Abstract
Liver cancer is the sixth common cancer and forth cause of cancer-related death worldwide. Based on usually advanced stages of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) at the time of diagnosis, therapeutic options are limited and, in many cases, not effective, and typically result in the tumor recurrence with a poor prognosis. Radioimmunotherapy (RIT) offers a selective internal radiation therapy approach using beta or alpha emitting radionuclides conjugated with tumor-specific monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), or specific selective peptides. When compared to chemotherapy or radiotherapy, radiolabeled mAbs against cancer-associated antigens could provide a high therapeutic and exclusive radiation dose for cancerous cells while decreasing the exposure-induced side effects to healthy tissues. The recent advances in cancer immunotherapy, such as blockade of immune-checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), has changed the landscape of cancer therapy, and the efficacy of different classes of immunotherapy has been tested in many clinical trials. Taking into account the use of ICIs in the liver tumor microenvironment, combined therapies with different approaches may enhance the outcome in the future clinical studies. With the development of novel immunotherapy treatment options in the recent years, there has been a great deal of information about combining the diverse treatment modalities to boost the effectiveness of immunomodulatory drugs. In this opinion review, we will discuss the recent advancements in RIT. The current status of immunotherapy and internal radiotherapy will be updated, and we will propose novel approaches for the combination of both techniques.
Graphical abstract
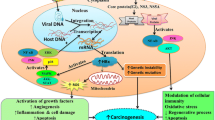
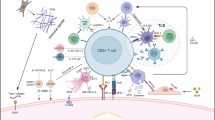
Potential target antigens for radioimmunotherapy in Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). HCC radioimmunotherapy target antigens are the most specific and commonly accessible antigens on the surface of HCC cells. CTLA-4 ligand and receptor, TAMs, PD-1/PD-L, TIM-3, specific IEXs/TEXs, ROBO1, and cluster of differentiation antigens CD105, CD147 could all be used in HCC radioimmunotherapy. Abbreviations: TAMs, tumor-associated macrophages; CTLA-4, cytotoxic T-lymphocyte associated antigen-4; PD-1, Programmed cell death protein 1; PD-L, programmed death-ligand1; TIM-3, T-cell immunoglobulin (Ig) and mucin-domain containing protein-3; IEXs, immune cell-derived exosomes; TEXs, tumor-derived exosomes.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A (2018) Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: Cancer J Clin 68(6):394–424
Shokoohian B, Negahdari B, Aboulkheyr Es H, Abedi-Valugerdi M, Baghaei K, Agarwal T et al (2021) Advanced therapeutic modalities in hepatocellular carcinoma: novel insights. J Cell Mol Med 25(18):8602–8614
Kang-Da L, Zhao-You T, Yan-Ming B, Ji-Zhen L, Feng Q, Ai-Na Y et al (1989) Radioimmunotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) using 131I-anti HCC isoferritin IgG: preliminary results of experimental and clinical studies. Int J Radiat Oncol* Biol* Phys 16(2):319–323
Larson SM, Carrasquillo JA (2015) Cheung N-KV, Press OWJNRC. Radioimmunother Hum Tumours 15(6):347
Sahlin M, Bauden MP, Andersson R, Ansari DJTB (2015) Radioimmunotherapy—a potential novel tool for pancreatic cancer therapy? Tumor Biol 36(6):4053–4062
Wu L, Yang Y-F, Ge N-J, Shen S-Q, Liang J, Wang Y et al (2010) Hepatic arterial Iodine-131–labeled metuximab injection combined with chemoembolization for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: interim safety and survival data from 110 patients. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 25(6):657–663
Tartarone A, Lapadula V, Di Micco C, Rossi G, Ottanelli C, Marini A et al (2021) Beyond conventional: the new horizon of targeted therapy for the treatment of advanced non small cell lung cancer. Front Oncol 11:632256
