Abstract
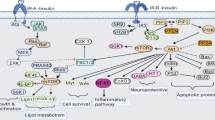
Emerging evidences demonstrate that excess aldosterone and insulin interact at target tissues. It has been shown that increased levels of aldosterone contribute to the development of insulin resistance and thus act as a risk factor for the development of type-2 diabetes mellitus. However, the molecular mechanisms involved in this scenario are yet to be identified. This study was designed to assess the dose-dependent effects of aldosterone on insulin signal transduction and glucose oxidation in the skeletal muscle (gastrocnemius) of adult male rat. Healthy adult male albino rats of Wistar strain (Rattus norvegicus) weighing 180–200 g were used in this study. Rats were divided into four groups. Group I: control (treated with 1 % ethanol only), group II: aldosterone treated (10 μg /kg body weight, twice daily for 15 days), group III: aldosterone treated (20 μg /kg body weight, twice daily for 15 days), and group IV: aldosterone treated (40 μg/kg body weight, twice daily for 15 days). Excess aldosterone caused glucose intolerance in a dose-dependent manner. Serum insulin and aldosterone were significantly increased, whereas serum testosterone was decreased. Aldosterone treatment impaired the rate of glucose uptake, oxidation, and insulin signal transduction in the gastrocnemius muscle through defective expression of IR, IRS-1, Akt, AS160, and GLUT4 genes. Phosphorylation of IRS-1, β-arrestin-2, and Akt was also reduced in a dose-dependent manner. Excess aldosterone results in glucose intolerance as a result of impaired insulin signal transduction leading to decreased glucose uptake and oxidation in skeletal muscle. In addition to this, it is inferred that excess aldosterone may act as one of the causative factors for the onset of insulin resistance and thus increased incidence of type-2 diabetes.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Menon VU, Kumar KV, Gilchrist A, Sugathan TN, Sundaram KR, Nair V (2006) Prevalence of known and undetected diabetes and associated risk factors in central Kerala—ADEPS. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 74:289–294
Jain S, Saraf S (2008) Type 2 diabetes mellitus—its global prevalence and therapeutic strategies. Diabetes Metab Syndr: Clin Res Rev 4:48–56
Le Roith D, Quon MJ, Zick Y (2003) Molecular and cellular aspects of insulin resistance: implications for diabetes. In: Finkel T, Gutkind JS (eds) Signal transduction and human disease. Wiley-Interscience, Hoboken, pp 171–200
Kahn SE, Hull RL, Utzschneider KM (2006) Mechanisms linking obesity to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nature 444:840–846
Sowers JR (2004) Insulin resistance and hypertension. AJP Heart Circ Physiol 286:H1597–H1602
Taniguchi CM, Emanuelli B, Kahn CR (2006) Critical nodes in signalling pathways: insights into insulin action. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7:85–96
Farese RV, Sajan MP, Standaert ML (2005) Insulin-sensitive protein kinases (atypical protein kinase C and protein kinase B/Akt): actions and defects in obesity and type II diabetes. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 230:593–605
Sale EM, Sale GJ (2008) Protein kinase B: signalling roles and therapeutic targeting. Cell Mol Life Sci 65:113–127
Sano H, Kane S, Sano E, Minea CP, Asara JM, Lane WS et al (2003) Insulin stimulated phosphorylation of Rab GTPase activating protein regulates GLUT4 translocation. J Biol Chem 278:14599–14602
Baron AD, Brechtel G, Wallace P, Edelman SV (1988) Rates and tissue sites of non- insulin and insulin-mediated glucose uptake in humans. Am J Physiol 255:E769–E774
De Fronzo RA (1997) Pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus: metabolic and molecular implications for identifying diabetes genes. Diabetes 5:117–169
Funder JW, Pearce PT, Smith R, Smith AI (1988) Mineralocorticoid action is enzyme, not receptor mediated. Science 242:583–585
Conn JW, Knopf RF, Nesbit RM (1964) Clinical characteristics of primary aldosteronism from an analysis of 145 cases. Am J Surg 107:159–172
Fallo F, Federspil G, Veglio F, Mulatero P (2008) The metabolic syndrome in primary aldosteronism. Curr Diabetes Rep 8:42–47
Campion J, Maestro B, Molero S, Davila N, Carranza MC, Calle C (2002) Aldosterone impairs insulin responsiveness in U-937 human promonocytic cells via the down regulation of its own receptor. Cell Biochem Funct 20:237–245
Calle C, Campion J, Garcia-Arencibia M, Maestro B, Davila N (2003) Transcriptional inhibition of the human insulin receptor gene by aldosterone. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 84:543–553
