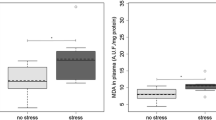
Abstract
For the past 40 years, anabolic–androgenic steroids have been used by a wide variety of athletes with the hope of improving their training, endurance, and performance. The aim of this study was to examine the chronic effects of nandrolone decanoate (20 mg/kg, s.c, Deca-Durabolin DECA®) on oxidative stress biomarkers in the hearts of sedentary and exercised rats. The male Wistar albino rats (n = 180, four groups with three subgroups, 15 per subgroup, age 10 weeks, body mass 200–220 g) were sacrificed, and in the collected samples of blood, the following markers of oxidative stress were measured spectrophotometrically: (1) index of lipid peroxidation (measured as TBARS-thiobarbituric acid reactive substances); (2) nitrites (NO2 −); (3) hydrogen peroxide (H2O2); (4) superoxide anion radical (O2 −), and superoxide dismutase, catalase, and glutathione reductase. The results clearly show that the impact of ND alone, or in combination with physical training in general, is mildly pro-oxidative. The chronic physical training probably induces the protective antioxidant enzyme system , which may be of clinical interest when faced with overdosage of this drug.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AAS:
-
Anabolic androgenic steroids
- ND:
-
Nandrolone decanoate
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- RNS:
-
Reactive nitrogen species
- NO:
-
Nitric oxide
- ·OH:
-
Hydroxyl radical
- ROO·:
-
Peroxyl radical
- SEM:
-
Standard error mean
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
References
Lukas SE (1993) Current perspectives on anabolic-androgenic steroid abuse. Trends Pharmacol Sci 14:61–68
Socas L, Zumbado M, Pérez-Luzardo O, Ramos A, Pérez C, Hernández JR, Boada LD (2005) Hepatocellular adenomas associated with anabolic androgenic steroid abuse in bodybuilders: a report of two cases and a review of the literature. Br J Sports Med 39:27–28
García-Esperón C, Hervás-García JV, Jiménez-González M, Pérez de la Ossa-Herrero N, Gomis-Cortina M, Dorado-Bouix L, López-Cancio Martinez E, Castaño-Duque CH, Millán-Torné M, Dávalos A (2013) Ingestion of anabolic steroids and ischaemic stroke. A clinical case report and review of the literature. Rev Neurol 56:327–331
Dolgov IM, Badtieva VA (2014) Certain molecular effects of physical exercises. Vopr Kurortol Fizioter Lech Fiz Kult 6:62–67
Eto M (2013) Role of androgen in the elderly. Exercise and androgens. Clin Calcium 23:1191–1196
Pingitore A, Lima GP, Mastorci F, Quinones A, Iervasi G, Vassalle C (2015) Exercise and oxidative stress: potential effects of antioxidant dietary strategies in sports. Nutrition 31:916–922
Yavari A, Javadi M, Mirmiran P, Bahadoran Z (2015) Exercise-induced oxidative stress and dietary antioxidants. Asian J Sports Med 6:248–298
Powers SK, Jackson MJ (2008) Exercise-induced oxidative stress: cellular mechanisms and impact on muscle force production. Physiol Rev 88:1243–1276
Kinnunen S, Atalay M, Hyyppa S, Lehmuskero A, Hanninen O, Oksala N (2005) Effects of prolonged exercise on oxidative stress and antioxidant defense in endurance horse. J Sports Sci Med 4:415–421
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95:351–358
Green LC, Wagner DA, Glogowski J, Skipper PL, Wishnok JS, Tannenbaum SR (1982) Analysis of nitrate, nitrite and [15 N] nitrate in biological fluids. Anal Biochem 126:131–138
Pick E, Keisari Y (1980) A simple colorimetric method for the measurement of hydrogen peroxide produced by cells in culture. J Immunol Meth 38:161–170
Auclair C, Voisin E (1985) Nitroblue tetrazolium reduction. In: Greenvvald RA (ed) Handbook of methods for oxygen radical research. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 123–132
McCord JM, Fridovich I (1969) The utility of superoxide dismutase in studying free radical reactions. I. Radicals generated by the interaction of sulfite, dimethyl sulfoxide, and oxygen. J Biol Chem 244:6056–6063
Beutler E (1982) Catalase, red cell metabolism. In: Beutler E (ed) Manual of biochemical methods. Grune and Stratton, New York, p 105
Tsuchihashi M (1923) Zur Kenntnis der Blutkatalase. Biochem Z 140:65–72
Misra HP, Fridovich I (1972) The role of superoxide-anion in the autoxidation of epinephrine and a simple assay for superoxide dismutase. J Biol Chem 247:3170–3175
Lee FT, Kuo TY, Liou SY, Chien CT (2009) Chronic Rhodiola rosea extract supplementation enforces exhaustive swimming tolerance. Am J Chin Med 37:557–572
Lima FD, Stamm DN, Della-Pace ID et al (2013) Swimming training induces liver mitochondrial adaptations to oxidative stress in rats submitted to repeated exhaustive swimming bouts. Sastre J 8:556–568