Tartarone A, Roviello G, Lerose R, Roudi R, Aieta M, Zoppoli P (2019) Anti-PD-1 versus anti-PD-L1 therapy in patients with pretreated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a meta-analysis. Future Oncol 15(20):2423–2433
Lee HW, Cho KJ, Park JY (2020) Current status and future direction of immunotherapy in hepatocellular carcinoma: what do the data suggest? Immune Netw 20(1):e11-e
Bourke JM, O’Sullivan M, Khattak MA (2016) Management of adverse events related to new cancer immunotherapy (immune checkpoint inhibitors). Med J Aust 205(9):418–424
Zongyi Y, Xiaowu L (2020) Immunotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett 470:8–17
Llovet JM, Real MI, Montaña X, Planas R, Coll S, Aponte J et al (2002) Arterial embolisation or chemoembolisation versus symptomatic treatment in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a randomised controlled trial. The Lancet 359(9319):1734–1739
Wang T-H, Huang P-I, Hu Y-W, Lin K-H, Liu C-S, Lin Y-Y et al (2018) Combined Yttrium-90 microsphere selective internal radiation therapy and external beam radiotherapy in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: from clinical aspects to dosimetry. PLoS ONE 13(1):e0190098
Asadian S, Piryaei A, Gheibi N, Aziz Kalantari B, Reza Davarpanah M, Azad M et al (2022) Rhenium Perrhenate ((188)ReO(4)) induced apoptosis and reduced cancerous phenotype in liver cancer cells. Cells 11(2):305
Sigmund P (2014) Particle penetration and radiation effects volume 2. Springer Series in Solid-State Sciences, vol 179. Springer, Berlin
Kim Y-S, Brechbiel MW (2012) An overview of targeted alpha therapy. Tumor Biol 33(3):573–590
Asadian S, Mirzaei H, Kalantari BA, Davarpanah MR, Mohamadi M, Shpichka A et al (2020) β-radiating radionuclides in cancer treatment, novel insight into promising approach. Pharmacol Res 160:105070
Kawashima H (2014) Radioimmunotherapy: a specific treatment protocol for cancer by cytotoxic radioisotopes conjugated to antibodies. Sci World J. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/492061
Heymann F, Tacke F (2016) Immunology in the liver—from homeostasis to disease. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 13(2):88
Trivedi PJ, Adams DH (2016) Gut–liver immunity. J Hepatol 64(5):1187–1189
Horst AK, Neumann K, Diehl L, Tiegs G (2016) Modulation of liver tolerance by conventional and nonconventional antigen-presenting cells and regulatory immune cells. Cell Mol Immunol 13(3):277–292
Jenne CN, Kubes P (2013) Immune surveillance by the liver. Nat Immunol 14(10):996–1006
Chen D-P, Ning W-R, Jiang Z-Z, Peng Z-P, Zhu L-Y, Zhuang S-M et al (2019) Glycolytic activation of peritumoral monocytes fosters immune privilege via the PFKFB3-PD-L1 axis in human hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 71(2):333–343
Nguyen LT, Ohashi PS (2015) Clinical blockade of PD1 and LAG3—potential mechanisms of action. Nat Rev Immunol 15(1):45
Wang B-J, Bao J-J, Wang J-Z, Wang Y, Jiang M, Xing M-Y et al (2011) Immunostaining of PD-1/PD-Ls in liver tissues of patients with hepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma. WJG 17(28):3322
Jung HI, Jeong D, Ji S, Ahn TS, Bae SH, Chin S et al (2017) Overexpression of PD-L1 and PD-L2 is associated with poor prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res treat 49(1):246
Gao Q, Wang X-Y, Qiu S-J, Yamato I, Sho M, Nakajima Y et al (2009) Overexpression of PD-L1 significantly associates with tumor aggressiveness and postoperative recurrence in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 15(3):971–979
Okusaka T, Ikeda M (2018) Immunotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: current status and future perspectives. ESMO open 3(Suppl 1):e000455
Adcock CS, Puneky LV, Campbell GS (2019) Favorable response of metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma to treatment with trans-arterial radioembolization followed by Sorafenib and Nivolumab. Cureus. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.4083
