Abstract
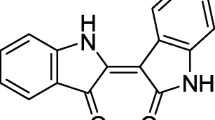
The aim of this study was to evaluate whether citreorosein (CIT), a naturally occurring anthraquinone isolated from Polygoni cuspidati (P. cuspidati) radix, modulates degranulation and 5-lipoxygenase (5-LO)-dependent leukotriene C4 (LTC4) generation in mast cells. Cit suppresses both degranulation and the generation of LTC4 in a dose-dependent manner in stem cell factor (SCF)-mediated mouse bone marrow-derived mast cells (BMMCs). With regard to its molecular mechanism of action, we investigated the effects of CIT on intracellular signaling and mast cell activation employing BMMCs. Binding of SCF to c-Kit on mast cell membranes induced increases in intrinsic tyrosine kinase Syk activity and activation of multiple downstream events including phosphorylation of phospholipase Cγ (PLCγ), mobilization of intracellular Ca2+, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K), Akt, MAP kinases (MAPKs), translocation of phospho-phospholipase A2 (PLA2) and 5-LO. The results from the biochemical analysis demonstrate that CIT attenuates degranulation and LTC4 generation through the suppression of multiple step signaling and would be beneficial for the prevention of allergic inflammation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Iwaki S, Spicka J, Tkaczyk C, Jensen BM, Furumoto Y, Charles N, Kovarova M, Rivera J, Horejsi V, Metcalfe DD, Gilfillan AM (2008) Kit- and Fc epsilonRI-induced differential phosphorylation of the transmembrane adaptor molecule NTAL/LAB/LAT2 allows flexibility in its scaffolding function in mast cells. Cell Signal 20:195–205
Gilfillan AM, Tkaczyk C (2006) Integrated signalling pathways for mast-cell activation. Nat Rev Immunol 6:218–230
Roskoski R Jr (2005) Structure and regulation of Kit protein-tyrosine kinase—the stem cell factor receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 338:1307–1315
Nocka K, Buck J, Levi E, Besmer P (1990) Candidate ligand for the c-kit transmembrane kinase receptor: KL, a fibroblast derived growth factor stimulates mast cells and erythroid progenitors. EMBO J 9:3287–3294
Tsai M, Takeishi T, Thompson H, Langley KE, Zsebo KM, Metcalfe DD, Geissler EN, Galli SJ (1991) Induction of mast cell proliferation, maturation, and heparin synthesis by the rat c-kit ligand, stem cell factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:6382–6386
Meininger CJ, Yano H, Rottapel R, Bernstein A, Zsebo KM, Zetter BR (1992) The c-kit receptor ligand functions as a mast cell chemoattractant. Blood 79:958–963
Columbo M, Horowitz EM, Botana LM, MacGlashan DW Jr, Bochner BS, Gillis S, Zsebo KM, Galli SJ, Lichtenstein LM (1992) The human recombinant c-kit receptor ligand, rhSCF, induces mediator release from human cutaneous mast cells and enhances IgE-dependent mediator release from both skin mast cells and peripheral blood basophils. J Immunol 149:599–608
Galli SJ, Iemura A, Garlick DS, Gamba-Vitalo C, Zsebo KM, Andrews RG (1993) Eversible expansion of primate mast cell populations in vivo by stem cell factor. J Clin Invest 91:148–152
Costa JJ, Demetri GD, Harrist TJ, Dvorak AM, Hayes DF, Merica EA, Menchaca DM, Gringeri AJ, Schwartz LB, Galli SJ (1996) Recombinant human stem cell factor (kit ligand) promotes human mast cell and melanocyte hyperplasia and functional activation in vivo. J Exp Med 183:2681–2686
Vosseller K, Stella G, Yee NS, Besmer P (1997) c-Kit receptor signaling through its phosphatidylinositide-3′-kinase-binding site and protein kinase C: role in mast cell enhancement of degranulation, adhesion, and membrane ruffling. Mol Biol Cell 8:909–922
Sundstrom M, Alfredsson J, Olsson N, Nilsson G (2001) Stem cell factor-induced migration of mast cells requires p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activity. Exp Cell Res 267:144–151
Blume-Jensen P, Ronnstrand L, Gout I, Waterfield MD, Heldin CH (1994) Modulation of Kit/stem cell factor receptor-induced signaling by protein kinase C. J Biol Chem 269:21793–21802
Yi T, Ihle JN (1993) Association of hematopoietic cell phosphatase with c-kit after stimulation with c-kit ligand. Mol Cell Biol 13:3350–3358
Reith AD, Ellis C, Lyman SD, Anderson DM, Williams DE, Bernstein A, Pawson T (1991) Signal transduction by normal isoforms and W mutant variants of the Kit receptor tyrosine kinase. EMBO J 10:2451–2459
Marone R, Cmiljanovic V, Giese B, Wymann MP (2008) Targeting phosphoinositide 3-kinase: moving towards therapy. Biochim Biophys Acta 1784:159–185
Foltz IN, Lee JC, Young PR, Schrader JW (1997) Hemopoietic growth factors with the exception of interleukin-4 activate the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. J Biol Chem 272:3296–3301
Welham MJ, Duronio V, Sanghera JS, Pelech SL, Schrader JW (1992) Multiple hemopoietic growth factors stimulate activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase family members. J Immunol 149:1683–1693
Evans JH, Spencer DM, Zweifach A, Leslie CC (2001) Intracellular calcium signals regulating cytosolic phospholipase A2 translocation to internal membranes. J Biol Chem 276:30150–30160
