Abstract
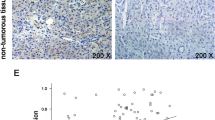
Lung cancer is the most frequent cancer in the world. Previous studies have shown that ubiquitin-specific protease 39 (USP39) is upregulated in several cancers and associated with tumor malignant characters. However, the effects of USP39 in lung cancer have not been well understood. In the present study, we found USP39 was generally expressed higher in human lung cancer tissues than in normal tissues by Oncomine database mining, qRT-PCR, and western blot assay. Knockdown of USP39 expression markedly reduced the proliferative and colony-forming ability of lung cancer cell lines 95D and A549. Flow cytometric analysis showed that USP39 knockdown induced cell cycle arrest at G2/M phase and enhanced cell apoptosis in 95D cells. Moreover, depletion of USP39 blocked activation of Akt, mTOR, p53, and PARP signaling pathways. Taken together, our study indicates that USP39 may be functionally involved in lung cancer growth and act as a potential molecular target for human lung cancer diagnosis and treatment.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang J, Wu Q, Wang Z, Zhang Y, Zhang G, Fu J, Liu C (2014) Knockdown of PSF1 expression inhibits cell proliferation in lung cancer cells in vitro. Tumour Biol. doi:10.1007/s13277-014-2826-8
Polanski J, Jankowska-Polanska B, Rosinczuk J, Chabowski M, Szymanska-Chabowska A (2016) Quality of life of patients with lung cancer. OncoTargets Ther 9:1023–1028. doi:10.2147/OTT.S100685
Zeng H, Zheng R, Guo Y, Zhang S, Zou X, Wang N, Zhang L, Tang J, Chen J, Wei K, Huang S, Wang J, Yu L, Zhao D, Song G, Chen J, Shen Y, Yang X, Gu X, Jin F, Li Q, Li Y, Ge H, Zhu F, Dong J, Guo G, Wu M, Du L, Sun X, He Y, Coleman MP, Baade P, Chen W, Yu XQ (2015) Cancer survival in China, 2003–2005: a population-based study. Int J Cancer 136(8):1921–1930. doi:10.1002/ijc.29227
Izquierdo M (2005) Short interfering RNAs as a tool for cancer gene therapy. Cancer Gene Ther 12(3):217–227. doi:10.1038/sj.cgt.7700791
McGarrity GJ, Hoyah G, Winemiller A, Andre K, Stein D, Blick G, Greenberg RN, Kinder C, Zolopa A, Binder-Scholl G, Tebas P, June CH, Humeau LM, Rebello T (2013) Patient monitoring and follow-up in lentiviral clinical trials. J Gene Med 15(2):78–82. doi:10.1002/jgm.2691
Coux O, Tanaka K, Goldberg AL (1996) Structure and functions of the 20S and 26S proteasomes. Annu Rev Biochem 65:801–847. doi:10.1146/annurev.bi.65.070196.004101
Hershko A, Ciechanover A (1998) The ubiquitin system. Annu Rev Biochem 67:425–479. doi:10.1146/annurev.biochem.67.1.425
Sakurai M, Ayukawa K, Setsuie R, Nishikawa K, Hara Y, Ohashi H, Nishimoto M, Abe T, Kudo Y, Sekiguchi M, Sato Y, Aoki S, Noda M, Wada K (2006) Ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase L1 regulates the morphology of neural progenitor cells and modulates their differentiation. J Cell Sci 119(Pt 1):162–171. doi:10.1242/jcs.02716
Stevenson LF, Sparks A, Allende-Vega N, Xirodimas DP, Lane DP, Saville MK (2007) The deubiquitinating enzyme USP2a regulates the p53 pathway by targeting Mdm2. EMBO J 26(4):976–986. doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7601567
Wang H, Ji X, Liu X, Yao R, Chi J, Liu S, Wang Y, Cao W, Zhou Q (2013) Lentivirus-mediated inhibition of USP39 suppresses the growth of breast cancer cells in vitro. Oncol Rep 30(6):2871–2877. doi:10.3892/or.2013.2798
Chen FZ, Zhao XK (2013) Ubiquitin-proteasome pathway and prostate cancer. Onkologie 36(10):592–596. doi:10.1159/000355166
van Leuken RJ, Luna-Vargas MP, Sixma TK, Wolthuis RM, Medema RH (2008) Usp39 is essential for mitotic spindle checkpoint integrity and controls mRNA-levels of aurora B. Cell Cycle 7(17):2710–2719
Makarova OV, Makarov EM, Luhrmann R (2001) The 65 and 110 kDa SR-related proteins of the U4/U6.U5 tri-snRNP are essential for the assembly of mature spliceosomes. EMBO J 20(10):2553–2563. doi:10.1093/emboj/20.10.2553
Rios Y, Melmed S, Lin S, Liu NA (2011) Zebrafish usp39 mutation leads to rb1 mRNA splicing defect and pituitary lineage expansion. PLoS Genet 7(1):e1001271. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1001271
An Y, Yang S, Guo K, Ma B, Wang Y (2015) Reduced USP39 expression inhibits malignant proliferation of medullary thyroid carcinoma in vitro. World J Surg Oncol 13(1):255. doi:10.1186/s12957-015-0669-4