El-Khoueiry AB, Sangro B, Yau T, Crocenzi TS, Kudo M, Hsu C et al (2017) Nivolumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (CheckMate 040): an open-label, non-comparative, phase 1/2 dose escalation and expansion trial. The Lancet 389(10088):2492–2502
Merck (2019) Merck provides update on KEYNOTE‐240, a phase 3 study of KEYTRUDA®(pembrolizumab) in previously treated patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma [press release]
Yan W, Liu X, Ma H, Zhang H, Song X, Gao L et al (2015) Tim-3 fosters HCC development by enhancing TGF-β-mediated alternative activation of macrophages. Gut 64(10):1593–1604
Liu F, Zeng G, Zhou S, He X, Sun N, Zhu X et al (2018) Blocking Tim-3 or/and PD-1 reverses dysfunction of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Bull Cancer 105(5):493–501
Farzaneh Z, Vosough M, Agarwal T, Farzaneh M (2021) Critical signaling pathways governing hepatocellular carcinoma behavior; small molecule-based approaches. Cancer Cell Int 21(1):1–15
Koyama S, Akbay EA, Li YY, Herter-Sprie GS, Buczkowski KA, Richards WG et al (2016) Adaptive resistance to therapeutic PD-1 blockade is associated with upregulation of alternative immune checkpoints. Nat Commun 7(1):1–9
Wolf Y, Anderson AC, Kuchroo VK (2020) TIM3 comes of age as an inhibitory receptor. Nat Rev Immunol 20(3):173–185
Zhang H, Song Y, Yang H, Liu Z, Gao L, Liang X et al (2018) Tumor cell-intrinsic Tim-3 promotes liver cancer via NF-κB/IL-6/STAT3 axis. Oncogene 37(18):2456–2468
Sobhani N, Tardiel-Cyril DR, Davtyan A, Generali D, Roudi R, Li Y (2021) CTLA-4 in regulatory T cells for cancer immunotherapy. Cancers 13(6):1440
Han Y, Chen Z, Yang Y, Jiang Z, Gu Y, Liu Y et al (2014) Human CD14+ CTLA-4+ regulatory dendritic cells suppress T-cell response by cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen-4-dependent IL-10 and indoleamine-2, 3-dioxygenase production in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 59(2):567–579
Sangro B, Gomez-Martin C, de la Mata M, Iñarrairaegui M, Garralda E, Barrera P et al (2013) A clinical trial of CTLA-4 blockade with tremelimumab in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and chronic hepatitis C. J Hepatol 59(1):81–88
Yau T, Kang Y-K, Kim T-Y, El-Khoueiry AB, Santoro A, Sangro B et al (2019) Nivolumab (NIVO)+ ipilimumab (IPI) combination therapy in patients (pts) with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (aHCC): results from CheckMate 040. Am Soc Clin Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2019.37.15_suppl.4012
Duffy AG, Ulahannan SV, Makorova-Rusher O, Rahma O, Wedemeyer H, Pratt D et al (2017) Tremelimumab in combination with ablation in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 66(3):545–551
Lu M, Wu J, Hao ZW, Shang YK, Xu J, Nan G et al (2018) Basolateral CD147 induces hepatocyte polarity loss by E-cadherin ubiquitination and degradation in hepatocellular carcinoma progress. Hepatology 68(1):317–332
Wu J, Ru N, Zhang Y, Li Y, Wei D, Ren Z et al (2011) HAb18G/CD147 promotes epithelial–mesenchymal transition through TGF-β signaling and is transcriptionally regulated by Slug. Oncogene 30(43):4410
Huang Q, Li J, Xing J, Li W, Li H, Ke X et al (2014) CD147 promotes reprogramming of glucose metabolism and cell proliferation in HCC cells by inhibiting the p53-dependent signaling pathway. J Hepatol 61(4):859–866
Li J, Huang Q, Long X, Zhang J, Huang X, Aa J et al (2015) CD147 reprograms fatty acid metabolism in hepatocellular carcinoma cells through Akt/mTOR/SREBP1c and P38/PPARα pathways. J Hepatol 63(6):1378–1389
Felmlee DJ, Baumert TF (2016) CD147 handles lipid: a new role for anti-cancer target. Transl Cancer Res 5(3):238–240
Ju H-L, Ro SW (2016) Making cancer fat: reprogramming of lipid metabolism by CD147 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Chin J Cancer Res 28(3):380
Xiao W, Zhao S, Shen F, Liang J, Chen J (2017) Overexpression of CD147 is associated with poor prognosis, tumor cell migration and ERK signaling pathway activation in hepatocellular carcinoma. Exp Ther Med 14(3):2637–2642
