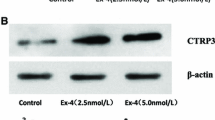
Abstract
The purposes of this study were to examine whether thermogenesis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes is related to variations in thyroid hormone receptors (TRs) that are differently regulated by triiodothyronine (T3), and the possible role of AMP-activated protein (AMPK) in thermogenesis after cell differentiation. Differentiated 3T3-L1 adipocytes were maintained under four conditions: normal control group, T3 treatment group, AMPK agonist (5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide-1-β-D-ribofuranoside) treatment group, and T3 and AMPK inhibitor (Compound C) treatment group. Real-time polymerase chain reaction was then performed to evaluate the changes in TRα and TRβ mRNA levels in the cells, as well as marker genes for brown adipose tissue including uncoupling protein (UCP)-1 and Cidea. Western blotting was carried out for the cells to detect the expressions of TRα, TRβ, and AMPK protein levels. After T3 treatment, the mRNA and protein levels of TRα decreased compared with the control group, while TRβ mRNA and protein levels increased markedly at the same time. We also found elevated mRNA levels of UCP-1 and Cidea after exposure to T3. However, the distribution of TRs was reversed by Compound C. AMPK protein levels were clearly activated by T3. Our results suggest that the distribution of TRs is related to thermogenesis, and AMPK may participate in the alterations.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhu XG, Cheng SY (2010) New insights into regulation of lipid metabolism by thyroid hormone. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes 17:408–413. doi:10.1097/med
Laurberg P, Andersen S, Karmisholt J (2005) Cold adaptation and thyroid hormone metabolism. Horm Metab Res 37:545–549. doi:10.1055/s-2005-870420
Pontikides N, Krassas GE (2007) Basic endocrine products of adipose tissue in states of thyroid dysfunction. Thyroid 17:421–431. doi:10.1089/thy.2007.0016
Yen PM (2001) Physiological and molecular basis of thyroid hormone action. Physiol Rev 81:1097–1142
Viguerie N, Langin D (2003) Effect of thyroid hormone on gene expression. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 6:377–381. doi:10.1097/01.mco.0000078998.96795.e7
Dace A, Sarkissian G, Schneider L, Martin-El Yazidi C, Bonne J, Margotat A, Planells R, Torresani J (1999) Transient expression of c-erbA beta 1 messenger ribonucleic acid and beta 1 thyroid hormone receptor early in adipogenesis of Ob17 cells. Endocrinology 140:2983–2990. doi:10.1210/endo.140.7.6860
Jiang W, Miyamoto T, Kakizawa T, Sakuma T, Nishio S, Takeda T, Suzuki S, Hashizume K (2004) Expression of thyroid hormone receptor alpha in 3T3-L1 adipocytes; triiodothyronine increases the expression of lipogenic enzyme and triglyceride accumulation. J Endocrinol 182:295–302
Silva JE (2001) The multiple contributions of thyroid hormone to heat production. J Clin Invest 108:35–37. doi:10.1172/JCI13397
Lanni A, Moreno M, Lombardi A, Goglia F (2003) Thyroid hormone and uncoupling proteins. FEBS Lett 543:5–10. doi:10.1016/s0014-5793(03)00320-x
Lee JY, Takahashi N, Yasubuchi M, Kim YI, Hashizaki H, Kim MJ, Sakamoto T, Goto T, Kawada T (2012) Triiodothyronine induces UCP-1 expression and mitochondrial biogenesis in human adipocytes. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 302:C463–C472. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00010.2011
Winder WW, Hardie DG (1999) AMP-activated protein kinase, a metabolic master switch: possible roles in type 2 diabetes. Am J Physiol 277:E1–10
Kahn BB, Alquier T, Carling D, Hardie DG (2005) AMP-activated protein kinase: ancient energy gauge provides clues to modern understanding of metabolism. Cell Metab 1:15–25. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2004.12.003
Kemp BE, Stapleton D, Campbell DJ, Chen ZP, Murthy S, Walter M, Gupta A, Adams JJ, Katsis F, van Denderen B, Jennings IG, Iseli T, Michell BJ, Witters LA (2003) AMP-activated protein kinase, super metabolic regulator. Biochem Soc Trans 31:162–168. doi:10.1042/BST0310162
An Z, Wang H, Song P, Zhang M, Geng X, Zou MH (2007) Nicotine-induced activation of AMP-activated protein kinase inhibits fatty acid synthase in 3T3L1 adipocytes: a role for oxidant stress. J Biol Chem 282:26793–26801. doi:10.1074/jbc.M703701200
