation.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Pelcovits A, Niroula R (2020) Acute myeloid leukemia: a review. R I Med J 103:38–40
De Kouchkovsky I, Abdul-Hay M (2016) Acute myeloid leukemia: a comprehensive review and 2016 update. Blood Cancer J 6:e441. https://doi.org/10.1038/bcj.2016.50
Infante MS, Piris MA, Hernandez-Rivas JA (2018) Molecular alterations in acute myeloid leukemia and their clinical and therapeutical implications. Med Clin 151:362–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.medcli.2018.05.002
Kayser S, Levis MJ (2019) Clinical implications of molecular markers in acute myeloid leukemia. Eur J Haematol 102:20–35. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejh.13172
Liu H (2021) Emerging agents and regimens for AML. J Hematol Oncol 14:49. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-021-01062-w
Yi M, Li A, Zhou L, Chu Q, Song Y, Wu K (2020) The global burden and attributable risk factor analysis of acute myeloid leukemia in 195 countries and territories from 1990 to 2017: estimates based on the global burden of disease study 2017. J Hematol Oncol 13:72. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-020-00908-z
Megias-Vericat JE, Ballesta-Lopez O, Barragan E, Martinez-Cuadron D, Montesinos P (2020) Tyrosine kinase inhibitors for acute myeloid leukemia: a step toward disease control? Blood Rev 44:100675. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.blre.2020.100675
Lindauer M, Hochhaus A (2018) Dasatinib. Recent Results Cancer Res 212:29–68. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-91439-8_2
Duncan EA, Goetz CA, Stein SJ, Mayo KJ, Skaggs BJ, Ziegelbauer K, Sawyers CL, Baldwin AS (2008) IkappaB kinase beta inhibition induces cell death in Imatinib-resistant and T315I Dasatinib-resistant BCR-ABL+ cells. Mol Cancer Ther 7:391–397. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-07-0305
Baker WJ, Royer GL Jr, Weiss RB (1991) Cytarabine and neurologic toxicity. J Clin Oncol 9:679–693. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.1991.9.4.679
Patzke CL, Emadi A (2020) High dose cytarabine, mitoxantrone, pegasapargase (HAM-pegA) in combination with dasatinib for the first-line treatment of Philadelphia chromosome positive mixed phenotype acute leukemia. Am J Leuk Res 4:1020
Seto E, Yoshida M (2014) Erasers of histone acetylation: the histone deacetylase enzymes. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 6:a018713. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a018713
Xu QY, Yu L (2020) Epigenetic therapies in acute myeloid leukemia: the role of hypomethylating agents, histone deacetylase inhibitors and the combination of hypomethylating agents with histone deacetylase inhibitors. Chin Med J. https://doi.org/10.1097/CM9.0000000000000685
Shi Y, Jia B, Xu W, Li W, Liu T, Liu P, Zhao W, Zhang H, Sun X, Yang H, Zhang X, Jin J, Jin Z, Li Z, Qiu L, Dong M, Huang X, Luo Y, Wang X, Wang X, Wu J, Xu J, Yi P, Zhou J, He H, Liu L, Shen J, Tang X, Wang J, Yang J, Zeng Q, Zhang Z, Cai Z, Chen X, Ding K, Hou M, Huang H, Li X, Liang R, Liu Q, Song Y, Su H, Gao Y, Liu L, Luo J, Su L, Sun Z, Tan H, Wang H, Wang J, Wang S, Zhang H, Zhang X, Zhou D, Bai O, Wu G, Zhang L, Zhang Y (2017) Chidamide in relapsed or refractory peripheral T cell lymphoma: a multicenter real-world study in China. J Hematol Oncol 10:69. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-017-0439-6
Nguyen T, Dai Y, Attkisson E, Kramer L, Jordan N, Nguyen N, Kolluri N, Muschen M, Grant S (2011) HDAC inhibitors potentiate the activity of the BCR/ABL kinase inhibitor KW-2449 in imatinib-sensitive or -resistant BCR/ABL+ leukemia cells in vitro and in vivo. Clin Cancer Res 17:3219–3232. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-0234