Bian H, Zheng J-S, Nan G, Li R, Chen C, Hu C-X et al (2014) Randomized trial of [131I] metuximab in treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma after percutaneous radiofrequency ablation. J Natl Cancer Inst 106(9):dju239
Wang Y, Yuan L, Yang X-M, Wei D, Wang B, Sun X-X et al (2015) A chimeric antibody targeting CD147 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell motility via FAK-PI3K-Akt-Girdin signaling pathway. Clin Exp Metastasis 32(1):39–53
Duan C, Li Y, Yang W, Zhang C (2018) Combination of 131I-anti-endoglin monoclonal antibody and 5-fluorouracil may be a promising combined-modality radioimmunotherapy strategy for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip 32(4):974–981
Kasprzak A, Adamek A (2018) Role of Endoglin (CD105) in the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma and anti-angiogenic therapy. Int J Mol Sci 9(12):3887
Liu Q, Zhang R-Z, Li D, Cheng S, Yang Y-H, Tian T et al (2016) Muse cells, a new type of pluripotent stem cell derived from human fibroblasts. Cell Reprogram 18(2):67–77
El-Kehdy H, Sargiacomo C, Fayyad-Kazan M, Fayyad-Kazan H, Lombard C, Lagneaux L et al (2017) Immunoprofiling of adult-derived human liver stem/progenitor cells: impact of hepatogenic differentiation and inflammation. Stem Cells Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/2679518
Fu Y, Deng J, Jiang Q, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Yao Y et al (2016) Rapid generation of functional hepatocyte-like cells from human adipose-derived stem cells. Stem cell Res Ther 7(1):1–12
Shenoy PS, Bose B (2018) Hepatic perivascular mesenchymal stem cells with myogenic properties. J Tissue Eng Regener Med 12(3):e1297–e1310
Li Y, Zhai Z, Liu D, Zhong X, Meng X, Yang Q et al (2015) CD105 promotes hepatocarcinoma cell invasion and metastasis through VEGF. Tumor Biol 36(2):737–745
Lin Y, Huang Y, Wu M, Wu S, Chi H, Liao C et al (2013) Thyroid hormone suppresses cell proliferation through endoglin-mediated promotion of p21 stability. Oncogene 32(33):3904–3914
Muñoz R, Arias Y, Ferreras JM, Jiménez P, Langa C, Rojo MA et al (2013) In vitro and in vivo effects of an anti-mouse endoglin (CD105)–immunotoxin on the early stages of mouse B16MEL4A5 melanoma tumours. Cancer Immunol Immunother 62(3):541–551
Tansi FL, Rüger R, Kollmeier AM, Rabenhold M, Steiniger F, Kontermann RE et al (2018) Endoglin based in vivo near-infrared fluorescence imaging of tumor models in mice using activatable liposomes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1862(6):1389–1400
Mehlen P, Delloye-Bourgeois C, Chédotal A (2011) Novel roles for Slits and netrins: axon guidance cues as anticancer targets? Nat Rev Cancer 11(3):188–197
Ao J-Y, Chai Z-T, Zhang Y-Y, Zhu X-D, Kong L-Q, Zhang N et al (2015) ROBO1 promotes angiogenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma through the Rho family of guanosine triphosphatases’ signaling pathway. Tumor Biol 36(11):8413–8424
Zheng F, Liao Y-J, Cai M-Y, Liu T-H, Chen S-P, Wu P-H et al (2015) Systemic delivery of microRNA-101 potently inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma in vivo by repressing multiple targets. PLoS Genet 11(2):e1004873
Fujiwara K, Koyama K, Suga K, Ikemura M, Saito Y, Hino A et al (2014) A 90 Y-labelled anti-ROBO1 monoclonal antibody exhibits antitumour activity against hepatocellular carcinoma xenografts during ROBO1-targeted radioimmunotherapy. EJNMMI Res 4(1):1–10
Rai V, Abdo J, Alsuwaidan AN, Agrawal S, Sharma P, Agrawal DK et al (2018) Cellular and molecular targets for the immunotherapy of hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cell Biochem 437(1–2):13–36
Zhou J, Hu P, Si Z, Tan H, Qiu L, Zhang H et al (2019) Treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma by intratumoral injection of 125I-AA98 mAb and its efficacy assessments by molecular imaging. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 7:319