Torpy DJ (1999) Leptin levels are suppressed in primary aldosteronism. Horm Metab Res 31:533–536
Yamashita R, Kikuchi T, Mori Y, Kaburagi Y, Yasuda K (2004) Aldosterone stimulates gene expression of hepatic gluconeogenic enzymes through the glucocorticoids receptor in a manner independent of protein kinase B cascade. Endocrinol 51:243–251
Cooper SA, Connel AW, Habibi J, Wei Y, Lastra G, Manrique C et al (2007) Renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system and oxidative stress I cardiovascular insulin resistance. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 293:H2009–H2023
Giacchetti G, Ronconi V, Turchi F, Agostinelli L, Mantero F, Rilli S et al (2007) Aldosterone as a key mediator of the cardiometabolic syndrome in primary aldosteronism: an observational study. J Hypertens 25:177–186
Hayden MR, Sowers JR (2008) Pancreatic renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in the cardiometabolic syndrome and type-2 diabetes mellitus. J Cardiometab Syndr Summer 3(3):129–131
Bentley-Lewis R, Adler GK, Perlstein T, Seely EW, Hopkins PN, Williams GH et al (2007) Body mass index predicts aldosterone production in normotensive adults on a high-salt diet. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 92:4472–4475
Garg R, Shelley Hurwitz S, Williams GH, Hopkins PN, Adler GK (2010) Aldosterone production and insulin resistance in healthy adults. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 95:1986–1990
Freel EM, Tsorlalis IK, Lewsey JD, Latini R, Solomon S, Pitt B, Connell JMC, McMurray JJV (2009) Aldosterone status associated with insulin resistance in patients with heart failure-data from the ALOFT study. Heart 95:1920–1924
Guo C, Ricchiuti V, Lian BQ, Yao TM, Coutinho P, Romero JR et al (2008) Mineralocorticoid receptor blockade reverses obesity-related changes in expression of adiponectin, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma, and proinflammatory adipokines. Circulation 117:2253–2261
Hirata A, Maeda N, Hiuge A, Hibuse T, Fujita K, Okada T et al (2009) Blockade of mineralocorticoid receptor reverses adipocytes dysfunction and insulin resistance in obese mice. Cardiovasc Res 84:164–172
Wada T, Ohshima S, Fujisawa E, Koya D, Tsuneki H et al (2009) Aldosterone inhibits insulin-induced glucose uptake by degradation of insulin receptor substrate (IRS) 1 and IRS2 via a reactive oxygen species-mediated pathway in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Endocrinology 150:1662–1669
Selvaraj J, Muthusamy T, Srinivasan C, Balasubramanian K (2009) Impact of excess aldosterone on glucose homeostasis in adult male rat. Clin Chim Acta 407:51–57
Triosh A, Garg R, Alder GK (2010) Minerolocorticoid receptor antogonists and the metabolic syndrome. Curr Hypertens Rep 12:252–257
Rocha R, Chander PN, Zuckerman A, Stier CT (1999) Role of aldosterone in renal vascular injury in stroke-prone hypertensive rats. Hypertension 33:232–237
Hlavacova N, Jezova D (2008) Chronic treatment with the mineralocorticoid hormone aldosterone results in increased anxiety-like behavior. Horm Behav 54:90–97
Gonzalez CG, Alonso A, Balbin M, Diaz F, Fernandez S, Patterson AM (2002) Effects of pregnancy on insulin receptor in liver, skeletal muscle and adipose tissue of rats. Gynecol Endocrinol 16:93–205
Gonzalez C, Alonso A, Fernández R, Patterson AM (2003) Regulation of insulin receptor substrate-1 in the liver, skeletal muscle and adipose tissue of rats throughout pregnancy. Gynecol Endocrinol 17:187–197
Liu Y, Wan Q, Guan O, Gao L, Zhao J (2006) High-fat diet feeding impairs both the expression and activity of AMPKa in rats skeletal muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 339:701–70735
Dombrowski L, Roy D, Mareotte B, Marette A (1996) A new procedure for the isolation of plasma membrane, T-tubules and internal membranes from skeletal muscles. Am J Physiol 270:E667–E676
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Valverde AM, Navarro P, Teruel T, Conejo R, Benito M, Lorenzo M (1999) Insulin and insulin-like growth factor I up-regulate GLUT4 gene expression in fetal brown adipocytes, in a phosphoinositide 3-kinase-dependent manner. Biochem J 337:397–405
Kraft LA, Johnson AD (1972) Epididymal carbohydrate metabolism II. Substrates and pathway utilization of caput and cauda epididymal tissue from the rabbit, rat and mouse. Comp Biochem Physiol 42(3):451–461
Hassid WZ, Abraham S (1975) Determination of glycogen with anthrone reagent. Methods Enzymol 3:34–37
Devasagayam TP, Tarachand U (1987) Decreased lipid peroxidation in rat kidneys during gestation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 145:134–138
