Abstract
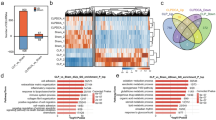
Obesity is becoming an epidemic of widespread concern, but the underlying causes remain elusive. In this study, whole transcriptome RNA sequencing revealed differential profiles of noncoding (nc) RNAs and mRNAs in visceral adipose tissue from obese (BMI > 32.5 kg/m2) and lean (BMI < 20 kg/m2) individuals, with 1920 differentially expressed genes, 1466 long noncoding (lnc) RNAs, 122 micro (mi) RNAs, and 52 circular (circ) RNAs identified. Gene Set Enrichment Analysis, Gene Ontology analysis, Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes analysis revealed that these ncRNAs were involved in inflammation-related pathways that included cytokine–cytokine receptor interaction, the tumor necrosis factor and nuclear factor kappa B signaling pathways. The results indicated a critical role of inflammation in the pathogenesis of obesity. The network interaction of lncRNA, circRNA, and miRNA revealed a competing endogenous (ce) RNA network that was associated with inflammation. The ceRNA network included circORC5/miR-197-5p/TNFRSF10D and circNTRK2/miR-760/LAT, which were dysregulated in obese patients. In conclusion, this whole transcriptome study provided a pool of data that will be useful for identifying biomarkers of obesity and identified an obesity-associated ceRNA network that is regulated by circORC5 and circNTRK2.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The primary RNA-Seq datasets are available in https://submit.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov, with a grant number PRJNA763819.
References
Dixon JB (2016) Obesity in 2015: advances in managing obesity. Nat Rev Endocrinol 12(2):65–66. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrendo.2015.221
El-Sayed Moustafa JS, Froguel P (2013) From obesity genetics to the future of personalized obesity therapy. Nat Rev Endocrinol 9(7):402–413. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrendo.2013.57
Mouton AJ, Li X, Hall ME, Hall JE (2020) Obesity, hypertension, and cardiac dysfunction: novel roles of immunometabolism in macrophage activation and inflammation. Circ Res 126(6):789–806. https://doi.org/10.1161/circresaha.119.312321
Petrus P, Lecoutre S, Dollet L, Wiel C, Sulen A, Gao H, Tavira B, Laurencikiene J, Rooyackers O, Checa A, Douagi I, Wheelock CE, Arner P, McCarthy M, Bergo MO, Edgar L, Choudhury RP, Aouadi M, Krook A, Rydén M (2020) Glutamine links obesity to inflammation in human white adipose tissue. Cell Metab 31(2):375-390.e311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2019.11.019
Kawashima K, Maeda K, Saigo C, Kito Y, Yoshida K, Takeuchi T (2017) Adiponectin and intelectin-1: important adipokine players in obesity-related colorectal carcinogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18040866
Deng T, Lyon CJ, Bergin S, Caligiuri MA, Hsueh WA (2016) Obesity, inflammation, and cancer. Annu Rev Pathol 11:421–449. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pathol-012615-044359
Carpi S, Scoditti E, Massaro M, Polini B, Manera C, Digiacomo M, Esposito Salsano J, Poli G, Tuccinardi T, Doccini S, Santorelli FM, Carluccio MA, Macchia M, Wabitsch M, De Caterina R, Nieri P (2019) The extra-virgin olive oil polyphenols oleocanthal and oleacein counteract inflammation-related gene and miRNA expression in adipocytes by attenuating NF-κB activation. Nutrients. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11122855
Rohm B, Holik AK, Kretschy N, Somoza MM, Ley JP, Widder S, Krammer GE, Marko D, Somoza V (2015) Nonivamide enhances miRNA let-7d expression and decreases adipogenesis PPARγ expression in 3T3-L1 cells. J Cell Biochem 116(6):1153–1163. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.25052
Zhao XY, Xiong X, Liu T, Mi L, Peng X, Rui C, Guo L, Li S, Li X, Lin JD (2018) Long noncoding RNA licensing of obesity-linked hepatic lipogenesis and NAFLD pathogenesis. Nat Commun 9(1):2986. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-05383-2
Li M, Xie Z, Wang P, Li J, Liu W, Tang S, Liu Z, Wu X, Wu Y, Shen H (2018) The long noncoding RNA GAS5 negatively regulates the adipogenic differentiation of MSCs by modulating the miR-18a/CTGF axis as a ceRNA. Cell Death Dis 9(5):554. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-018-0627-5
Wang Y, Liu J, Ma J, Sun T, Zhou Q, Wang W, Wang G, Wu P, Wang H, Jiang L, Yuan W, Sun Z, Ming L (2019) Exosomal circRNAs: biogenesis, effect and application in human diseases. Mol Cancer 18(1):116. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-019-1041-z
Zhou ZB, Huang GX, Fu Q, Han B, Lu JJ, Chen AM, Zhu L (2019) circRNA.33186 contributes to the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis by sponging miR-127-5p. Mol Ther J Am Soc Gene Therapy 27(3):531–541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2019.01.006