Duan C-L, Hou G-H, Liu Y-P, Liang T, Song J, Han J-K et al (2014) Tumor vascular homing endgolin-targeted radioimmunotherapy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumor Biol 35(12):12205–12215
Sitohy B, Nagy JA, Dvorak HF (2012) Anti-VEGF/VEGFR therapy for cancer: reassessing the target. Cancer Res 72(8):1909–1914
Ghavimi S, Apfel T, Azimi H, Persaud A, Pyrsopoulos NT (2020) Management and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with immunotherapy: a review of current and future options. J Clin Transl Hepatol 8(2):168
Han Q, Zhao H, Jiang Y, Yin C, Zhang J (2019) HCC-derived exosomes: critical player and target for cancer immune escape. Cells 8(6):558
Dai W, Wang Y, Yang T, Wang J, Wu W, Gu J et al (2019) Downregulation of exosomal CLEC3B in hepatocellular carcinoma promotes metastasis and angiogenesis via AMPK and VEGF signals. Cell Commun Signal 17(1):113
Xie F, Xu M, Lu J, Mao L, Wang S (2019) The role of exosomal PD-L1 in tumor progression and immunotherapy. Mol Cancer 18(1):146
Chen W, Jiang J, Xia W, Huang J (2017) Tumor-related exosomes contribute to tumor-promoting microenvironment: an immunological perspective. J Immunol Res. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/1073947
Olejarz W, Dominiak A, Żołnierzak A, Kubiak-Tomaszewska G, Lorenc T (2020) Tumor-derived exosomes in immunosuppression and immunotherapy. J Immunol Res. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/6272498
Shi S, Rao Q, Zhang C, Zhang X, Qin Y, Niu Z (2018) Dendritic cells pulsed with exosomes in combination with PD-1 antibody increase the efficacy of Sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma model. Transl Oncol 11(2):250–258
Rao Q, Zuo B, Lu Z, Gao X, You A, Wu C et al (2016) Tumor-derived exosomes elicit tumor suppression in murine hepatocellular carcinoma models and humans in vitro. Hepatology 64(2):456–472
Liu H, Gao W, Yuan J, Wu C, Yao K, Zhang L et al (2016) Exosomes derived from dendritic cells improve cardiac function via activation of CD4+ T lymphocytes after myocardial infarction. J Mol Cell Cardiol 91:123–133
Herbst RS, Soria J-C, Kowanetz M, Fine GD, Hamid O, Gordon MS et al (2014) Predictive correlates of response to the anti-PD-L1 antibody MPDL3280A in cancer patients. Nature 515(7528):563–567
Sasaki R, Kanda T, Yokosuka O, Kato N, Matsuoka S, Moriyama M (2019) Exosomes and hepatocellular carcinoma: from bench to bedside. Int J Mol Sci 20(6):1406
Liu J, Fan L, Yu H, Zhang J, He Y, Feng D et al (2019) Endoplasmic reticulum stress causes liver cancer cells to release exosomal miR-23a-3p and up-regulate programmed death ligand 1 expression in macrophages. Hepatology 70(1):241–258
Cheng L, Liu J, Liu Q, Liu Y, Fan L, Wang F et al (2017) Exosomes from melatonin treated hepatocellularcarcinoma cells alter the immunosupression status through STAT3 pathway in macrophages. Int J Biol Sci 13(6):723–734
Sideras K, Robert A, Harrington SM, Polak WG, Zhou G, Schutz HM et al (2019) Circulating levels of PD-L1 and Galectin-9 are associated with patient survival in surgically treated Hepatocellular Carcinoma independent of their intra-tumoral expression levels. Sci Rep 9(1):1–10
Lu Z, Zuo B, Jing R, Gao X, Rao Q, Liu Z et al (2017) Dendritic cell-derived exosomes elicit tumor regression in autochthonous hepatocellular carcinoma mouse models. J Hepatol 67(4):739–748
Qu Z, Feng J, Pan H, Jiang Y, Duan Y, Fa ZJO et al (2019) Exosomes derived from HCC cells with different invasion characteristics mediated EMT through TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway. OncoTargets Ther 12:6897
Ge Y, Mu W, Ba Q, Li J, Jiang Y, Xia Q et al (2020) Hepatocellular carcinoma-derived exosomes in organotropic metastasis, recurrence and early diagnosis application. Cancer Lett 477:41–48
Vella L (2014) The emerging role of exosomes in epithelial–mesenchymal-transition in cancer. Front Oncol 4:361
Yang T, Martin P, Fogarty B, Brown A, Schurman K, Phipps R et al (2015) Exosome delivered anticancer drugs across the blood-brain barrier for brain cancer therapy in Danio rerio. Pharm Res 32(6):2003–2014
