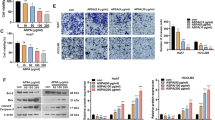
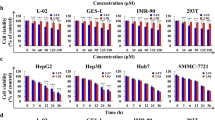
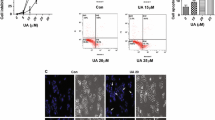
Abstract
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is among the most common lethal cancers of the digestive system with poor prognosis rates and ineffective therapeutic options. Matrine, a traditional Chinese medicine found in the roots of sophora species, has been used in the clinical treatment of liver fibrosis, chronic hepatitis B and other diseases. We have synthesized a matrine derivatives named WM622 (C26H35ON3S2) with a significant inhibitory effect on transplanted tumors in vivo. The half inhibitory concentration (IC50) of WM622 is 34 µM, which is much lower than matrine. WM622 inhibited the proliferation and promoted apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells significantly, and the cell cycle was blocked in G0/G1 phase. The protein phosphorylation levels of EGFR, AKT, PI3K and GSK3β (p-EGFR, p-AKT, p-PI3K, and p-GSK3β) were also decreased by WM622 treatment dose dependently. In tumor-bearing mice, WM622 could reduce the tumor volumes. In conclusion, the study demonstrated that WM622 could inhibit the proliferation of the hepatocellular carcinoma both in vivo and in vitro by inducing apoptosis, blocking cell cycle in G0/G1 phase and inhibiting the PI3K/AKT signal pathways.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wei KR, Yu X, Zheng RS, Peng XB, Zhang SW, Ji MF, Liang ZH, Ou ZX, Chen WQ (2014) Incidence and mortality of liver cancer in China, 2010. Chin J Cancer 33(8):388. https://doi.org/10.5732/cjc.014.10088
Ang C, O’Reilly EM, Abou-Alfa GK (2013) Targeted agents and systemic therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Recent Results Cancer Res 190:225–246. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-16037-0_15
Liu Y, Xu Y, Ji W, Li X, Sun B, Gao Q, Su C (2014) Anti-tumor activities of matrine and oxymatrine: literature review. Tumour Biol 35(6):5111–5119. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-1680-z
Chai NL, Fu Q, Shi H, Cai CH, Wan J, Xu SP, Wu BY (2012) Oxymatrine liposome attenuates hepatic fibrosis via targeting hepatic stellate cells. World J Gastroenterol 18(31):4199. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i31.4199
Yang Y, Xiu J, Zhang X, Zhang L, Yan K, Qin C, Liu J (2012) Antiviral effect of matrine against human enterovirus 71. Molecules 17(9):10370–10376. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules170910370
Zhang Y, Wang S, Li Y, Xiao Z, Hu Z, Zhang J (2008) Sophocarpine and matrine inhibit the production of TNF-alpha and IL-6 in murine macrophages and prevent cachexia-related symptoms induced by colon26 adenocarcinoma in mice. Int Immunopharmacol 8(13–14):1767–1772. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2008.08.008
Liu XY1, Fang H, Yang ZG, Wang XY, Ruan LM, Fang DR, Ding YG, Wang YN, Zhang Y, Jiang XL, Chen HC (2008) Matrine inhibits invasiveness and metastasis of human malignant melanoma cell line A375 in vitro. Int J Dermatol 47(5):448–456. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-4632.2008.03627.x
Qian L, Liu Y, Xu Y, Ji W, Wu Q, Liu Y, Gao Q, Su C (2015) Matrine derivative WM130 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma by suppressing EGFR/ERK/MMP-2 and PTEN/AKT signaling pathways. Cancer Lett 368(1):126–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2015.07.035
Liu Y, Qi Y, Bai ZH, Ni CX, Ren QH, Xu WH, Xu J, Hu HG, Qiu L, Li JZ, He ZG, Zhang JP (2016) A novel matrine derivate inhibits differentiated human hepatoma cells and hepatic cancer stem-like cells by suppressing PI3K/AKT signaling pathways. Acta Pharmacol Sin 38(1):120–132. https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2016.104
Zhang LP, Jiang JK, Tam JW, Zhang Y, Liu XS, Xu XR, Liu BZ, He YJ (2001) Effects of matrine on proliferation and differentiation in K-562 cells. Leuk Res 25(9):793–800
Zhang L, Wang T, Wen X, Wei Y, Peng X, Li H, Wei L (2007) Effect of matrine on HeLa cell adhesion and migration. Eur J Pharmacol 563(1–3):69–76