Werz O, Burkert E, Fischer L, Szellas D, Dishart D, Samuelsson B, Radmark O, Steinhilber D (2002) Extracellular signal-regulated kinases phosphorylate 5-lipoxygenase and stimulate 5-lipoxygenase product formation in leukocytes. Faseb J 16:1441–1443
Werz O, Klemm J, Samuelsson B, Radmark O (2000) 5-lipoxygenase is phosphorylated by p38 kinase-dependent MAPKAP kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:5261–5266
Pergola C, Werz O (2010) 5-Lipoxygenase inhibitors: a review of recent developments and patents. Expert Opin Ther Pat 20:355–375
Flamand N, Lefebvre J, Surette ME, Picard S, Borgeat P (2006) Arachidonic acid regulates the translocation of 5-lipoxygenase to the nuclear membranes in human neutrophils. J Biol Chem 281:129–136
Xiao K, Xuan L, Xu Y, Bai D, Zhong D (2002) Constituents from Polygonum cuspidatum. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 50:605–608
Zhang C, Wang X, Zhang X, Zhang Y, Xiao H, Liang X (2009) Bioassay-guided separation of citreorosein and other oestrogenic compounds from Polygonum cuspidatum. Phytother Res 23:740–741
Leu YL, Hwang TL, Hu JW, Fang JY (2008) Anthraquinones from Polygonum cuspidatum as tyrosinase inhibitors for dermal use. Phytother Res 22:552–556
Lu Y, Suh SJ, Li X, Hwang SL, Li Y, Hwangbo K, Park SJ, Murakami M, Lee SH, Jahng Y, Son JK, Kim CH, Chang HW (2012) Citreorosein, a naturally occurring anthraquinone derivative isolated from Polygoni cuspidati radix, attenuates cyclooxygenase-2-dependent prostaglandin D(2) generation by blocking Akt and JNK pathways in mouse bone marrow-derived mast cells. Food Chem Toxicol 50:913–919
Murakami M, Matsumoto R, Austen KF, Arm JP (1994) Prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase-1 and -2 couple to different transmembrane stimuli to generate prostaglandin D2 in mouse bone marrow-derived mast cells. J Biol Chem 269:22269–22275
Fischer L, Poeckel D, Buerkert E, Steinhilber D, Werz O (2005) Inhibitors of actin polymerisation stimulate arachidonic acid release and 5-lipoxygenase activation by upregulation of Ca2+ mobilisation in polymorphonuclear leukocytes involving Src family kinases. Biochim Biophys Acta 1736:109–119
Kurosawa T, Nakamura H, Yamaura E, Fujino H, Matsuzawa Y, Kawashima T, Murayama T (2009) Cytotoxicity induced by inhibition of thioredoxin reductases via multiple signaling pathways: role of cytosolic phospholipase A(2)alpha-dependent and -independent release of arachidonic acid. J Cell Physiol 219:606–616
Lee CW, Lee IT, Lin CC, Lee HC, Lin WN, Yang CM (2010) Activation and induction of cytosolic phospholipase A2 by IL-1beta in human tracheal smooth muscle cells: role of MAPKs/p300 and NF-kappaB. J Cell Biochem 109:1045–1056
Masuda ES, Schmitz J (2008) Syk inhibitors as treatment for allergic rhinitis. Pulm Pharmacol Ther 21:461–467
Siraganian RP (2003) Mast cell signal transduction from the high-affinity IgE receptor. Curr Opin Immunol 15:639–646
Samayawardhena LA, Kapur R, Craig AW (2007) Involvement of Fyn kinase in Kit and integrin-mediated Rac activation, cytoskeletal reorganization, and chemotaxis of mast cells. Blood 109:3679–3686
Timokhina I, Kissel H, Stella G, Besmer P (1998) Kit signaling through PI 3-kinase and Src kinase pathways: an essential role for Rac1 and JNK activation in mast cell proliferation. EMBO J 17:6250–6262
Baba Y, Hashimoto S, Matsushita M, Watanabe D, Kishimoto T, Kurosaki T, Tsukada S (2001) BLNK mediates Syk-dependent Btk activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:2582–2586
Kramer RM, Sharp JD (1997) Structure, function and regulation of Ca2+-sensitive cytosolic phospholipase A2 (cPLA2). FEBS Lett 410:49–53
Rouzer CA, Kargman S (1988) Translocation of 5-lipoxygenase to the membrane in human leukocytes challenged with ionophore A23187. J Biol Chem 263:10980–10988
Lee JH, Kim JW, Ko NY, Mun SH, Her E, Kim BK, Han JW, Lee HY, Beaven MA, Kim YM, Choi WS (2008) Curcumin, a constituent of curry, suppresses IgE-mediated allergic response and mast cell activation at the level of Syk. J Allergy Clin Immunol 121:1225–1231
Parravicini V, Gadina M, Kovarova M, Odom S, Gonzalez-Espinosa C, Furumoto Y, Saitoh S, Samelson LE, O’Shea JJ, Rivera J (2002) Fyn kinase initiates complementary signals required for IgE-dependent mast cell degranulation. Nat Immunol 3:741–748
Lim BO, Lee JH, Ko NY, Mun SH, Kim JW, Kim do K, Kim JD, Kim BK, Kim HS, Her E, Lee HY, Choi WS (2007) Polygoni cuspidati radix inhibits the activation of Syk kinase in mast cells for antiallergic activity. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 232:1425–1431
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea Grant funded by the Korea government (NRF-2010-616-E00011 and MEST-2011-0006179).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Yue Lu and Ying Li contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, Y., Li, Y., Jahng, Y. et al. Citreorosein inhibits degranulation and leukotriene C4 generation through suppression of Syk pathway in mast cells. Mol Cell Biochem 365, 333–341 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-012-1273-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-012-1273-3