Ha D, Yang N, Nadithe V (2016) Exosomes as therapeutic drug carriers and delivery vehicles across biological membranes: current perspectives and future challenges. Acta Pharm Sin 6(4):287–296
Johnsen KB, Gudbergsson JM, Skov MN, Pilgaard L, Moos T, Duroux M (2014) A comprehensive overview of exosomes as drug delivery vehicles—endogenous nanocarriers for targeted cancer therapy. Biochim Biophys Acta 1846(1):75–87
Wang F, Li L, Piontek K, Sakaguchi M, Selaru FM (2018) Exosome miR-335 as a novel therapeutic strategy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 67(3):940–954
Lou G, Song X, Yang F, Wu S, Wang J, Chen Z et al (2015) Exosomes derived from miR-122-modified adipose tissue-derived MSCs increase chemosensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hematol Oncol 8(1):1–11
Lou G, Chen L, Xia C, Wang W, Qi J, Li A et al (2020) MiR-199a-modified exosomes from adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve hepatocellular carcinoma chemosensitivity through mTOR pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 39(1):4
Bonnet M, Maisonial-Besset A, Zhu Y, Witkowski T, Roche G, Boucheix C et al (2019) Targeting the tetraspanins with monoclonal antibodies in oncology: focus on Tspan8/Co-029. Cancers 11(2):179
Fang T, Lin J, Wang Y, Chen G, Huang J, Chen J et al (2016) Tetraspanin-8 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis by increasing ADAM12m expression. Oncotarget 7(26):40630
Huang M-Y, Wang H-M, Chang H-J, Hsiao C-P, Wang J-Y, Lin S-RJD et al (2012) Overexpression of S100B, TM4SF4, and OLFM4 genes is correlated with liver metastasis in Taiwanese colorectal cancer patients. DNA Cell Biol 31(1):43–49
Yue S, Mu W, Erb U, Zöller M (2015) The tetraspanins CD151 and Tspan8 are essential exosome components for the crosstalk between cancer initiating cells and their surrounding. Oncotarget 6(4):2366
Elsharkasy OM, Nordin JZ, Hagey DW, de Jong OG, Schiffelers RM, Andaloussi SE et al (2020) Extracellular vesicles as drug delivery systems: why and how? Adv Drug Deliv Rev 159:332–343
Herrmann IK, Wood MJA, Fuhrmann G (2021) Extracellular vesicles as a next-generation drug delivery platform. Nat Nanotechnol 16(7):748–759
Mir B, Goettsch C (2020) Extracellular vesicles as delivery vehicles of specific cellular cargo. Cells 9(7):1601
Forner A, Reig M, Bruix J (2018) Hepatocellular carcinoma 391(10127):1301–1314
Vilgrain V, Pereira H, Assenat E, Guiu B, Ilonca AD, Pageaux G-P et al (2017) Efficacy and safety of selective internal radiotherapy with yttrium-90 resin microspheres compared with sorafenib in locally advanced and inoperable hepatocellular carcinoma (SARAH): an open-label randomised controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 18(12):1624–1636
Nishida N, Kudo M (2018) Immune checkpoint blockade for the treatment of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol Res 48(8):622–634
Bruix J, Takayama T, Mazzaferro V, Chau G-Y, Yang J, Kudo M et al (2015) Adjuvant sorafenib for hepatocellular carcinoma after resection or ablation (STORM): a phase 3, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol 16(13):1344–1354
Chen G, Huang AC, Zhang W, Zhang G, Wu M, Xu W et al (2018) Exosomal PD-L1 contributes to immunosuppression and is associated with anti-PD-1 response. Nature 560(7718):382–386
Lesokhin AM, Ansell SM, Armand P, Scott EC, Halwani A, Gutierrez M et al (2016) Nivolumab in patients with relapsed or refractory hematologic malignancy: preliminary results of a phase Ib study. J Clin Oncol 34(23):2698
Morris VK, Salem ME, Nimeiri H, Iqbal S, Singh P, Ciombor K et al (2017) Nivolumab for previously treated unresectable metastatic anal cancer (NCI9673): a multicentre, single-arm, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol 18(4):446–453
Kudo M (2017) Immune checkpoint blockade in hepatocellular carcinoma: 2017 update. Liver Cancer 6(1):1–12
