Abstract
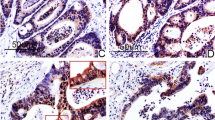
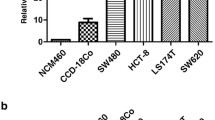
As a member of the tight junction family, CLDN6 is a tumor suppressor in breast cancer, but its role in colon cancer is unknown. In this research, we aimed at revealing the function of CLDN6 in colon cancer. We found that colon cancer tissues lowly expressed CLDN6, and the expression of CLDN6 was negatively correlated with lymph node metastasis. Similarly, CLDN6 was lowly expressed in the colon cancer cell line SW1116, and overexpression of CLDN6 inhibited cell proliferation in vitro and in vivo. Consistently, the migration and invasion abilities of cells were significantly inhibited after CLDN6 overexpression. In addition, we demonstrated that CLDN6 may inhibit the migration and invasion abilities by activating the TYK2/STAT3 pathway. Therefore, our data indicated that CLDN6 acted as a tumor suppressor and had the potential to be regarded as a biomarker for the progression of colon cancer.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Dekker E, Tanis PJ, Vleugels JLA, Kasi PM, Wallace MB (2019) Colorectal cancer. Lancet 394:1467–1480. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(19)32319-0
DeSantis CE, Lin CC, Mariotto AB, Siegel RL, Stein KD, Kramer JL, Alteri R, Robbins AS, Jemal A (2014) Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin 64:252–271. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21235
Tabariès S, Siegel PM (2017) The role of claudins in cancer metastasis. Oncogene 36:1176–1190. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.289
Shen Z, Song W, Qian L, Zhu J, Li Y, Li M, Zhang T, Zhao W, Zhou Y, Yang X (2021) Effect of claudin 1 on cell proliferation, migration and apoptosis in human cervical squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep 45:606–618. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2020.7889
Zhang X, Ruan Y, Li Y, Lin D, Quan C (2015) Tight junction protein claudin-6 inhibits growth and induces the apoptosis of cervical carcinoma cells in vitro and in vivo. Med Oncol 32:148. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-015-0600-4
Lu YZ, Li Y, Zhang T, Han ST (2020) Claudin-6 is down-regulated in gastric cancer and its potential pathway. Cancer Biomark 28:329–340. https://doi.org/10.3233/cbm-201554
Tong H, Li T, Qiu W, Zhu Z (2019) Claudin-1 silencing increases sensitivity of liver cancer HepG2 cells to 5-fluorouracil by inhibiting autophagy. Oncol Lett 18:5709–5716. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2019.10967
Wu J, Gao F, Xu T, Li J, Hu Z, Wang C, Long Y, He X, Deng X, Ren D, Zhou B, Dai T (2020) CLDN1 induces autophagy to promote proliferation and metastasis of esophageal squamous carcinoma through AMPK/STAT1/ULK1 signaling. J Cell Physiol 235:2245–2259. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.29133
Song P, Li Y, Dong Y, Liang Y, Qu H, Qi D, Lu Y, Jin X, Guo Y, Jia Y, Wang X, Xu W, Quan C (2019) Estrogen receptor β inhibits breast cancer cells migration and invasion through CLDN6-mediated autophagy. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 38:354. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-019-1359-9
Visco ZR, Sfakianos G, Grenier C, Boudreau MH, Simpson S, Rodriguez I, Whitaker R, Yao DY, Berchuck A, Murphy SK, Huang Z (2021) Epigenetic regulation of Claudin-1 in the development of ovarian cancer recurrence and drug resistance. Front Oncol 11:620873. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.620873
Dhawan P, Singh AB, Deane NG, No Y, Shiou SR, Schmidt C, Neff J, Washington MK, Beauchamp RD (2005) Claudin-1 regulates cellular transformation and metastatic behavior in colon cancer. J Clin Investig 115:1765–1776. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci24543
