Abstract
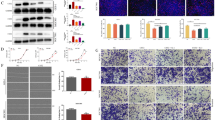
CCDC134 (coiled coil domain containing 134), a novel secretory protein, acts as an inhibitor of Erk1/2 and JNK/SAPK pathways. However, the role of CCDC134 in cancer development is still lacking. In this study, we found that CCDC134 expression significantly reduced in gastric cancer tissues compared with normal tissues (P < 0.001) and lesion tissues (P < 0.001). But no statistically significant difference was observed between normal and lesion tissues (P = 0.842). In vitro transient transfection of CCDC134-specific siRNA significantly promoted the migration and invasion of both the normal gastric epithelial cell line GES-1 and gastric cancer cell line AGS cells. Further analysis revealed that the attenuated expression of CCDC134 promoted the activation of Erk1/2 and JNK/SAPK, but had no effect on p38. The activation of Erk1/2 and JNK/SAPK was required for CCDC134-mediated migration and invasion. Besides, CCDC134-RNAi could induce the expression of MMP-2 and MMP-9, which are key molecules involved in regulating cell migration and invasion. Therefore, CCDC134 may be a candidate biomarker for malignant transformation. It plays a role in regulation of cell migration and invasion, and could be a therapeutic target of gastric cancer.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P (2005) Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin 55(2):74–108
Cunningham D, Chua YJ (2007) East meets west in the treatment of gastric cancer. N Engl J Med 357:1863–1865
De Vita F, Vecchione L, Galizia G, Di Martino N, Fabozzi T, Catalano G, Ciardiello F, Orditura M (2009) Perspectives in adjuvant therapy of gastric cancer. Oncology 77(Suppl 1):38–42
Reddy KB, Nabha SM, Atanaskova N (2003) Role of MAP kinase in tumor progression and invasion. Cancer Metastasis Rev 22:395–403
Wagner EF, Nebreda AR (2009) Signal integration by JNK and p38 MAPK pathways in cancer development. Nat Rev Cancer 9:537–549
Liang B, Wang S, Zhu XG, Yu YX, Cui ZR, Yu YZ (2005) Increased expression of mitogen-activated protein kinase and its upstream regulation signal in human gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol 11(5):623–628
Huang J, Shi T, Ma T, Zhang Y, Ma X, Lu Y, Song Q, Liu W, Ma D, Qiu X (2008) CCDC134, a novel secretory protein, inhibits activation of ERK and JNK, but not p38 MAPK. Cell Mol Life Sci 65:338–349
Guo X, Ma N, Wang J, Song J, Bu X, Cheng Y, Sun K, Xiong H, Jiang G, Zhang B, Wu M, Wei L (2008) Increased p38-MAPK is responsible for chemotherapy resistance in human gastric cancer cells. BMC cancer 8:375
Whyte J, Bergin O, Bianchi A, McNally S, Martin F (2009) Key signalling nodes in mammary gland development and cancer. Mitogen-activated protein kinase signalling in experimental models of breast cancer progression and in mammary gland development. Breast Cancer Res 11(5):209–222
Schubbert S, Shannon K, Bollag G (2007) Hyperactive ras in developmental disorders and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 7(4):295–308
Zhang C, Zhu H, Yang X, Lou J, Zhu D, Lu W, He Q, Yang B (2010) P53 and p38 MAPK pathways are involved in MONCPT-induced cell cycle G2/M arrest in human non-small cell lung cancer A549. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 136(3):437–445
Uzgare AR, Kaplan PJ, Greenberg NM (2003) Differential expression and/or activation of p38MAPK, erk1/2, and jnk during the initiation and progression of prostate cancer. Prostate 55(2):128–139
McCubrey JA, Steelman LS, Chappell WH, Abrams SL, Wong EW, Chang F, Lehmann B, Terrian DM, Milella M, Tafuri A, Stivala F, Libra M, Basecke J, Evangelisti C, Martelli AM, Franklin RA (2007) Role of the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway in cell growth, malignant, transformation and drug resistance. Biochim Biophys Acta 1773(8):1263–1284
Roberts PJ, Der CJ (2007) Targeting the Raf-MEK-ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade for the treatment of cancer. Oncogene 26(22):3291–3310
Wang L, Gao X, Gao P, Deng W, Yu P, Ma J, Guo J, Wang X, Cheng H, Zhang C, Yu C, Ma X, Lv B, Lu Y, Shi T, Ma D (2006) Cell-based screening and validation of human novel genes associated with cell viability. J Biomol Screen 11(4):369–376
Tian L, Wang P, Guo J, Wang X, Deng W, Zhang C, Fu D, Gao X, Shi T, Ma D (2007) Screening for novel human genes associated with CRE path-way activation with cell microarray. Genomics 90(1):28–34
Huang C, Rajfur Z, Borchers C, Schaller MD, Jacobson K (2003) JNK phosphorylates paxillin and regulates cell migration. Nature 424:219–223
Huang C, Jacobson K, Schaller MD (2004) MAP kinases and cell migration. J Cell Sci 117:4619–4628
Egeblad M, Werb Z (2002) New function for matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression. Nat Rev Cancer 2(3):161–174
Gialel C, Theocharis AD, Karamanos NK (2011) Roles of matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression and their pharmacological targeting. FEBS J 278(1):16–27
Overall CM, López-Otín C (2002) Strategies for MMP inhibition in cancer: innovations for the post-trial era. Nat Rev Cancer 2(9):657–672
Behren A, Simon C, Schwab RM, Loetzsch E, Brodbeck S, Huber E, Stubenrauch F, Zenner HP, Iftner T (2005) Papillomavirus E2 protein induces expression of the matrix metalloproteinase-9 via the extracellular signal-regulated kinase/activator protein-1 signaling pathway. Cancer Res 65(24):11613–11621
Kajanne R, Miettinen P, Mehlem A, Leivonen SK, Birrer M, Foschi M, Kähäri VM, Leppä S (2007) EGF-R regulates MMP function in fibroblasts through MAPK and AP-1 pathways. J Cell Physiol 212(2):489–497
Tang FY, Chiang EP, Sun YC (2008) Resveratrol inhibits heregulin-beta1-mediated matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression and cell invasion in human breast cancer Cells. J Nutr Biochem 19(5):287–294
Cheng YC, Chen LM, Chang MH, Chen WK, Tsai FJ, Tsai CH, Lai TY, Kuo WW, Huang CY, Liu CJ (2009) Lipopolysaccharide upregulates uPA, MMP-2 and MMP-9 via ERK1/2 signaling in H9c2 cardiomyoblast cells. Mol Cell Biochem 325(1–2):15–23
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Key Basic Research Program of China (2007CB914700) and Open projects (201102) of Key Laboratory of Cell Proliferation and Regulation Biology (Beijing Normal University), Ministry of Education. We are grateful to Professor Xiaoyan Qiu (Peking University, Beijing, P.R. China) for providing us with antibody of CCDC134.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhong, J., Zhao, M., Luo, Q. et al. CCDC134 is down-regulated in gastric cancer and its silencing promotes cell migration and invasion of GES-1 and AGS cells via the MAPK pathway. Mol Cell Biochem 372, 1–8 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-012-1418-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-012-1418-4