Singh P, Toom S, Avula A, Kumar V, Rahma OE (2020) The immune modulation effect of locoregional therapies and its potential synergy with immunotherapy in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatocell Carcinoma 7:11
Longo V, Brunetti O, Gnoni A, Licchetta A, Delcuratolo S, Memeo R et al (2019) Emerging role of immune checkpoint inhibitors in hepatocellular carcinoma. Medicina 55(10):698
Xu J, Zhang Y, Jia R, Yue C, Chang L, Liu R et al (2019) Anti-PD-1 antibody SHR-1210 combined with apatinib for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma, gastric, or esophagogastric junction cancer: an open-label, dose escalation and expansion study. Clin Cancer Res 25(2):515–523
Kudo M (2018) Combination cancer immunotherapy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Cancer 7(1):20
Duffy AG, Ulahannan SV, Fioravanti S, Walker M, Figg WD, Compton K et al (2014) A pilot study of tremelimumab, a monoclonal antibody against CTLA-4, in combination with either transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) or radiofrequency ablation (RFA) in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Am Soc Clin Oncol
Di Maria Jiang AF, Nguyen LT, Neel BG, Sacher A, Rottapel R, Wang BX et al (2019) Phase I study of local radiation and tremelimumab in patients with inoperable locally recurrent or metastatic breast cancer. Oncotarget 10(31):2947
Li J, Xing J, Yang Y, Liu J, Wang W, Xia Y et al (2018) Adjuvant 131 I-Metuximab for hepatocellular carcinoma after liver resection: an open-label, randomised, Phase 2 Trial
Li J, Xing J, Yang Y, Liu J, Wang W, Xia Y et al (2020) Adjuvant 131I-metuximab for hepatocellular carcinoma after liver resection: a randomised, controlled, multicentre, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol 5(6):548–560
Zhang J-C, Tian Y-Y, Yang C, Ma J-P, Jiang F-Q, Yang J et al (2018) Effect of licartin combined with pirarubicin TACE on apoptosis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in unresectable liver cancer tissue. J Hainan Med Univ 24(2):111–114
Karzai FH, Apolo AB, Cao L, Madan RA, Adelberg DE, Parnes H et al (2015) A phase I study of TRC 105 anti-endoglin (CD 105) antibody in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. BJU Int 116(4):546–555
Gordon MS, Robert F, Matei D, Mendelson DS, Goldman JW, Chiorean EG et al (2014) An open-label phase Ib dose-escalation study of TRC105 (anti-endoglin antibody) with bevacizumab in patients with advanced cancer. Clin Cancer Res 20(23):5918–5926
Duffy A, Ulahannan S, Cao L, Rahma O, Makarova-Rusher O, Kleiner D et al (2015) A phase II study of TRC105 in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma who have progressed on sorafenib. U Eur Gastroenterol J 3(5):453–461
Raghav KPS, Mody K, Greten TF, Paluri RK, Lee RT, Simpson BE et al (2018) An open label phase 1b/2 trial of TRC105 and sorafenib in patient with advanced/metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)(NCT01806064). Am Soc Clin Oncol
Roudi R, D’Angelo A, Sirico M, Sobhani N (2021) Immunotherapeutic treatments in hepatocellular carcinoma; achievements, challenges and future prospects. Int Immunopharmacol 101:108322
Zhu AX, Finn RS, Edeline J, Cattan S, Ogasawara S, Palmer D et al (2018) Pembrolizumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma previously treated with sorafenib (KEYNOTE-224): a non-randomised, open-label phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol 19(7):940–952
Li B, Yan C, Zhu J, Chen X, Fu Q, Zhang H et al (2020) Anti–PD-1/PD-L1 blockade immunotherapy employed in treating hepatitis B virus infection–related advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a literature review. Front Immunol 11:1037
Pfister D, Núñez NG, Pinyol R, Govaere O, Pinter M, Szydlowska M et al (2021) NASH limits anti-tumour surveillance in immunotherapy-treated HCC. Nature 592(7854):450–456
Lee S, Loecher M, Iyer R (2018) Immunomodulation in hepatocellular cancer. J Gastrointest Oncol 9(1):208