Liu Y, Liu H, Li Y, Mao R, Yang H, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Guo P, Zhan D, Zhang T (2020) Circular RNA SAMD4A controls adipogenesis in obesity through the miR-138-5p/EZH2 axis. Theranostics 10(10):4705–4719. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.42417
Trapnell C, Roberts A, Goff L, Pertea G, Kim D, Kelley DR, Pimentel H, Salzberg SL, Rinn JL, Pachter L (2012) Differential gene and transcript expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with TopHat and Cufflinks. Nat Protoc 7(3):562–578. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2012.016
Guttman M, Garber M, Levin JZ, Donaghey J, Robinson J, Adiconis X, Fan L, Koziol MJ, Gnirke A, Nusbaum C, Rinn JL, Lander ES, Regev A (2010) Ab initio reconstruction of cell type-specific transcriptomes in mouse reveals the conserved multi-exonic structure of lincRNAs. Nat Biotechnol 28(5):503–510. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.1633
Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK, Mukherjee S, Ebert BL, Gillette MA, Paulovich A, Pomeroy SL, Golub TR, Lander ES, Mesirov JP (2005) Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(43):15545–15550. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0506580102
Doncheva NT, Morris JH, Gorodkin J, Jensen LJ (2019) Cytoscape StringApp: network analysis and visualization of proteomics data. J Proteome Res 18(2):623–632. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jproteome.8b00702
Rohm TV, Fuchs R, Müller RL, Keller L, Baumann Z, Bosch AJT, Schneider R, Labes D, Langer I, Pilz JB, Niess JH, Delko T, Hruz P, Cavelti-Weder C (2021) Obesity in humans is characterized by gut inflammation as shown by pro-inflammatory intestinal macrophage accumulation. Front Immunol 12:668654. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.668654
Kiran S, Kumar V, Kumar S, Price RL, Singh UP (2021) Adipocyte, immune cells, and miRNA crosstalk: a novel regulator of metabolic dysfunction and obesity. Cells. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10051004
Prats-Puig A, Ortega FJ, Mercader JM, Moreno-Navarrete JM, Moreno M, Bonet N, Ricart W, López-Bermejo A, Fernández-Real JM (2013) Changes in circulating microRNAs are associated with childhood obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2013-1496
Villard A, Marchand L, Thivolet C, Rome S (2015) Diagnostic value of cell-free circulating microRNAs for obesity and type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis. J Mol Biomark Diagnosis. https://doi.org/10.4172/2155-9929.1000251
Benito-Vicente A, Uribe KB, Rotllan N, Ramírez CM, Jebari-Benslaiman S, Goedeke L, Canfrán-Duque A, Galicia-García U, Saenz De Urturi D, Aspichueta P, Suárez Y, Fernández-Hernando C, Martín C (2020) miR-27b modulates insulin signaling in hepatocytes by regulating insulin receptor expression. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21228675
Al-Rawaf HA (2019) Circulating microRNAs and adipokines as markers of metabolic syndrome in adolescents with obesity. Clin Nutr (Edinburgh, Scotland) 38(5):2231–2238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2018.09.024
Tay Y, Rinn J, Pandolfi PP (2014) The multilayered complexity of ceRNA crosstalk and competition. Nature 505(7483):344–352. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12986
Salmena L, Poliseno L, Tay Y, Kats L, Pandolfi PP (2011) A ceRNA hypothesis: the Rosetta Stone of a hidden RNA language? Cell 146(3):353–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2011.07.014
Li Z, Jin C, Chen S, Zheng Y, Huang Y, Jia L, Ge W, Zhou Y (2017) Long non-coding RNA MEG3 inhibits adipogenesis and promotes osteogenesis of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells via miR-140-5p. Mol Cell Biochem 433(1–2):51–60. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-017-3015-z
Zhang F, Yang Y, Chen X, Liu Y, Hu Q, Huang B, Liu Y, Pan Y, Zhang Y, Liu D, Liang R, Li G, Wei Q, Li L, Jin L (2021) The long non-coding RNA βFaar regulates islet β-cell function and survival during obesity in mice. Nat Commun 12(1):3997. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-24302-6
Xu X, Zhang J, Tian Y, Gao Y, Dong X, Chen W, Yuan X, Yin W, Xu J, Chen K, He C, Wei L (2020) CircRNA inhibits DNA damage repair by interacting with host gene. Mol Cancer 19(1):128. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-020-01246-x
Alexaki VI (2021) The impact of obesity on microglial function: immune, metabolic and endocrine perspectives. Cells. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10071584
Kim JN, Han SN, Kim HK (2021) Anti-inflammatory and anti-diabetic effect of black Soybean Anthocyanins: data from a dual cooperative cellular system. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland). https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26113363
Ghanbari M, Momen Maragheh S, Aghazadeh A, Mehrjuyan SR, Hussen BM, Abdoli Shadbad M, Dastmalchi N, Safaralizadeh R (2021) Interleukin-1 in obesity-related low-grade inflammation: from molecular mechanisms to therapeutic strategies. Int Immunopharmacol 96:107765. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107765