Pick E, Keisari Y (1981) Superoxide anion and H2O2 production by chemically elicited peritoneal macrophages-induction by multiple nonphagocytic stimuli. Cell Immunol 59:301–318
Puntarulo S, Cederbaum AI (1998) Comparison of the ability of ferric complexes to catalyze microsomal chemiluminescence, lipid peroxidation, and hydroxyl radical generation. Arch Biochem Biophys 264(2):482–491
Jozsi AC, Goodyear LJ (2005) Biology of skeletal muscle. In: Kahn CR, Weir GC, King GL, Jacobsol AM, Moses AC, Smith RJ (eds) Joslin’s diabetes mellitus, 14th edn. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, pp 227–241
Ariano MA, Armstrong RB, Edgerton VR (1973) Hind limb muscle fiber populations of five mammals. J Histochem Cytochem 21:51–55
Mainwaring WIP, Mangan FR (1973) A study of the androgen receptors in a variety of androgen-sensitive tissues. J Endocrinol 10:121–139
Sheffield-Moore M, Urban RJ (2004) An overview of the endocrinology of skeletal muscle. Trends Endocrinol Metabol 15:110–115
Kahn CR, King GL, Moses AC, Weir GC, Jacobson AM, Smith RJ (2005) Joslin’s diabetes Mellitus, 14th edn. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Botson, pp 145–169
Ishihara M, Itoh M, Miyamoto K, Suna S, Takeuchi Y, Takenaka I, Jitsunari F (2000) Spermatogenic disturbance induced by di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate is significantly prevented by treatment with antioxidant vitamins in the rat. Int J Androl 23:85–94
Sowers JR, Whaley-connel A, Epstin M (2009) The emerging clinical implications of the role of aldosterone in the metabolic syndrome and resistance hypertension. Ann Intern Med 150:776–785
Zaid H, Antonescu CN, Randhawa VK, Klip A (2008) Insulin action on glucose transporters through molecular switches, tracks and tethers. Biochem J 413:201–215
Vanhaesebroeck B, Alessi DR (2000) The PI3 K-PDK1 connection: more than just a road to PKB. Biochem J 346:561–576
Luan B, Zhao J, Wu H, Duan B, Shu G, Wang X et al (2009) Deficiency of a β-arrestin-2 signal complex contributes to insulin resistance. Nature 457:1146–1150
Zierath JR, He L, Guma A, Odegaard-Wahlstrom E, Klip A, Wallberg-Henrikson H (1996) Insulin actions on glucose transport and plasma membrane content in skeletal muscle from patients with NIDDM. Diabetologia 39:1180–1189
Baudry A, Leroux L, Jackerott M, Joshi RL (2002) Genetic manipulation of insulin signaling, action and secretion in mice. Insights into glucose homeostasis and pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes. EMBO Rep 3:323–328
Colussi G, Catena C, Lapenna R, Nadalini E, Chiuch A, Sechi A (2007) Insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia are related to plasma aldosterone in hypertensive patients. Diabetes Care 30:2349–2354
Granner DK, Scott DK (2005) Regulation of hepatic glucose metabolism. In: Kahn CR, King GL, Moses AC, Weir GC, Jacobson AM, Smith RJ (Eds) Joslin’s diabetes mellitus, 14th edn. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Boston, pp 243–263
Marette A, Burdett E, Douen A, Vranic M, Klip A (1992) Insulin induces translocation of the GLUT4 from a unique intracellular organelle to the transverse tubules in rat skeletal muscle. Diabetes 41:1562–1569
Muthusamy T, Murugesan P, Srinivasan C, Balasubramanian K (2011) Sex steroids influence glucose oxidation through modulation of insulin receptor expression and IRS-1 serine phosphorylation in target tissues of adult male rat. Mol Cell Biochem 352(1–2):35–45
Ge RS, Dong Q, Sottas CM, Latif SA et al (2005) Stimulation of testosterone production in rat Leydig cells by aldosterone is mineralocorticoid receptor mediated. Mol Cell Endocrinol 243:35–42
Sindelka G, Widisky J, Haas T, Prazny M, Hilgertova J, Skrha J (2000) Insulin action in primary hyperaldosteronism before and after surgical or pharmacological treatment. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 108:21–25
Acknowledgments
University Grants Commission Special Assistance Programme (UGC-SAP), Department of Science and Technology (DST)–FIST Programme, UGC-Research Fellowship in Science for Meritorious Students (UGC-RFSMS) and Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) are gratefully acknowledged for the financial support.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Selvaraj, J., Sathish, S., Mayilvanan, C. et al. Excess aldosterone-induced changes in insulin signaling molecules and glucose oxidation in gastrocnemius muscle of adult male rat. Mol Cell Biochem 372, 113–126 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-012-1452-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-012-1452-2