Zhang B, Strauss AC, Chu S, Li M, Ho Y, Shiang KD, Snyder DS, Huettner CS, Shultz L, Holyoake T, Bhatia R (2010) Effective targeting of quiescent chronic myelogenous leukemia stem cells by histone deacetylase inhibitors in combination with imatinib mesylate. Cancer Cell 17:427–442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2010.03.011
Aggerholm-Pedersen N, Demuth C, Safwat A, Meldgaard P, Kassem M, Sandahl Sorensen B (2016) Dasatinib and doxorubicin treatment of sarcoma initiating cells: a possible new treatment strategy. Stem Cells Int 2016:9601493. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/9601493
Bose P, Vachhani P, Cortes JE (2017) Treatment of relapsed/refractory acute myeloid leukemia. Curr Treat Options Oncol 18:17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11864-017-0456-2
Short NJ, Konopleva M, Kadia TM, Borthakur G, Ravandi F, DiNardo CD, Daver N (2020) Advances in the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia: new drugs and new challenges. Cancer Discov 10:506–525. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.CD-19-1011
Witt O, Deubzer HE, Milde T, Oehme I (2009) HDAC family: What are the cancer relevant targets? Cancer Lett 277:8–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2008.08.016
de Ruijter AJ, van Gennip AH, Caron HN, Kemp S, van Kuilenburg AB (2003) Histone deacetylases (HDACs): characterization of the classical HDAC family. Biochem J 370:737–749. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20021321
San Jose-Eneriz E, Gimenez-Camino N, Agirre X, Prosper F (2019) HDAC inhibitors in acute myeloid leukemia. Cancers 11:1794. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11111794
Nakagawa M, Oda Y, Eguchi T, Aishima S, Yao T, Hosoi F, Basaki Y, Ono M, Kuwano M, Tanaka M, Tsuneyoshi M (2007) Expression profile of class I histone deacetylases in human cancer tissues. Oncol Rep 18:769–774
Lernoux M, Schnekenburger M, Dicato M, Diederich M (2020) Epigenetic mechanisms underlying the therapeutic effects of HDAC inhibitors in chronic myeloid leukemia. Biochem Pharmacol 173:113698. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2019.113698
Ho TCS, Chan AHY, Ganesan A (2020) Thirty years of HDAC inhibitors: 2020 insight and hindsight. J Med Chem 63:12460–12484. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c00830
Xu Y, Zhang P, Liu Y (2017) Chidamide tablets: HDAC inhibition to treat lymphoma. Drugs Today 53:167–176. https://doi.org/10.1358/dot.2017.53.3.2595452
Ding N, You A, Tian W, Gu L, Deng D (2020) Chidamide increases the sensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer to Crizotinib by decreasing c-MET mRNA methylation. Int J Biol Sci 16:2595–2611. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.45886
Chan TS, Tse E, Kwong YL (2017) Chidamide in the treatment of peripheral T-cell lymphoma. Onco Targets Ther 10:347–352. https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S93528
Peng J, Li SJ, Fu X, Liu Y, Zhao XL (2020) Chidamide acts on the histone deacetylase-mediated miR-34a/Bcl-2 axis to regulate NB4 cell line proliferation and apoptosis. Kaohsiung J Med Sci 36:1004–1013. https://doi.org/10.1002/kjm2.12283
Trenker R, Jura N (2020) Receptor tyrosine kinase activation: from the ligand perspective. Curr Opin Cell Biol 63:174–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceb.2020.01.016
Doepfner KT, Boller D, Arcaro A (2007) Targeting receptor tyrosine kinase signaling in acute myeloid leukemia. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 63:215–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.critrevonc.2007.05.005
McCafferty EH, Dhillon S, Deeks ED (2018) Dasatinib: a review in pediatric chronic myeloid leukemia. Paediatr Drugs 20:593–600. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40272-018-0319-8
