Abstract
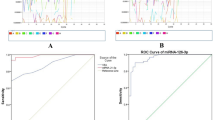
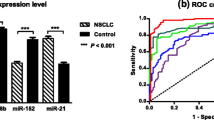
Objective was to assess and compare the relative expressions of miR-205-5p, miR-205-3p, and miR-21-3p in tissues and serum among non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) patients, benign pulmonary conditions patients, and healthy volunteers. Serum samples were obtained between October 2011 and September 2012 from 20 NSCLC patients undergoing surgical treatment, 20 patients diagnosed with a benign lung disease (pulmonary tuberculosis, pneumonia, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or interstitial pneumonia) (lesion group), and 20 healthy volunteers (control group). NSCLC patients provided cancer tissues and cancer-adjacent normal tissues during surgery (paired specimens). Quantitative RT-PCR was used to assess miR-205-5p, miR-205-3p, and miR-21-3p expressions in serum and tissue samples. The relative expressions of miR-205-5p and miR-205-3p were significantly higher in NSCLC tissues compared with cancer-adjacent paired specimens (both P < 0.001). In the serum, significantly higher miR-205-5p, miR-205-3p, and miR-21-3p relative expressions were observed in the NSCLC group compared with the two other groups (all P < 0.001). The relative expressions of miR-205-5p and miR-21-3p in NSCLC tissues and serum were significantly correlated (r = 0.553, P = 0.011; and r = −0.541, P = 0.014, respectively), while no significant correlation was observed for miR-205-3P (P = 0.120). Expressions of miR-205-5p and miR-205-3P in squamous cell carcinoma specimens were significantly higher than in lung adenocarcinoma specimens (both P = 0.001). Similarly, higher serum miR-205-5p and miR-205-3p levels were observed in squamous cell carcinoma patients (P = 0.033 and P = 0.002, respectively). In this preliminary and novel study, miR-205-5p was more useful as a marker for NSCLC than miR-205-3p or miR-21, indicating a potential for future applications in NSCLC diagnosis and prognosis.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- NSCLC:
-
Non-small cell lung cancer
- TNM:
-
Tumor node metastasis staging
- miR:
-
MicroRNAs
- SCC:
-
Squamous cell carcinoma
- COPD:
-
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
References
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Thun MJ (2009) Cancer statistics 2009. CA Cancer J Clin 59(4):225–249. doi:10.3322/caac.20006
Miller YE (2005) Pathogenesis of lung cancer: 100 year report. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 33(3):216–223. doi:10.1165/rcmb.2005-0158OE
Lin PY, Yu SL, Yang PC (2010) MicroRNA in lung cancer. Br J Cancer 103(8):1144–1148. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6605901
Calin GA, Croce CM (2006) MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer 6(11):857–866. doi:10.1038/nrc1997
Calin GA, Sevignani C, Dumitru CD, Hyslop T, Noch E, Yendamuri S, Shimizu M, Rattan S, Bullrich F, Negrini M, Croce CM (2004) Human microRNA genes are frequently located at fragile sites and genomic regions involved in cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101(9):2999–3004. doi:10.1073/pnas.03073231010307323101
Croce CM (2009) Causes and consequences of microRNA dysregulation in cancer. Nat Rev Genet 10(10):704–714. doi:10.1038/nrg2634
Yanaihara N, Caplen N, Bowman E, Seike M, Kumamoto K, Yi M, Stephens RM, Okamoto A, Yokota J, Tanaka T, Calin GA, Liu CG, Croce CM, Harris CC (2006) Unique microRNA molecular profiles in lung cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Cancer Cell 9(3):189–198. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2006.01.025
Lebanony D, Benjamin H, Gilad S, Ezagouri M, Dov A, Ashkenazi K, Gefen N, Izraeli S, Rechavi G, Pass H, Nonaka D, Li J, Spector Y, Rosenfeld N, Chajut A, Cohen D, Aharonov R, Mansukhani M (2009) Diagnostic assay based on hsa-miR-205 expression distinguishes squamous from nonsquamous non-small-cell lung carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 27(12):2030–2037. doi:10.1200/JCO.2008.19.4134
Hu Z, Chen X, Zhao Y, Tian T, Jin G, Shu Y, Chen Y, Xu L, Zen K, Zhang C, Shen H (2010) Serum microRNA signatures identified in a genome-wide serum microRNA expression profiling predict survival of non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 28(10):1721–1726. doi:10.1200/JCO.2009.24.9342
Hwang JH, Voortman J, Giovannetti E, Steinberg SM, Leon LG, Kim YT, Funel N, Park JK, Kim MA, Kang GH, Kim SW, Del Chiaro M, Peters GJ, Giaccone G (2010) Identification of microRNA-21 as a biomarker for chemoresistance and clinical outcome following adjuvant therapy in resectable pancreatic cancer. PLoS ONE 5(5):e10630. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0010630
WHO Classification of Tumours. Pathology & Genetics. Tumours of the Lung, Pleura, Thymus and Heart (2004). International Agency fo Research on Cancer, Lyon
Wang ZX, Bian HB, Wang JR, Cheng ZX, Wang KM, De W (2011) Prognostic significance of serum miRNA-21 expression in human non-small cell lung cancer. J Surg Oncol 104(7):847–851. doi:10.1002/jso.22008
Le HB, Zhu WY, Chen DD, He JY, Huang YY, Liu XG, Zhang YK (2012) Evaluation of dynamic change of serum miR-21 and miR-24 in pre- and post-operative lung carcinoma patients. Med Oncol 29(5):3190–3197. doi:10.1007/s12032-012-0303-z
Bishop JA, Benjamin H, Cholakh H, Chajut A, Clark DP, Westra WH (2010) Accurate classification of non-small cell lung carcinoma using a novel microRNA-based approach. Clin Cancer Res 16(2):610–619. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-2638
Ryan DG, Oliveira-Fernandes M, Lavker RM (2006) MicroRNAs of the mammalian eye display distinct and overlapping tissue specificity. Mol Vis 12:1175–1184. doi:v12/a134
Liu XG, Zhu WY, Huang YY, Ma LN, Zhou SQ, Wang YK, Zeng F, Zhou JH, Zhang YK (2012) High expression of serum miR-21 and tumor miR-200c associated with poor prognosis in patients with lung cancer. Med Oncol 29(2):618–626. doi:10.1007/s12032-011-9923-y
Mathe EA, Nguyen GH, Bowman ED, Zhao Y, Budhu A, Schetter AJ, Braun R, Reimers M, Kumamoto K, Hughes D, Altorki NK, Casson AG, Liu CG, Wang XW, Yanaihara N, Hagiwara N, Dannenberg AJ, Miyashita M, Croce CM, Harris CC (2009) MicroRNA expression in squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma of the esophagus: associations with survival. Clin Cancer Res 15(19):6192–6200. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-1467
Raponi M, Dossey L, Jatkoe T, Wu X, Chen G, Fan H, Beer DG (2009) MicroRNA classifiers for predicting prognosis of squamous cell lung cancer. Cancer Res 69(14):5776–5783. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-0587
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the patients, faculty, and practitioners who contributed to this research. The study was supported by The National Natural Science Foundation of China 81270668, 31260248 and the Science and Technology Department of the Jiangxi province social development support plan (20123BBG70232).
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, M., Zhang, P., Hu, G. et al. Relative expressions of miR-205-5p, miR-205-3p, and miR-21 in tissues and serum of non-small cell lung cancer patients. Mol Cell Biochem 383, 67–75 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-013-1755-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-013-1755-y