Lopez M, Varela L, Vazquez MJ, Rodriguez-Cuenca S, Gonzalez CR, Velagapudi VR, Morgan DA, Schoenmakers E, Agassandian K, Lage R, Martinez de Morentin PB, Tovar S, Nogueiras R, Carling D, Lelliott C, Gallego R, Oresic M, Chatterjee K, Saha AK, Rahmouni K, Dieguez C, Vidal-Puig A (2010) Hypothalamic AMPK and fatty acid metabolism mediate thyroid regulation of energy balance. Nat Med 16:1001–1008. doi:10.1038/nm.2207
Pfaffl MW (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantitation in real-time RT-PCR. Nucl Acid Res 29:45. doi:10.1093/nar/29.9.e45
Azzu V, Jastroch M, Divakaruni AS, Brand MD (2010) The regulation and turnover of mitochondrial uncoupling proteins. Biochim Biophysm Acta 1797:785–791. doi:10.1016/j.bbabio.2010.02.035
Jia JJ, Tian YB, Cao ZH, Tao LL, Zhang X, Gao SZ, Ge CR, Lin QY, Jois M (2010) The polymorphisms of UCP1 genes associated with fat metabolism, obesity and diabetes. Mol Biol Rep 37:1513–1522. doi:10.1007/s11033-009-9550-2
Townsend KL, Tseng YH (2012) Brown adipose tissue recent insights into development, metabolic function and therapeutic potential. Adipocytes 1:1–12. doi:10.4161/adip.18951
Hernandez A, Obregon MJ (2000) Triiodothyronine amplifies the adrenergic stimulation of uncoupling protein expression in rat brown adipocytes. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 278:769–777
Hernandez A, Martinez-de-Mena R, Martin E, Obregon MJ (2011) Differences in the Response of UCP1 mRNA to hormonal stimulation between rat and mouse primary cultures of brown adipocytes. Cell Physiol Biochem 28:969–980. doi:10.1159/000335810
Mishra A, Zhu XG, Ge K, Cheng SY (2010) Adipogenesis is differentially impaired by thyroid hormone receptor mutant isoforms. J Mol Endocrinol 44:247–255. doi:10.1677/JME-09-0137
Zhu XG, Kim DW, Goodson ML, Privalsky ML, Cheng SY (2011) NCoR1 regulates thyroid hormone receptor isoform-dependent adipogenesis. J Mol Endocrinol 46:233–244. doi:10.1530/JME-10-0163
de Oliveira M, Luvizotto Rde A, Olimpio RM, de Sibio MT, Silva CB, Conde SJ, Padovani CR, Nogueira CR (2013) Modulation of thyroid hormone receptors, TRα and TRβ, by using different doses of triiodothyronine (T3) at different times. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metab 57:368–374. doi:10.1590/S0004-27302013000500006
de Jesus LA, Carvalho SD, Ribeiro MO, Schneider M, Kim SW, Harney JW, Larsen PR, Bianco AC (2001) The type 2 iodothyronine deiodinase is essential for adaptive thermogenesis in brown adipose tissue. J Clin Invest 108:1379–1385. doi:10.1172/JCI13803
Martinez de Mena R, Scanlan TS, Obregon MJ (2010) The T3 receptor beta1 isoform regulates UCP1 and D2 deiodinase in rat brown adipocytes. Endocrinology 151:5074–5083. doi:10.1210/en.2010-0533
Hardie DG (2007) AMP-activated/SNF1 protein kinases: conserved guardians of cellular energy. Nature Rev Mol Cell Biol 8:774–785. doi:10.1038/nrm2249
Curfman GD, Morrissey S, Drazen JM (2010) Sibutramine—another flawed diet pill. N Engl J Med 363:972–974. doi:10.1056/NEJMe1007993
Baretić M (2013) Obesity drug therapy. Minerva Endocrinol 38:245–254
Carlsson LM, Peltonen M, Ahlin S, Anveden Å, Bouchard C, Carlsson B, Jacobson P, Lönroth H, Maglio C, Näslund I, Pirazzi C, Romeo S, Sjöholm K, Sjöström E, Wedel H, Svensson PA, Sjöström L (2012) Bariatric surgery and prevention of type 2 diabetes in Swedish obese subjects. N Engl J Med 367:695–704. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1112082
Schultze SM, Hemmings BA, Niessen M, Tschopp O (2012) PI3K/AKT, MAPK and AMPK signalling: protein kinases in glucose homeostasis. Expert Rev Mol Med 14:21. doi:10.1017/S1462399411002109
Zhang Y, Guan M, Zheng Z, Zhang Q, Gao F, Xue Y (2013) Effects of metformin on CD133+ colorectal cancer cells in diabetic patients. PLoS ONE 8:e81264. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0081264
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Prof. W. B. Xie (School of Basic Medical Sciences, Southern Medical University) for helpful advice for this study, and we are also grateful to Prof. J. Xu (School of Foreign Studies, Southern Medical University) for revision of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, CZ., Wei, D., Guan, MP. et al. Triiodothyronine regulates distribution of thyroid hormone receptors by activating AMP-activated protein kinase in 3T3-L1 adipocytes and induces uncoupling protein-1 expression. Mol Cell Biochem 393, 247–254 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-014-2067-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-014-2067-6