Luan N, Chen Y, Li Q, Mu Y, Zhou Q, Ye X, Deng Q, Ling L, Wang J, Wang J (2021) TRF-20-M0NK5Y93 suppresses the metastasis of colon cancer cells by impairing the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition through targeting Claudin-1. Am J Transl Res 13:124–142
Resnick MB, Konkin T, Routhier J, Sabo E, Pricolo VE (2005) Claudin-1 is a strong prognostic indicator in stage II colonic cancer: a tissue microarray study. Mod Pathol 18:511–518. https://doi.org/10.1038/modpathol.3800301
Ahmad R, Kumar B, Chen Z, Chen X, Müller D, Lele SM, Washington MK, Batra SK, Dhawan P, Singh AB (2017) Loss of claudin-3 expression induces IL6/gp130/Stat3 signaling to promote colon cancer malignancy by hyperactivating Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Oncogene 36:6592–6604. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2017.259
Oshima T, Kunisaki C, Yoshihara K, Yamada R, Yamamoto N, Sato T, Makino H, Yamagishi S, Nagano Y, Fujii S, Shiozawa M, Akaike M, Wada N, Rino Y, Masuda M, Tanaka K, Imada T (2008) Reduced expression of the claudin-7 gene correlates with venous invasion and liver metastasis in colorectal cancer. Oncol Rep 19:953–959
Wöss K, Simonović N, Strobl B, Macho-Maschler S, Müller M (2019) TYK2: an upstream kinase of STATs in cancer. Cancers (Basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11111728
Yu H, Lee H, Herrmann A, Buettner R, Jove R (2014) Revisiting STAT3 signalling in cancer: new and unexpected biological functions. Nat Rev Cancer 14:736–746. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc3818
Avalle L, Camporeale A, Camperi A, Poli V (2017) STAT3 in cancer: a double edged sword. Cytokine 98:42–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cyto.2017.03.018
Lin D, Guo Y, Li Y, Ruan Y, Zhang M, Jin X, Yang M, Lu Y, Song P, Zhao S, Dong B, Xie Y, Dang Q, Quan C (2017) Bioinformatic analysis reveals potential properties of human Claudin-6 regulation and functions. Oncol Rep 38:875–885. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2017.5756
Sugimoto K, Ichikawa-Tomikawa N, Kashiwagi K, Endo C, Tanaka S, Sawada N, Watabe T, Higashi T, Chiba H (2019) Cell adhesion signals regulate the nuclear receptor activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 116:24600–24609. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1913346116
Yang M, Li Y, Ruan Y, Lu Y, Lin D, Xie Y, Dong B, Dang Q, Quan C (2018) CLDN6 enhances chemoresistance to ADM via AF-6/ERKs pathway in TNBC cell line MDAMB231. Mol Cell Biochem 443:169–180. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-017-3221-8
Guo Y, Lin D, Zhang M, Zhang X, Li Y, Yang R, Lu Y, Jin X, Yang M, Wang M, Zhao S, Quan C (2016) CLDN6-induced apoptosis via regulating ASK1-p38/JNK signaling in breast cancer MCF-7 cells. Int J Oncol 48:2435–2444. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2016.3469
Yu S, Zhang Y, Li Q, Zhang Z, Zhao G, Xu J (2019) CLDN6 promotes tumor progression through the YAP1-snail1 axis in gastric cancer. Cell Death Dis 10:949. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-019-2168-y
Cao X, He GZ (2018) Knockdown of CLDN6 inhibits cell proliferation and migration via PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in endometrial carcinoma cell line HEC-1-B. OncoTargets Ther 11:6351–6360. https://doi.org/10.2147/ott.S174618
Lin Z, Zhang XW, Liu ZJ, Liu QH, Wang LP, Lu Y, Liu YY, Wang M, Yang ML, Jin XS, Quan CS (2013) The distinct expression patterns of claudin-2, -6, and -11 between human gastric neoplasms and adjacent non-neoplastic tissues. Diagn Pathol. https://doi.org/10.1186/1746-1596-8-133
Wu Q, Liu Y, Ren Y, Xu X, Yu L, Li Y, Quan C (2010) Tight junction protein, claudin-6, downregulates the malignant phenotype of breast carcinoma. Eur J Cancer Prev 19:186–194. https://doi.org/10.1097/CEJ.0b013e328337210e
Kohmoto T, Masuda K, Shoda K, Takahashi R, Ujiro S, Tange S, Ichikawa D, Otsuji E, Imoto I (2020) Claudin-6 is a single prognostic marker and functions as a tumor-promoting gene in a subgroup of intestinal type gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer 23:403–417. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10120-019-01014-x