Liu XS, Jiang J, Jiao XY, Wu YE, Lin JH (2006) Matrine-induced apoptosis in leukemia U937 cells: involvement of caspases activation and MAPK-independent pathways. Planta Med 72(6):501–506
Jiang H, Hou C, Zhang S, Xie H, Zhou W, Jin Q, Cheng X, Qian R, Zhang X. (2007) Matrine upregulates the cell cycle protein E2F-1 and triggers apoptosis via the mitochondrial pathway in K562 cells. Eur J Pharmacol 559(2–3):98–108
Zhang S, Qi J, Sun L, Cheng B, Pan S, Zhou M, Sun X (2009) Matrine induces programmed cell death and regulates expression of relevant genes based on PCR array analysis in C6 glioma cells. Mol Biol Rep 36(4):791–799. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-008-9247-y
Manning BD, Cantley LC (2007) AKT/PKB signaling: navigating downstream. Cell 129(7):1261–1274
Cheng GZ, Park S, Shu S, He L, Kong W, Zhang W, Yuan Z, Wang LH, Cheng JQ (2008) Advances of AKT pathway in human oncogenesis and as a target for anti-cancer drug discovery. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 8(1):2–6
Voigt P, Brock C, Nürnberg B, Schaefer M (2005) Assigning functional domains within the p101 regulatory subunit of phosphoinositide 3-kinase gamma. J Biol Chem 280(6):5121–5127
Embi N, Rylatt DB, Cohen P (1980) Glycogen synthase kinase-3 from rabbit skeletal muscle. Separation from cyclic-AMP-dependent protein kinase and phosphorylase kinase. Eur J Biochem 107(2):519–527
Primot A, Baratte B, Gompel M, Borgne A, Liabeuf S, Romette JL, Jho EH, Costantini F, Meijer L (2000) Purification of GSK-3 by affinity chromatography on immobilized axin. Protein Expr Purif 20(3):394–404
Crowder RJ, Freeman RS (2000) Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta activity is critical for neuronal death caused by inhibiting phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase or Akt but not for death caused by nerve growth factor withdrawal. J Biol Chem 275(44):34266–34271
Bianchi M, De Lucchini S, Marin O, Turner DL, Hanks SK, Villa-Moruzzi E (2005) Regulation of FAK Ser-722 phosphorylation and kinase activity by GSK3 and PP1 during cell spreading and migration. Biochem J 391(Pt 2):359–370
Liang J, Slingerland JM (2003) Multiple roles of the PI3K/PKB (Akt) pathway in cell cycle progression. Cell Cycle 2(4):339–345
Li Y, Dowbenko D, Lasky LA (2001) AKT/PKB phosphorylation of p21Cip/WAF1 enhances protein stability of p21Cip/WAF1 and promotes cell survival. J Biol Chem 277(13):11352–11361
Hwangbo W, Lee JH, Ahn S, Kim S, Park KH, Kim CH, Kim I (2013) EGFR gene amplification and protein expression in invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast. Korean J Pathol 47(2):107. https://doi.org/10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2013.47.2.107
Kalman B, Szep E, Garzuly F, Post DE (2013) Epidermal growth factor receptor as a therapeutic target in glioblastoma. Neuromolecular Med 15(2):420–434. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-013-8229-y
Colakoglu T, Yildirim S, Kayaselcuk F, Nursal TZ, Ezer A, Noyan T, Karakayali H, Haberal M (2008) Clinicopathological significance of PTEN loss and the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt pathway in sporadic colorectal neoplasms: is PTEN loss predictor of local recurrence? Am J Surg 195(6):719–725. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjsurg.2007.05.061
Acknowledgements
The work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21502225 and 30872120/H2603) and The Shanghai Pujiang Talent program (No. 17PJD042).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Additional information
Xiao Sun and Xiao-bin Zhuo have contributed equally to this work and should be considered co-first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, X., Zhuo, Xb., Hu, Yp. et al. A novel matrine derivative WM622 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting PI3K/AKT signaling pathways. Mol Cell Biochem 449, 47–54 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-018-3341-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-018-3341-9