Wang X, Ba T, Cheng Y, Zhang P, Chang X (2021) Probiotics alleviate adipose inflammation in high-fat diet-induced obesity by restoring adipose invariant natural killer T cells. Nutrition (Burbank, Los Angeles County, Calif) 89:111285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2021.111285
Miller AM, Asquith DL, Hueber AJ, Anderson LA, Holmes WM, McKenzie AN, Xu D, Sattar N, McInnes IB, Liew FY (2010) Interleukin-33 induces protective effects in adipose tissue inflammation during obesity in mice. Circ Res 107(5):650–658. https://doi.org/10.1161/circresaha.110.218867
Zeyda M, Wernly B, Demyanets S, Kaun C, Hämmerle M, Hantusch B, Schranz M, Neuhofer A, Itariu BK, Keck M, Prager G, Wojta J, Stulnig TM (2013) Severe obesity increases adipose tissue expression of interleukin-33 and its receptor ST2, both predominantly detectable in endothelial cells of human adipose tissue. Int J Obesity (2005) 37(5):658–665. https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2012.118
Law YY, Lee WF, Hsu CJ, Lin YY, Tsai CH, Huang CC, Wu MH, Tang CH, Liu JF (2021) miR-let-7c-5p and miR-149-5p inhibit proinflammatory cytokine production in osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts. Aging 13(13):17227–17236
Wang J, Luo X, Cai S, Sun J, Wang S, Wei X (2021) Blocking HOTAIR protects human chondrocytes against IL-1β-induced cell apoptosis, ECM degradation, inflammatory response and oxidative stress via regulating miR-222-3p/ADAM10 axis. Int Immunopharmacol 98:107903. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107903
Li W, Pan X, Cheng W, Cheng Y, Yin Y, Chen J, Xu G, Xie L (2018) Serum biochemistry, histology and transcriptomic profile analysis reflect liver inflammation and damage following dietary histamine supplementation in yellow catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco). Fish Shellfish Immunol 77:83–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2018.03.036
Wang X, Dai Y, Zhang X, Pan K, Deng Y, Wang J, Xu T (2021) CXCL6 regulates cell permeability, proliferation, and apoptosis after ischemia-reperfusion injury by modulating Sirt3 expression via AKT/FOXO3a activation. Cancer Biol Therapy 22(1):30–39. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384047.2020.1842705
Mauer J, Chaurasia B, Goldau J, Vogt MC, Ruud J, Nguyen KD, Theurich S, Hausen AC, Schmitz J, Brönneke HS, Estevez E, Allen TL, Mesaros A, Partridge L, Febbraio MA, Chawla A, Wunderlich FT, Brüning JC (2014) Signaling by IL-6 promotes alternative activation of macrophages to limit endotoxemia and obesity-associated resistance to insulin. Nat Immunol 15(5):423–430. https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.2865
Yamamoto-Furusho JK, Fonseca-Camarillo G, Furuzawa-Carballeda J, Sarmiento-Aguilar A, Barreto-Zuñiga R, Martínez-Benitez B, Lara-Velazquez MA (2018) Caspase recruitment domain (CARD) family (CARD9, CARD10, CARD11, CARD14 and CARD15) are increased during active inflammation in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. J Inflamm (London, England) 15:13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12950-018-0189-4
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, G-BL and ZWZ; Data curation, G-BL, HYZ, KC, ZWZ and ZJW; Formal analysis, G-BL and ZWZ; Funding acquisition, G-BL, LY and J-GH; Investigation, HYZ and LY; Methodology, G-BL, KC, ZWZ, ZJW, LY and J-GH; Project administration, ZJW; Resources, HYZ, KC and LY; Software, G-BL, KC and J-GH; Supervision, HYZ and ZWZ; Validation, G-BL, HYZ and ZJW; Writing—original draft, G-BL and LY; Writing—review & editing, ZJW and J-GH.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Ethics Committee of Beijing Chaoyang Hospital, Capital Medical University (2021-scientific-367).
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study, written informed consent has been obtained from the patient(s) to publish this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11010_2022_4362_MOESM1_ESM.tif
FIGURE S1 Samples selected for RNA-seq were confirmed as VAT by histopathologic examination. Supplementary file1 (TIF 1528 KB)
11010_2022_4362_MOESM2_ESM.tif
FIGURE S2 GO and KEGG enrichment analysis of key genes (hub genes, target gene of DE lncRNAs and host genes of circRNAs). A The top 10 significantly enriched GO items of BP, MF and CC of key genes, respectively. B The top 10 significantly enriched KEGG pathways of key genes. Supplementary file2 (TIF 1078 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, G., Zhang, H., Cao, K. et al. Transcriptome of visceral adipose tissue identifies an inflammation-related ceRNA network that regulates obesity. Mol Cell Biochem 477, 1095–1106 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-022-04362-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-022-04362-y