Micke P, Mattsson JS, Edlund K, Lohr M, Jirström K, Berglund A, Botling J, Rahnenfuehrer J, Marincevic M, Pontén F, Ekman S, Hengstler J, Wöll S, Sahin U, Türeci O (2014) Aberrantly activated claudin 6 and 18.2 as potential therapy targets in non-small-cell lung cancer. Int J Cancer 135:2206–2214. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.28857
Birks DK, Kleinschmidt-DeMasters BK, Donson AM, Barton VN, McNatt SA, Foreman NK, Handler MH (2010) Claudin 6 is a positive marker for atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumors. Brain Pathol 20:140–150. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1750-3639.2008.00255.x
Kong FE, Li GM, Tang YQ, Xi SY, Loong JHC, Li MM, Li HL, Cheng W, Zhu WJ, Mo JQ, Gong YF, Tang H, Zhao Y, Zhang Y, Ma S, Guan XY, Ma NF, Xie MB, Liu M (2021) Targeting tumor lineage plasticity in hepatocellular carcinoma using an anti-CLDN6 antibody-drug conjugate. Sci Transl Med. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.abb6282
Liu Y, Jin X, Li Y, Ruan Y, Lu Y, Yang M, Lin D, Song P, Guo Y, Zhao S, Dong B, Xie Y, Dang Q, Quan C (2016) DNA methylation of claudin-6 promotes breast cancer cell migration and invasion by recruiting MeCP2 and deacetylating H3Ac and H4Ac. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 35:120. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-016-0396-x
Lu Y, Wang L, Li H, Li Y, Ruan Y, Lin D, Yang M, Jin X, Guo Y, Zhang X, Quan C (2017) SMAD2 inactivation inhibits CLDN6 methylation to suppress migration and invasion of breast cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18091863
O’Shea JJ, Schwartz DM, Villarino AV, Gadina M, McInnes IB, Laurence A (2015) The JAK-STAT pathway: impact on human disease and therapeutic intervention. Annu Rev Med 66:311–328. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-med-051113-024537
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2011) Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 144:646–674. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.013
Ubel C, Mousset S, Trufa D, Sirbu H, Finotto S (2013) Establishing the role of tyrosine kinase 2 in cancer. Oncoimmunology 2:e22840. https://doi.org/10.4161/onci.22840
Ide H, Nakagawa T, Terado Y, Kamiyama Y, Muto S, Horie S (2008) Tyk2 expression and its signaling enhances the invasiveness of prostate cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 369:292–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.08.160
Muller S, Chen Y, Ginter T, Schafer C, Buchwald M, Schmitz LM, Klitzsch J, Schutz A, Haitel A, Schmid K, Moriggl R, Kenner L, Friedrich K, Haan C, Petersen I, Heinzel T, Kramer OH (2014) SIAH2 antagonizes TYK2-STAT3 signaling in lung carcinoma cells. Oncotarget 5:3184–3196. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.1899
Herrmann A, Lahtz C, Nagao T, Song JY, Chan WC, Lee H, Yue C, Look T, Mulfarth R, Li W, Jenkins K, Williams J, Budde LE, Forman S, Kwak L, Blankenstein T, Yu H (2017) CTLA4 promotes Tyk2-STAT3-dependent B-cell oncogenicity. Cancer Res 77:5118–5128. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-0342
Liu H, Wang M, Liang N, Guan L (2019) Claudin-9 enhances the metastatic potential of hepatocytes via Tyk2/Stat3 signaling. Turk J Gastroenterol 30:722–731. https://doi.org/10.5152/tjg.2019.18513
Sun L, Feng L, Cui J (2018) Increased expression of claudin-17 promotes a malignant phenotype in hepatocyte via Tyk2/Stat3 signaling and is associated with poor prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Diagn Pathol 13:72. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13000-018-0749-1