Mpakou VE, Kontsioti F, Papageorgiou S, Spathis A, Kottaridi C, Girkas K, Karakitsos P, Dimitriadis G, Dervenoulas I, Pappa V (2013) Dasatinib inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in the KASUMI-1 cell line bearing the t(8;21)(q22;q22) and the N822K c-kit mutation. Leuk Res 37:175–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.leukres.2012.10.011
Hackl H, Astanina K, Wieser R (2017) Molecular and genetic alterations associated with therapy resistance and relapse of acute myeloid leukemia. J Hematol Oncol 10:51. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-017-0416-0
Shi Y, Dong M, Hong X, Zhang W, Feng J, Zhu J, Yu L, Ke X, Huang H, Shen Z, Fan Y, Li W, Zhao X, Qi J, Huang H, Zhou D, Ning Z, Lu X (2015) Results from a multicenter, open-label, pivotal phase II study of chidamide in relapsed or refractory peripheral T-cell lymphoma. Ann Oncol 26:1766–1771. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdv237
Wang L, Luo J, Chen G, Fang M, Wei X, Li Y, Liu Z, Zhang Y, Gao S, Shen J, Wang X, Gao X, Zhou W, Ma Y, Liu H, Li X, Yang L, Sun K, Yu L (2020) Chidamide, decitabine, cytarabine, aclarubicin, and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (CDCAG) in patients with relapsed/refractory acute myeloid leukemia: a single-arm, phase 1/2 study. Clin Epigenet 12:132. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13148-020-00923-4
Eckschlager T, Plch J, Stiborova M, Hrabeta J (2017) Histone deacetylase inhibitors as anticancer drugs. Int J Mol Sci 18:1414. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18071414
Liang S, Zhou X, Cai D, Rodrigues-Lima F, Wang L (2021) Chidamide inhibits cell proliferation via the PI3K/AKT pathway in K562 cells based on network pharmacology and experimental validation. Curr Pharm Des. https://doi.org/10.2174/1381612827666210701152250
Thomas D, Majeti R (2017) Biology and relevance of human acute myeloid leukemia stem cells. Blood 129:1577–1585. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2016-10-696054
Li Y, Wang Y, Zhou Y, Li J, Chen K, Zhang L, Deng M, Deng S, Li P, Xu B (2017) Cooperative effect of chidamide and chemotherapeutic drugs induce apoptosis by DNA damage accumulation and repair defects in acute myeloid leukemia stem and progenitor cells. Clin Epigenet 9:83. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13148-017-0377-8
Liu L, Yin S, Brobbey C, Gan W (2020) Ubiquitination in cancer stem cell: roles and targeted cancer therapy. STEMedicine 1:e37. https://doi.org/10.37175/stemedicine.v1i3.37
Li Y, Chen K, Zhou Y, Xiao Y, Deng M, Jiang Z, Ye W, Wang X, Wei X, Li J, Liang J, Zheng Z, Yao Y, Wang W, Li P, Xu B (2015) A new strategy to target acute myeloid leukemia stem and progenitor cells using chidamide, a histone Deacetylase inhibitor. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 15:493–503. https://doi.org/10.2174/156800961506150805153230
He B, Wang Q, Liu X, Lu Z, Han J, Pan C, Carter BZ, Liu Q, Xu N, Zhou H (2020) A novel HDAC inhibitor chidamide combined with imatinib synergistically targets tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistant chronic myeloid leukemia cells. Biomed Pharmacother 129:110390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110390
Funding
The study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province (2018JJ2581).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The study was approved by Xiangya Second Hospital, Central South University.
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, M., Xiao, H., Peng, H. et al. Chidamide works synergistically with Dasatinib by inducing cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis in acute myeloid leukemia cells. Mol Cell Biochem 478, 851–860 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-022-04554-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-022-04554-6