Lu C, Rong D, Zhang B, Zheng W, Wang X, Chen Z et al (2019) Current perspectives on the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma: challenges and opportunities. Mol Cancer 18(1):1–12
Choi C, Yoo GS, Cho WK, Park HC (2019) Optimizing radiotherapy with immune checkpoint blockade in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 25(20):2416
Kon E, Benhar I (2019) Immune checkpoint inhibitor combinations: current efforts and important aspects for success. Drug Resist Updates 45:13–29
Chan TA, Yarchoan M, Jaffee E, Swanton C, Quezada SA, Stenzinger A et al (2019) Development of tumor mutation burden as an immunotherapy biomarker: utility for the oncology clinic. Ann Oncol 30(1):44–56
Bernicker E (2016) Next-generation sequencing and immunotherapy biomarkers: a medical oncology perspective. Arch Pathol Lab Med 140(3):245–248
Pinter M, Trauner M, Peck-Radosavljevic M, Sieghart W (2016) Cancer and liver cirrhosis: implications on prognosis and management. ESMO Open 1(2):e000042-e
Schuch A, Hoh A, Thimme R (2014) The role of natural killer cells and CD8+ T cells in hepatitis B virus infection. Front Immunol 5:258
Moawad AW, Szklaruk J, Lall C, Blair KJ, Kaseb AO, Kamath A et al (2020) Angiogenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma; pathophysiology, targeted therapy, and role of imaging. J Hepatocell Carcinoma 7:77
Liu X, Qin S (2019) Immune checkpoint inhibitors in hepatocellular carcinoma: opportunities and challenges. Oncologist 24(Suppl 1):S3
Kudo M (2017) Molecular targeted agents for hepatocellular carcinoma: current status and future perspectives. Liver Cancer 6(2):101–112
Kudo M, Finn RS, Qin S, Han K-H, Ikeda K, Piscaglia F et al (2018) Lenvatinib versus sorafenib in first-line treatment of patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a randomised phase 3 non-inferiority trial. The Lancet 391(10126):1163–1173
Cheng A-L, Finn RS, Qin S, Han K-H, Ikeda K, Piscaglia F et al (2017) Phase III trial of lenvatinib (LEN) vs sorafenib (SOR) in first-line treatment of patients (pts) with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (uHCC). Am Soc Clin Oncol
Personeni N, Pressiani T, Santoro A, Rimassa L (2018) Regorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma: latest evidence and clinical implications. Drugs Context 7:212533
Zhu AX, Kang Y-K, Yen C-J, Finn RS, Galle PR, Llovet JM et al (2019) Ramucirumab after sorafenib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma and increased α-fetoprotein concentrations (REACH-2): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 20(2):282–296
Medavaram S, Zhang Y (2018) Emerging therapies in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Exp Hematol Oncol 7(1):17
Acknowledgements
Authors would like to express their gratitude to their colleagues in Royan institute for their support.
Funding
The authors would like to thank the Royan Institute, Tehran, Iran, for supporting this study. The study was partly supported by “National Cancer Control Charity Foundation”, to MV, registration number 41476, Tehran, IRAN. AS and PT were supported by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation within the framework of state support for the creation and development of World-Class Research Centers “Digital biodesign and personalized healthcare” (No 075-15-2020-926).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MP, SA, and MV outlined the manuscript. SA and MP drafted the manuscript with primary editing and revision support from HM, PM, AM, ES, AS, HAE, PT, MH, and MV. PT, MH, and MV critically revised the manuscript for all content and coordinated the manuscript preparation and submission. All authors read and approved the final version.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pourhamzeh, M., Asadian, S., Mirzaei, H. et al. Novel antigens for targeted radioimmunotherapy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cell Biochem 478, 23–37 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-022-04483-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-022-04483-4