Bekki H, Kohashi K, Yamada Y, Iura K, Ishii T, Maekawa A, Otsuka H, Yamamoto H, Hakozaki M, Nabeshima K, Iwamoto Y, Oda Y (2017) Phosphorylation of STAT3 in undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma is correlated with a favorable prognosis. Pathobiology 84:161–169. https://doi.org/10.1159/000448524
Wu P, Wu D, Zhao L, Huang L, Shen G, Huang J, Chai Y (2016) Prognostic role of STAT3 in solid tumors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncotarget 7:19863–19883. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.7887
Nielsen M, Kaltoft K, Nordahl M, Röpke C, Geisler C, Mustelin T, Dobson P, Svejgaard A, Odum N (1997) Constitutive activation of a slowly migrating isoform of Stat3 in mycosis fungoides: tyrphostin AG490 inhibits Stat3 activation and growth of mycosis fungoides tumor cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:6764–6769. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.94.13.6764
Meydan N, Grunberger T, Dadi H, Shahar M, Arpaia E, Lapidot Z, Leeder JS, Freedman M, Cohen A, Gazit A, Levitzki A, Roifman CM (1996) Inhibition of acute lymphoblastic leukaemia by a Jak-2 inhibitor. Nature 379:645–648. https://doi.org/10.1038/379645a0
Sanda T, Tyner JW, Gutierrez A, Ngo VN, Glover J, Chang BH, Yost A, Ma W, Fleischman AG, Zhou W, Yang Y, Kleppe M, Ahn Y, Tatarek J, Kelliher MA, Neuberg DS, Levine RL, Moriggl R, Müller M, Gray NS, Jamieson CH, Weng AP, Staudt LM, Druker BJ, Look AT (2013) TYK2-STAT1-BCL2 pathway dependence in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Discov 3:564–577. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.Cd-12-0504
De Vos J, Jourdan M, Tarte K, Jasmin C, Klein B (2000) JAK2 tyrosine kinase inhibitor tyrphostin AG490 downregulates the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) pathways and induces apoptosis in myeloma cells. Br J Haematol 109:823–828. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2141.2000.02127.x
Zhang J, Liu C, You G (2018) AG490, a JAK2-specific inhibitor, downregulates the expression and activity of organic anion transporter-3. J Pharmacol Sci 136:142–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphs.2018.01.006
Fan Z, Zhang W, Cao Q, Zou L, Fan X, Qi C, Yan Y, Song B, Wu B (2022) JAK2/STAT3 pathway regulates microglia polarization involved in hippocampal inflammatory damage due to acute paraquat exposure. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 234:113372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.113372
Tait Wojno ED, Hunter CA, Stumhofer JS (2019) the immunobiology of the interleukin-12 family: room for discovery. Immunity 50:851–870. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2019.03.011
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [Grant Numbers 81772816] and the Natural Science Foundation of Jilin Province [Grant Numbers 20210101329JC].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The first draft of the manuscript was written by HQ. Cell and animal experiments, data analysis were performed by MW. Molecular biology experiments were performed by MW. Immunohistochemistry experiments were performed by YL. Study design, funding acquisition, and supervision were completed by CQ.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethical approval
Tumor tissues were obtained from the Eastern Division of the First Hospital of Jilin University. This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Approval was granted by the Ethics Committee of Jilin University and informed consent was obtained from all patients. All animal experiments and their care were approved by the Experimental Animal Ethical Committee of Jilin University and were carried out following relevant institution guidelines.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qu, H., Wang, M., Wang, M. et al. The expression and the tumor suppressor role of CLDN6 in colon cancer. Mol Cell Biochem 477, 2883–2893 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-022-04450-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-022-04450-z