Yuan X, Sun X, Shi X, Jiang C, Yu D, Zhang W, Guan W, Zhou J, Wu Y, Qiu Y, Ding Y (2015) USP39 promotes the growth of human hepatocellular carcinoma in vitro and in vivo. Oncol Rep 34(2):823–832. doi:10.3892/or.2015.4065
Garber ME, Troyanskaya OG, Schluens K, Petersen S, Thaesler Z, Pacyna-Gengelbach M, van de Rijn M, Rosen GD, Perou CM, Whyte RI, Altman RB, Brown PO, Botstein D, Petersen I (2001) Diversity of gene expression in adenocarcinoma of the lung. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98(24):13784–13789. doi:10.1073/pnas.241500798
Hou J, Aerts J, den Hamer B, van Ijcken W, den Bakker M, Riegman P, van der Leest C, van der Spek P, Foekens JA, Hoogsteden HC, Grosveld F, Philipsen S (2010) Gene expression-based classification of non-small cell lung carcinomas and survival prediction. PLoS One 5(4):e10312. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0010312
Wachi S, Yoneda K, Wu R (2005) Interactome-transcriptome analysis reveals the high centrality of genes differentially expressed in lung cancer tissues. Bioinformatics 21(23):4205–4208. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/bti688
Landi MT, Dracheva T, Rotunno M, Figueroa JD, Liu H, Dasgupta A, Mann FE, Fukuoka J, Hames M, Bergen AW, Murphy SE, Yang P, Pesatori AC, Consonni D, Bertazzi PA, Wacholder S, Shih JH, Caporaso NE, Jen J (2008) Gene expression signature of cigarette smoking and its role in lung adenocarcinoma development and survival. PLoS One 3(2):e1651. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0001651
Selamat SA, Chung BS, Girard L, Zhang W, Zhang Y, Campan M, Siegmund KD, Koss MN, Hagen JA, Lam WL, Lam S, Gazdar AF, Laird-Offringa IA (2012) Genome-scale analysis of DNA methylation in lung adenocarcinoma and integration with mRNA expression. Genome Res 22(7):1197–1211. doi:10.1101/gr.132662.111
Okayama H, Kohno T, Ishii Y, Shimada Y, Shiraishi K, Iwakawa R, Furuta K, Tsuta K, Shibata T, Yamamoto S, Watanabe S, Sakamoto H, Kumamoto K, Takenoshita S, Gotoh N, Mizuno H, Sarai A, Kawano S, Yamaguchi R, Miyano S, Yokota J (2012) Identification of genes upregulated in ALK-positive and EGFR/KRAS/ALK-negative lung adenocarcinomas. Cancer Res 72(1):100–111. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-1403
Li D, Huang Y (2014) Knockdown of ubiquitin associated protein 2-like inhibits the growth and migration of prostate cancer cells. Oncol Rep 32(4):1578–1584. doi:10.3892/or.2014.3360
He X, Dong Y, Wu CW, Zhao Z, Ng SS, Chan FK, Sung JJ, Yu J (2012) MicroRNA-218 inhibits cell cycle progression and promotes apoptosis in colon cancer by downregulating BMI1 polycomb ring finger oncogene. Mol Med 18:1491–1498. doi:10.2119/molmed.2012.00304
Lygerou Z, Christophides G, Seraphin B (1999) A novel genetic screen for snRNP assembly factors in yeast identifies a conserved protein, Sad1p, also required for pre-mRNA splicing. Mol Cell Biol 19(3):2008–2020
Kolb RH, Greer PM, Cao PT, Cowan KH, Yan Y (2012) ERK1/2 signaling plays an important role in topoisomerase II poison-induced G2/M checkpoint activation. PLoS One 7(11):e50281. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0050281
Mistry H, Hsieh G, Buhrlage SJ, Huang M, Park E, Cuny GD, Galinsky I, Stone RM, Gray NS, D’Andrea AD, Parmar K (2013) Small-molecule inhibitors of USP1 target ID1 degradation in leukemic cells. Mol Cancer Ther 12(12):2651–2662. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-13-0103-T
Nijman SM, Huang TT, Dirac AM, Brummelkamp TR, Kerkhoven RM, D’Andrea AD, Bernards R (2005) The deubiquitinating enzyme USP1 regulates the fanconi anemia pathway. Mol Cell 17(3):331–339. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2005.01.008
Malapelle U, Morra F, Ilardi G, Visconti R, Merolla F, Cerrato A, Napolitano V, Monaco R, Guggino G, Monaco G, Staibano S, Troncone G, Celetti A (2016) USP7 inhibitors, downregulating CCDC6, sensitize lung neuroendocrine cancer cells to PARP-inhibitor drugs. Lung Cancer. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2016.06.015
Ma M, Yu N (2016) Ubiquitin-specific protease 7 expression is a prognostic factor in epithelial ovarian cancer and correlates with lymph node metastasis. OncoTargets Ther 9:1559–1569. doi:10.2147/OTT.S100050