Do Carmo EC, Fernandes T, Koike D, Da Silva ND, Jr Mattos KC et al (2011) Anabolic steroid associated to physical training induces deleterious cardiac effects. Med Sci Sports Exerc 43:1836–1848
Yavari A, Javadi M, Mirmiran P, Bahadoran Z (2015) Exercise-induced oxidative stress and dietary antioxidants. Asian J Sports Med 6:248–298
Ji LL (1999) Antioxidants and oxidative stress in exercise. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 222:283–292
Saborido A, Naudi A, Portero-Otin M, Pamplona R, Megias A (2011) Stanozolol treatment decreases the mitochondrial ROS generation and oxidative stress induced by acute exercise in rat skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol 110:661–669
Matthews C, Gorenne I, Scott S, Figg N, Kirkpatrick P, Ritchie A, Goddard M, Bennett M (2006) Vascular smooth muscle cells undergo telomere-based senescence in human atherosclerosis: effects of telomerase and oxidative stress. Circ Res 99:156–164
Sullivan ML, Martinez CM, Gennis P, Gallagher EJ (1998) The cardiac toxicity of anabolic steroids. Prog Cardiovasc Dis 41:1–15
Franquni JV, do Nascimento AM, de Lima EM, Brasil GA, Heringer OA, Cassaro KO, da Cunha TV, Musso C, Silva Santos MC, Kalil IC, Endringer DC, Boëchat GA, Bissoli NS, de Andrade TU (2013) Nandrolone decanoate determines cardiac remodelling and injury by an imbalance in cardiac inflammatory cytokines and ACE activity, blunting of the Bezold-Jarisch reflex, resulting in the development of hypertension. Steroids 78:379–385
Mohamed HM, Mohamed MA (2015) Effect of different doses of nandrolone decanoate on lipid peroxidation, DNA fragmentation, sperm abnormality and histopathology of testes of male Wister rats. Exp Toxicol Pathol 67:1–11
Ferrer M, Encabo A, Marín J, Balfagón G (1994) Chronic treatment with the anabolic steroid, nandrolone, inhibits vasodilator responses in rabbit aorta. Eur J Pharmacol 252:233–241
Cunha TS, Moura MJ, Bernardes CF, Tanno AP, Marcondes FK (2005) Vascular sensitivity to phenylephrine in rats submitted to anaerobic training and nandrolone treatment. Hypertension 46:1010–1015
Fineschi V, Riezzo I, Centini F et al (2007) Sudden cardiac death during anabolic steroid abuse: morphologic and toxicologic findings in two fatal cases of bodybuilders. Int J Legal Med 121:48–53
Powers SK, Criswell D, Lawler D, Martin D, Lieu FK, Ji LL, Herbet RA (1993) Rigorous exercise training increases superoxide dismutase activity in ventricular myocardium. Am J Physiol 265:2094–2098
Riezzo I, Turillazzi E, Bello S, Cantatore S, Cerretani D, Di Paolo M, Fiaschi AI, Frati P, Neri M, Pedretti M, Fineschi V (2014) Chronic nandrolone administration promotes oxidative stress, induction of pro-inflammatory cytokine and TNF-α mediated apoptosis in the kidneys of CD1 treated mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 280:97–106
Sun M, Shen W, Zhong M, Wu P, Chen H, Lu A (2013) Nandrolone attenuates aortic adaptation to exercise in rats. Cardiovasc Res 97:686–695
Chaves EA, Pereira-Junior PP, Fortunato RS, Masuda MO, de Carvalho AC, de Carvalho DP, Oliveira MF, Nascimento JH (2006) Nandrolone decanoate impairs exercise-induced cardioprotection: role of antioxidant enzymes. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 99:223–230
Marques-Neto SR, Ferraz EB, Rodrigues DC, Njaine B, Rondinelli E, Campos de Carvalho AC, Nascimento JH (2014) AT1 and aldosterone receptors blockade prevents the chronic effect of nandrolone on the exercise-induced cardioprotection in perfused rat heart subjected to ischemia and reperfusion. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 28:125–135. doi:10.1007/s1055701365038
Fineschi V (2013) Chronic, supra-physiological doses of nandrolone decanoate and exercise induced cardio-toxicity in an animal-model study. Acta Physiol 208:141–143. doi:10.1111/s12093
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technological Development of the Republic of Serbia (Grant No. 175043), and the Faculty of Medical Sciences, University of Kragujevac (Junior Project 09/2011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors of the present paper disclose no actual or potential conflicts of interest, including any financial, personal, or other relationships with people or organizations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nikolic, T., Zivkovic, V., Jevdjevic, M. et al. The effects of chronic administration of nandrolone decanoate on redox status in exercised rats. Mol Cell Biochem 411, 95–105 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-015-2571-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-015-2571-3