Geng J, Huang X, Li Y, Xu X, Li S, Jiang D, Liang J, Jiang D, Wang C, Dai H (2015) Down-regulation of USP13 mediates phenotype transformation of fibroblasts in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respir Res 16:124. doi:10.1186/s12931-015-0286-3
Zhu L, Yang S, He S, Qiang F, Cai J, Liu R, Gu C, Guo Z, Wang C, Zhang W, Zhang C, Wang Y (2016) Downregulation of ubiquitin-specific protease 14 (USP14) inhibits breast cancer cell proliferation and metastasis, but promotes apoptosis. J Mol Histol 47(1):69–80. doi:10.1007/s10735-015-9650-3
Vogel RI, Pulver T, Heilmann W, Mooneyham A, Mullany S, Zhao X, Shahi M, Richter J, Klein M, Chen L, Ding R, Konecny G, Kommoss S, Winterhoff B, Ghebre R, Bazzaro M (2016) USP14 is a predictor of recurrence in endometrial cancer and a molecular target for endometrial cancer treatment. Oncotarget. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.8821
Meitinger F, Anzola JV, Kaulich M, Richardson A, Stender JD, Benner C, Glass CK, Dowdy SF, Desai A, Shiau AK, Oegema K (2016) 53BP1 and USP28 mediate p53 activation and G1 arrest after centrosome loss or extended mitotic duration. J Cell Biol 214(2):155–166. doi:10.1083/jcb.201604081
Zhang L, Xu B, Qiang Y, Huang H, Wang C, Li D, Qian J (2015) Overexpression of deubiquitinating enzyme USP28 promoted non-small cell lung cancer growth. J Cell Mol Med 19(4):799–805. doi:10.1111/jcmm.12426
Madhunapantula SV, Robertson GP (2009) The PTEN-AKT3 signaling cascade as a therapeutic target in melanoma. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res 22(4):400–419. doi:10.1111/j.1755-148X.2009.00585.x
Laplante M, Sabatini DM (2009) mTOR signaling at a glance. J Cell Sci 122(Pt 20):3589–3594. doi:10.1242/jcs.051011
Li T, Liu X, Jiang L, Manfredi J, Zha S, Gu W (2016) Loss of p53-mediated cell-cycle arrest, senescence and apoptosis promotes genomic instability and premature aging. Oncotarget. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.7864
Bressenot A, Marchal S, Bezdetnaya L, Garrier J, Guillemin F, Plenat F (2009) Assessment of apoptosis by immunohistochemistry to active caspase-3, active caspase-7, or cleaved PARP in monolayer cells and spheroid and subcutaneous xenografts of human carcinoma. J Histochem Cytochem 57(4):289–300. doi:10.1369/jhc.2008.952044
Nicholson KM, Anderson NG (2002) The protein kinase B/Akt signalling pathway in human malignancy. Cell Signal 14(5):381–395
Wang X, Sun SY (2009) Enhancing mTOR-targeted cancer therapy. Expert Opin Ther Targets 13(10):1193–1203. doi:10.1517/14728220903225008
Laplante M, Sabatini DM (2012) mTOR signaling in growth control and disease. Cell 149(2):274–293. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.017
Feng Z, Lin M, Wu R (2011) The regulation of aging and longevity: a new and complex role of p53. Genes & Cancer 2(4):443–452. doi:10.1177/1947601911410223
Eischen CM, Lozano G (2014) The Mdm network and its regulation of p53 activities: a rheostat of cancer risk. Hum Mutat 35(6):728–737. doi:10.1002/humu.22524
Zheng B, Yu X, Chai R (2014) Myotubularin-related phosphatase 3 promotes growth of colorectal cancer cells. Scientific World J 2014:703804. doi:10.1155/2014/703804
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (The regulative mechanism of PRDM14 gene and its methylation on non-small cell lung cancer metastasis. No. 81372521).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed were in conformity to the ethical standards of the institutional and national committee on human experimentation and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and later amendments. Ethical approval was given by the medical ethics committee of Shanghai First People’s Hospital with the following reference number: 2013KY036.
Additional information
Zhifeng Lin and Liwen Xiong have contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, Z., Xiong, L. & Lin, Q. Ubiquitin-specific protease 39 is overexpressed in human lung cancer and promotes tumor cell proliferation in vitro. Mol Cell Biochem 422, 97–107 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-016-2809-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-016-2809-8